The Unseen Battle for Thermal Order
Every groundbreaking material, from a semiconductor wafer to a single-crystal turbine blade, begins as an idea subjected to extreme conditions. The most critical of these is often heat.
But heat is chaotic. Its natural tendency is to dissipate, to fluctuate, to defy order.
The challenge for a materials scientist isn't just to make something hot. It's to create a small, perfectly controlled thermal universe where temperature is uniform, stable, and predictable to a fraction of a degree. A tube furnace is not an oven; it is an instrument designed to win this battle for thermal order. The smallest deviation can ruin weeks of work, making the engineering behind this control paramount.
The Core Engine: From Electron to Photon
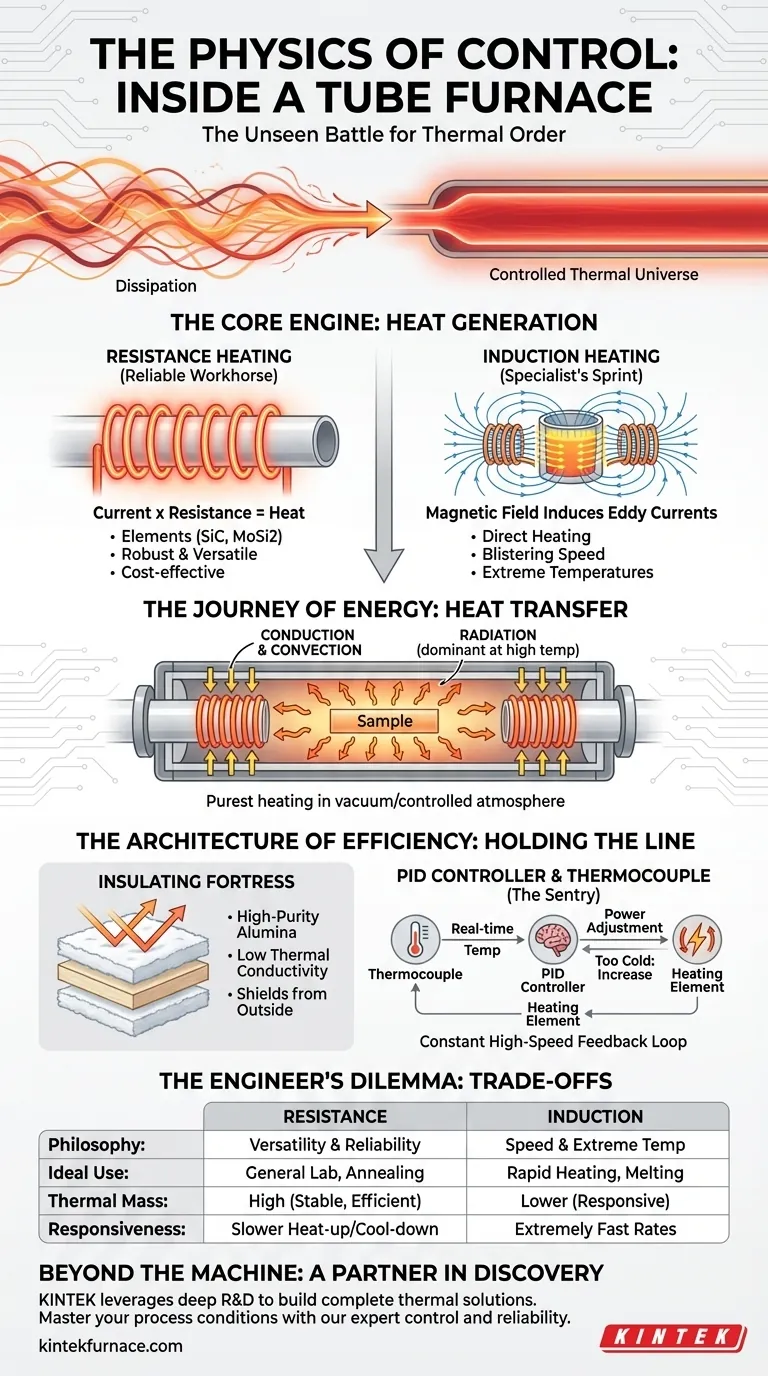
At its heart, a tube furnace masterfully converts electrical energy into thermal energy. The elegance is not in the conversion itself, but in the method and its application-specific purpose. Two primary philosophies dominate this process.
Resistance Heating: The Reliable Workhorse
The most common and trusted method is resistance heating. The principle is as beautiful as it is simple: current meets resistance, and the result is heat. This is Joule's first law in action.
An electrical current is passed through elements made of highly resistive materials, like silicon carbide or molybdenum disilicide. These elements encircle the process tube, glowing hot and bathing it in thermal energy. It is a robust, versatile, and cost-effective method—the backbone of countless laboratories and industrial processes.
Induction Heating: The Specialist's Sprint
For applications demanding blistering speed or temperatures beyond the practical limits of conventional elements, induction heating offers a more direct, intense approach.
Instead of heating elements, a high-frequency alternating current energizes a coil, creating a powerful magnetic field. When a conductive object, like a tungsten crucible, is placed inside, this field induces eddy currents directly within it. The crucible itself becomes the heat source—intensely and almost instantaneously. It's the difference between heating a room and heating the person within it directly.
The Journey of Energy: From Source to Sample
Generating heat is only the first step. The furnace's internal architecture is designed to manage the journey of that heat to the sample with maximum efficiency and uniformity.
-
Conduction & Convection: Initially, heat transfers through direct contact (conduction) and the movement of hot air (convection) from the heating element to the outer wall of the process tube.
-
Radiation: As temperatures climb past several hundred degrees Celsius, thermal radiation becomes the dominant force. The hot inner walls of the furnace tube radiate energy in the form of infrared waves, which are absorbed by the sample. In a vacuum or a controlled atmosphere, this is the purest and most effective way to ensure the sample is heated evenly from all sides.
The Architecture of Efficiency: Holding the Line
A furnace's true performance is defined by its ability to maintain a set temperature with unwavering stability. This is achieved through a combination of brute-force defense and intelligent offense.
The Insulating Fortress
To contain the immense energy required for high-temperature processing, the heating zone is encased in a fortress of insulation. Multi-layered, high-purity materials like alumina polycrystalline fibers create a barrier with extremely low thermal conductivity.
This isn't just about safety or saving energy; it's about creating a stable environment where the internal temperature is shielded from the fluctuations of the outside world.
The Unblinking Sentry: Thermocouple and Controller
The brain of the system is a constant, high-speed feedback loop.
A thermocouple—a highly sensitive sensor—continuously measures the temperature inside the furnace. It sends this information as a tiny voltage signal to a PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controller.
The controller instantly compares the real-time temperature to the user's setpoint. Is it too hot? It reduces power. Too cold? It increases power. This digital conversation happens many times per second, making minute adjustments to hold the temperature with astonishing precision.
The Engineer's Dilemma: Choosing Your Compromise
In engineering, there is rarely a single "best" solution—only the best solution for a specific objective. Choosing a furnace requires understanding the inherent trade-offs.
| Factor | Resistance Heating | Induction Heating |
|---|---|---|
| Philosophy | Versatility and reliability | Speed and extreme temperature |
| Ideal Use | General lab work, annealing, synthesis | Rapid heating of conductive materials, melting |
| Thermal Mass | High mass (thick insulation) = Stable, efficient | Lower mass systems can be more responsive |
| Responsiveness | Slower heat-up and cool-down times | Extremely fast heat-up rates |
A furnace with high thermal mass will be incredibly stable but will take longer to reach temperature. A lighter, more responsive system might heat up faster but be less efficient for long-duration processes. The right choice depends entirely on your priority: stability or agility?
Beyond the Machine: A Partner in Discovery
Ultimately, a tube furnace is more than a collection of heating elements and insulators. It is a precision tool that enables creation and discovery. Selecting the right one means matching the instrument's capabilities to your scientific ambition.
Understanding these core principles is what allows for true innovation. At KINTEK, we leverage our deep R&D and manufacturing expertise to build not just furnaces, but complete thermal solutions. Whether your work requires a versatile Tube Furnace, a specialized CVD system, or a custom-designed vacuum furnace, our focus is on providing the control and reliability your research demands.
If you are looking to master the thermal conditions of your process, let's build the perfect solution together. Contact Our Experts
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
Related Articles
- Mastering the Micro-Environment: The Unseen Power of the Tube Furnace
- Mastering the Micro-Environment: The Art and Science of the Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Your Furnace Isn't Just a Heater: Why 'Good Enough' Equipment Is Sabotaging Your Advanced Materials Research
- A War Against Chaos: The Elegant Engineering of the Modern Tube Furnace
- Why Your Tube Furnace Is Failing Your Experiments (And It’s Not the Temperature)




















