Yes, absolutely. Induction furnaces are not only capable of melting steel but are a widely used and highly efficient technology for this purpose, particularly in foundries and specialty steel production environments. They are valued for their speed, control, and ability to produce high-quality molten metal.
An induction furnace is a preferred tool for melting steel due to its underlying principle: it uses electromagnetic induction to generate intense heat directly within the steel itself. This provides superior efficiency, cleanliness, and process control compared to methods that apply heat externally.

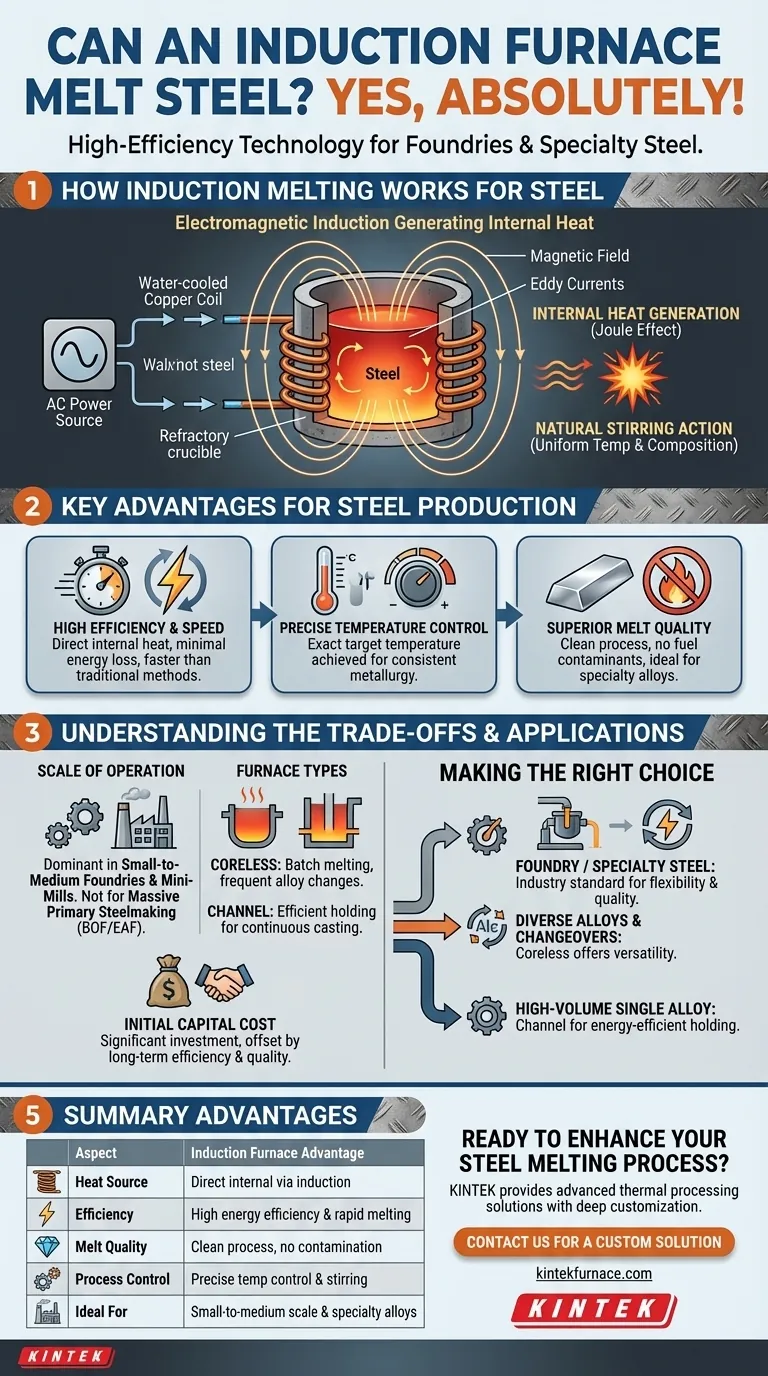
How Induction Melting Works for Steel
The process is fundamentally different from traditional fuel-fired furnaces. It relies on electrical and magnetic principles rather than combustion.
The Principle of Electromagnetic Induction
An induction furnace uses a powerful alternating current flowing through a water-cooled copper coil. This coil surrounds a refractory-lined crucible containing the steel charge (the solid metal to be melted). The current in the coil generates a strong, rapidly changing magnetic field.
Internal Heat Generation
This magnetic field penetrates the steel and induces powerful electrical currents within it, known as eddy currents. Due to the steel's natural electrical resistance, these eddy currents generate immense heat through the Joule effect (I²R heating), rapidly raising the steel's temperature past its melting point.
Natural Stirring Action
The intense magnetic forces also create a vigorous stirring action within the molten metal bath. This electromagnetic stirring ensures the melt has a uniform temperature and consistent chemical composition, which is critical for producing high-grade steel and alloys.
Key Advantages for Steel Production
Choosing induction technology for melting steel offers several distinct operational benefits that directly impact efficiency and final product quality.
High Efficiency and Speed
Because heat is generated directly inside the metal, very little energy is lost to the environment. This makes induction melting significantly more energy-efficient and faster than methods like cupola or reverberatory furnaces, where heat must be transferred from an external source.
Precise Temperature Control
The power supplied to the induction coil can be controlled with extreme precision. This allows operators to achieve and maintain the exact target temperature required for a specific grade of steel, ensuring consistent metallurgical properties.
Superior Melt Quality
Induction melting is an exceptionally clean process. Since there is no combustion, there is no risk of contaminating the steel with byproducts like sulfur or phosphorus from fuel. This cleanliness is essential for producing specialty steels and high-purity alloys.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, induction furnaces are not the universal solution for all steel melting applications. Understanding their context is key.
Scale of Operation
Induction furnaces are the dominant technology in small-to-medium-scale operations, such as metal foundries and mini-mills producing specialty products. They are not typically used for the massive-scale primary steelmaking (hundreds of tons per batch) handled by Basic Oxygen Furnaces (BOF) or Electric Arc Furnaces (EAF).
Furnace Types and Applications
Different induction furnaces serve different needs. Coreless induction furnaces are ideal for batch melting and frequent alloy changes as they can be completely emptied. Channel induction furnaces are more efficient for holding large volumes of molten metal at a constant temperature for continuous casting operations.
Initial Capital Cost
The power electronics, water-cooling systems, and copper coils associated with an induction furnace represent a significant initial investment. However, this is often offset by lower operational energy costs and higher product quality over the equipment's lifetime.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right furnace technology depends entirely on your operational objectives.
- If your primary focus is running a foundry or specialty steel operation: An induction furnace is the industry-standard choice for its flexibility, quality control, and speed.
- If your primary focus is melting diverse alloys with frequent changeovers: A coreless induction furnace provides the necessary versatility to switch between different metal grades without cross-contamination.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, continuous production of a single alloy: A channel induction furnace may be more energy-efficient for holding and dispensing large quantities of molten steel.
Ultimately, leveraging induction technology provides the control and purity necessary to produce high-grade steel with remarkable efficiency.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Induction Furnace Advantage |
|---|---|
| Heat Source | Direct internal heating via electromagnetic induction |
| Efficiency | High energy efficiency and rapid melting speeds |
| Melt Quality | Clean process; no contamination from combustion |
| Process Control | Precise temperature control and automatic stirring |
| Ideal For | Small-to-medium scale foundries and specialty alloys |
Ready to Enhance Your Steel Melting Process?
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories and foundries with advanced thermal processing solutions. Our product line, including high-temperature Muffle, Tube, and Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your unique steel melting requirements.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can bring efficiency, purity, and control to your operation.
Get in Touch for a Custom Solution
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control
- How has vacuum smelting impacted the development of superalloys? Unlock Higher Strength and Purity
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification



















