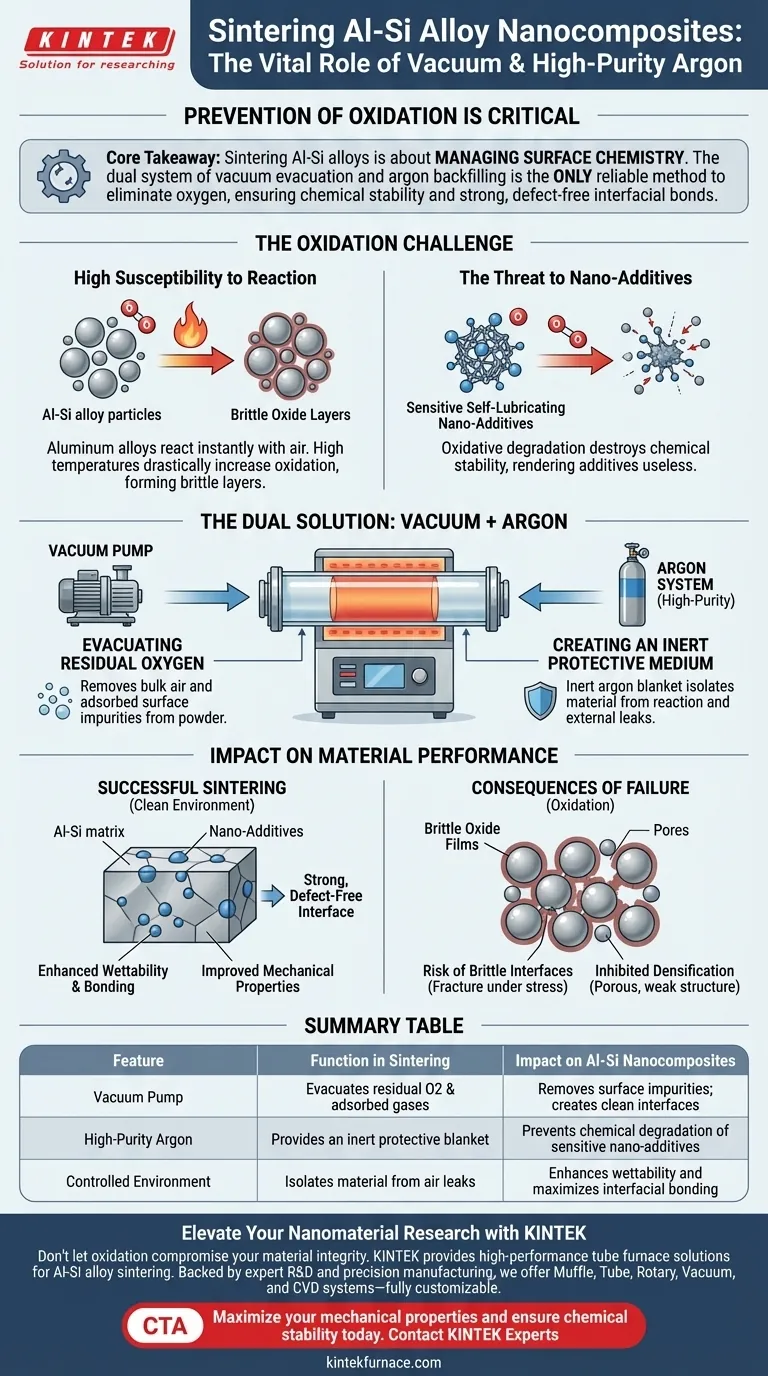
The prevention of oxidation is the single most critical factor in sintering Aluminum-Silicon (Al-Si) alloy nanocomposites. A tube furnace must employ a vacuum pump and high-purity argon system to create a strictly controlled environment; the vacuum evacuates residual oxygen and adsorbed gases, while the argon creates an inert protective shield to prevent the aluminum matrix and sensitive nano-additives from chemically degrading at high temperatures.
Core Takeaway: Sintering Al-Si alloys is not merely about applying heat; it is about managing surface chemistry. The dual system of vacuum evacuation and argon backfilling is the only reliable method to eliminate oxygen, ensuring the chemical stability of the nanocomposites and enabling the formation of strong, defect-free interfacial bonds.

The Oxidation Challenge in Al-Si Alloys
High Susceptibility to Reaction
Aluminum and its alloys are naturally reactive materials that form oxides almost instantly upon contact with air.
At the elevated temperatures required for sintering, this susceptibility to oxidation increases drastically.
Without intervention, oxygen in the furnace atmosphere will react with the metal to form brittle oxide layers that compromise the material's integrity.
The Threat to Nano-Additives
Al-Si nanocomposites often contain specialized components, such as self-lubricating nano-additives.
These additives rely on precise chemical compositions to function correctly.
Oxidative degradation destroys the chemical stability of these additives, rendering the self-lubricating properties of the final composite useless.
The Role of the Vacuum System
Evacuating Residual Oxygen
The primary function of the vacuum pump is to physically remove the air present in the tube furnace chamber.
This evacuation eliminates the bulk of the oxygen that would otherwise react with the alloy during the heating process.
Removing Surface Impurities
Beyond atmospheric air, raw powders often hold adsorbed gases and volatile impurities on their surfaces.
A high vacuum environment effectively strips these contaminants away from the powder particles.
This cleansing process is essential for creating a "clean interface" environment, which is a prerequisite for successful sintering.
The Role of High-Purity Argon
Creating an Inert Protective Medium
Once the vacuum has removed contaminants, high-purity argon is injected to act as a protective blanket.
Argon is an inert gas, meaning it will not react with the aluminum or the nano-additives, even at high temperatures.
Isolating the Material
The continuous presence of argon isolates the sintering material from any potential external air leaks or residual contamination.
This isolation is the final barrier against oxidative degradation, ensuring the material remains chemically pure throughout the thermal cycle.
Impact on Material Performance
Enhancing Wettability and Bonding
Oxidation creates a barrier that prevents the metal matrix from bonding with reinforcement materials.
By maintaining a clean, oxide-free environment, the vacuum and argon system significantly enhances wettability between the matrix and the reinforcement.
Improving Mechanical Properties
The ultimate goal of this atmospheric control is to improve the interfacial bonding strength.
When the interface between the Al-Si matrix and the nano-additives is free of brittle oxides, the mechanical properties of the composite are maximized.
Understanding the Consequences of Failure
The Risk of Brittle Interfaces
If the vacuum or argon systems are insufficient, oxide films will persist on the particle surfaces.
These films act as defects, leading to brittle interfaces that easily fracture under stress.
Inhibited Densification
Oxidation acts as a physical barrier to the diffusion processes required for sintering.
Without a pure environment, the material will fail to densify properly, leaving a porous and weak structure rather than a solid composite.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure the success of your sintering process, you must prioritize the integrity of your atmospheric control system.
- If your primary focus is Chemical Stability: Ensure your argon source is certified high-purity to protect sensitive self-lubricating additives from degradation.
- If your primary focus is Mechanical Strength: Prioritize a deep vacuum draw before heating to remove adsorbed gases and maximize interfacial bonding.
Success in sintering Al-Si nanocomposites is defined by the purity of the environment you create before the temperature ever rises.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in Sintering | Impact on Al-Si Nanocomposites |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum Pump | Evacuates residual O2 & adsorbed gases | Removes surface impurities; creates clean interfaces |
| High-Purity Argon | Provides an inert protective blanket | Prevents chemical degradation of sensitive nano-additives |
| Controlled Environment | Isolates material from air leaks | Enhances wettability and maximizes interfacial bonding |
Elevate Your Nanomaterial Research with KINTEK
Don't let oxidation compromise your material integrity. KINTEK provides high-performance tube furnace solutions specifically designed for the rigorous demands of Al-Si alloy sintering. Backed by expert R&D and precision manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to your unique atmospheric and temperature requirements.
Maximize your mechanical properties and ensure chemical stability today.
Visual Guide
References
- Mohammed Jabbar Fouad, İbrahim İnanç. Manufacture of Self-Lubricating Mechanical Parts from Al-Si Alloy Matrix Hybrid Nanocomposites. DOI: 10.24874/ti.1752.09.24.02
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How does a vacuum tube furnace work? Master Precise High-Temp Material Processing
- How is heat transferred to the materials inside the tube furnace? Master Uniform Heating for Your Lab
- What role does a horizontal quartz tube furnace play in the synthesis of Bi2Se3? Optimize CVD Nanosheet Production
- What role does a high-temperature tube furnace play in the initial pyrolysis of date palm leaf biomass? Key Insights
- How does annealing in a tube vacuum furnace optimize WS2 thin films? Master Structural Integrity & Efficiency
- What specific research applications demonstrate the capabilities of lab tubular furnaces? Unlock Precise Thermal Processing
- What is the function of a tube furnace during the hydrogen reduction phase? Optimize Catalyst Microstructures
- What is a laboratory tube furnace and how is it designed? Master Precise Heating for Your Lab



















