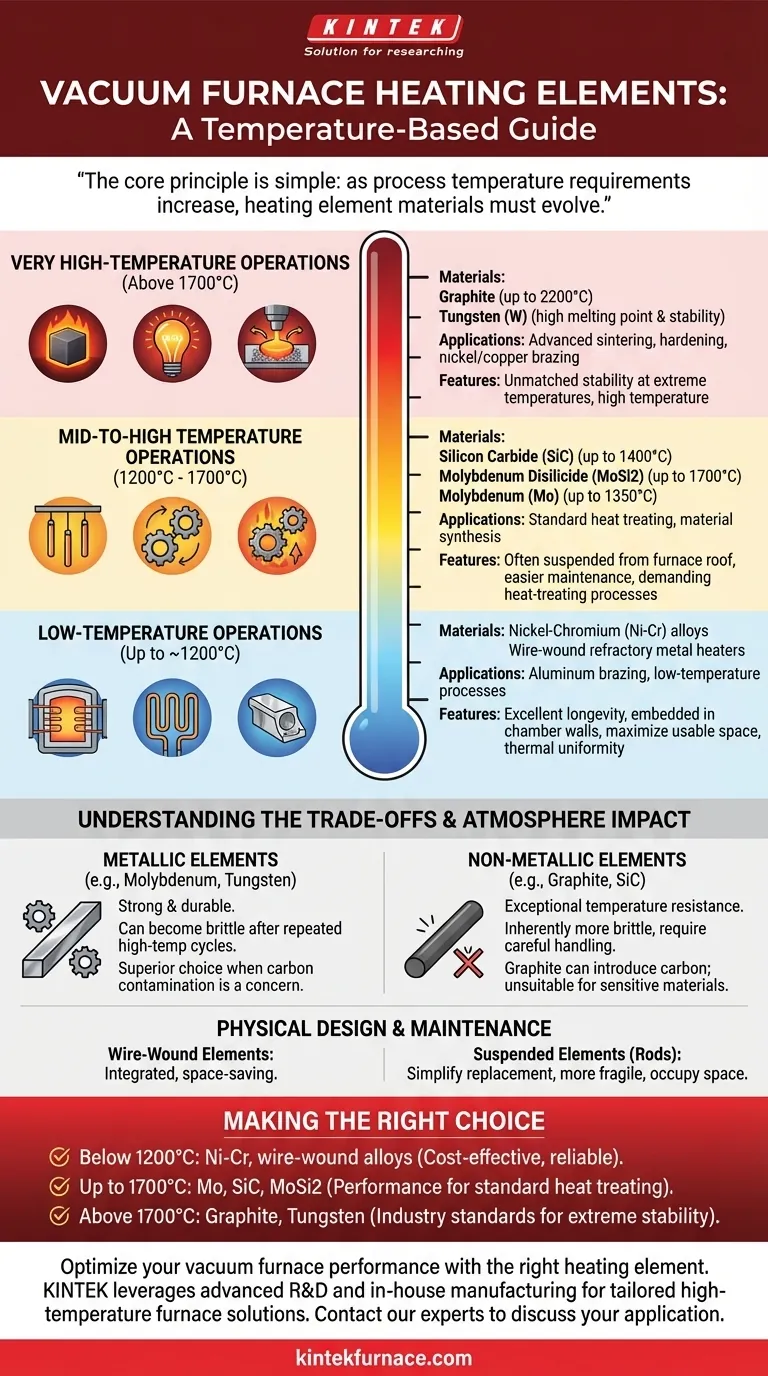
In vacuum furnaces, the choice of heating element material is dictated almost entirely by the target operating temperature. For lower-temperature processes up to around 1200°C, metallic alloys like nickel-chromium are standard. For higher-temperature applications such as sintering or hardening, the industry shifts to advanced materials like molybdenum, tungsten, and graphite, which can operate reliably at temperatures exceeding 2200°C.
The core principle is simple: as process temperature requirements increase, heating element materials must evolve from common alloys to specialized refractory metals, ceramics, and graphite, each bringing its own set of operational characteristics and trade-offs.

A Temperature-Based Guide to Heating Elements
Choosing the right heating element is fundamental to furnace design and performance. The material must not only reach the desired temperature but also maintain its structural integrity and chemical stability within the vacuum environment.
Low-Temperature Operations (Up to ~1200°C)
For applications like aluminum brazing, nickel-chromium (Ni-Cr) alloys and similar wire-wound refractory metal heaters are the most common choice.
These metallic elements offer excellent performance and longevity in the lower temperature range. They are often embedded directly into the furnace's insulated chamber walls, a design that maximizes usable space and promotes thermal uniformity.
Mid-to-High Temperature Operations (1200°C - 1700°C)
This range is dominated by more advanced materials capable of handling more demanding heat-treating processes.
Key materials include Silicon Carbide (SiC), which can reach up to 1400°C, and Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2), capable of operating up to 1700°C. Molybdenum (Mo) elements are also used in this range, typically up to 1350°C.
Unlike their lower-temperature counterparts, these elements are often suspended from the furnace roof, making them easier to access for maintenance.
Very High-Temperature Operations (Above 1700°C)
For the most extreme temperature processes, such as advanced sintering, hardening, and nickel or copper brazing, only a few materials are suitable.
Graphite is a dominant material in this category, capable of reaching temperatures as high as 2200°C. Tungsten (W) is another excellent choice for these high-heat applications, valued for its high melting point and stability.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Simply matching a material to a temperature is not enough. An effective selection requires understanding the inherent compromises between different material types.
Metallic vs. Non-Metallic Elements
Refractory metals like molybdenum and tungsten are strong and durable but can become brittle after repeated high-temperature cycles.
Non-metallic elements like graphite and silicon carbide offer exceptional temperature resistance but are inherently more brittle and require careful handling during installation and maintenance.
Impact on Furnace Atmosphere and Process
The heating element material can directly interact with the furnace atmosphere and the part being processed.
Graphite, for instance, can introduce carbon into the environment, which may be undesirable for certain materials sensitive to carburization. In these cases, a metallic element like molybdenum or tungsten is a superior choice.
Physical Design and Maintenance
The physical form of the element impacts furnace design. Wire-wound elements are integrated and space-saving.
Suspended elements (like SiC and MoSi2 rods) simplify replacement but can be more fragile and occupy more space within the hot zone. This distinction affects both the initial cost and the long-term serviceability of the furnace.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by your primary process requirements.
- If your primary focus is low-temperature brazing or tempering (below 1200°C): Nickel-chromium or other wire-wound metallic alloys provide a cost-effective and reliable solution.
- If your primary focus is standard heat treating or material synthesis (up to 1700°C): Molybdenum, SiC, or MoSi2 elements offer the necessary performance, with the final choice depending on your exact temperature and atmospheric needs.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature sintering or specialized brazing (above 1700°C): Graphite and tungsten are the industry standards, providing unmatched stability at extreme temperatures.
Ultimately, selecting the correct heating element is the critical first step in ensuring your vacuum furnace operates with precision, reliability, and efficiency.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Common Materials | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Up to ~1200°C | Nickel-Chromium (Ni-Cr) alloys | Aluminum brazing, low-temperature processes |
| 1200°C - 1700°C | Molybdenum, Silicon Carbide (SiC), Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) | Standard heat treating, material synthesis |
| Above 1700°C | Graphite, Tungsten | High-temperature sintering, specialized brazing |
Optimize your vacuum furnace performance with the right heating element. At KINTEK, we leverage our advanced R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide tailored high-temperature furnace solutions—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure your heating elements precisely match your unique temperature and process requirements. Contact our experts today to discuss your application and achieve superior thermal processing results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision



















