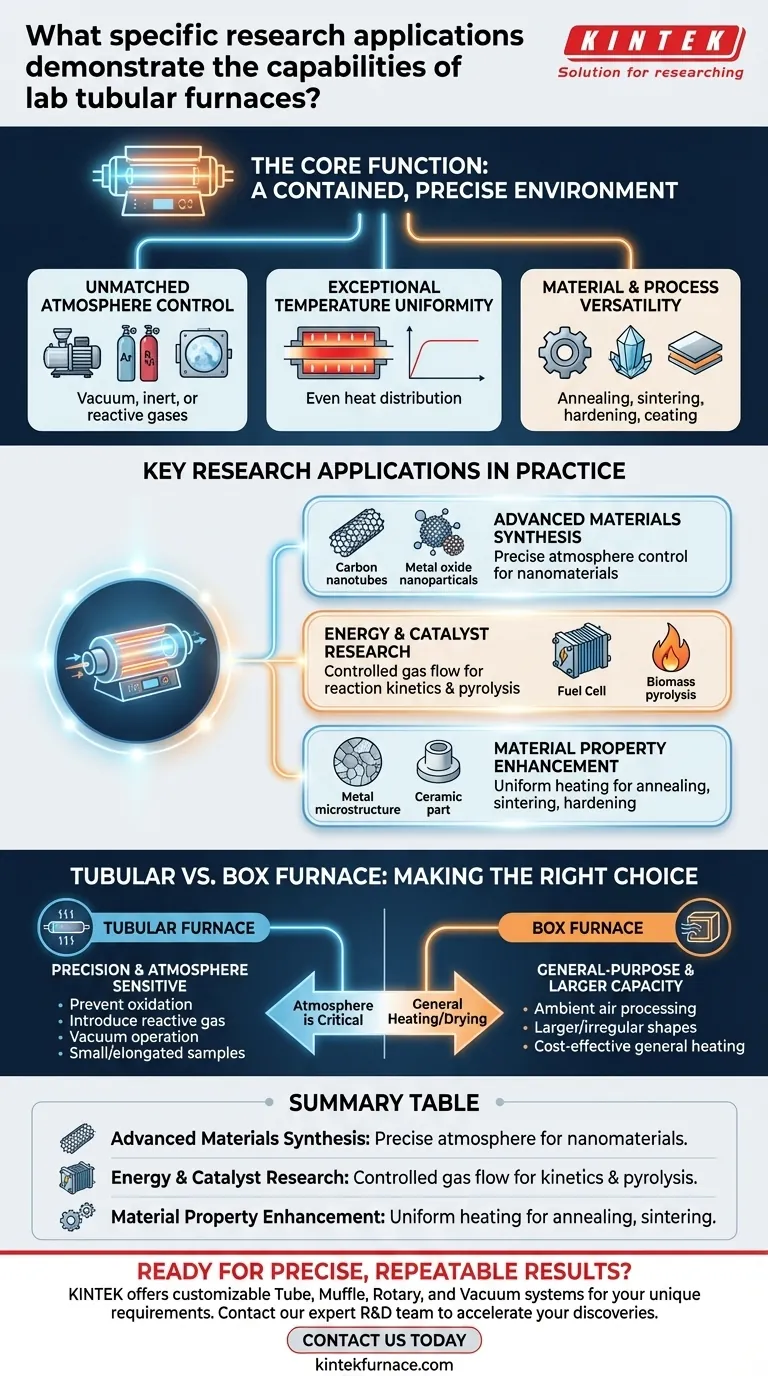
In research, lab tubular furnaces demonstrate their capabilities primarily in applications requiring precise thermal processing within a highly controlled atmosphere. They are essential for synthesizing advanced nanomaterials, testing the performance of fuel cell catalysts, and analyzing the byproducts of biomass pyrolysis for renewable energy studies.
The true value of a tubular furnace isn't just its ability to reach high temperatures, but its capacity to create a pristine, controllable, and uniform environment. This makes it indispensable for research where the sample's interaction with its atmospheric surroundings is as critical as the heat itself.
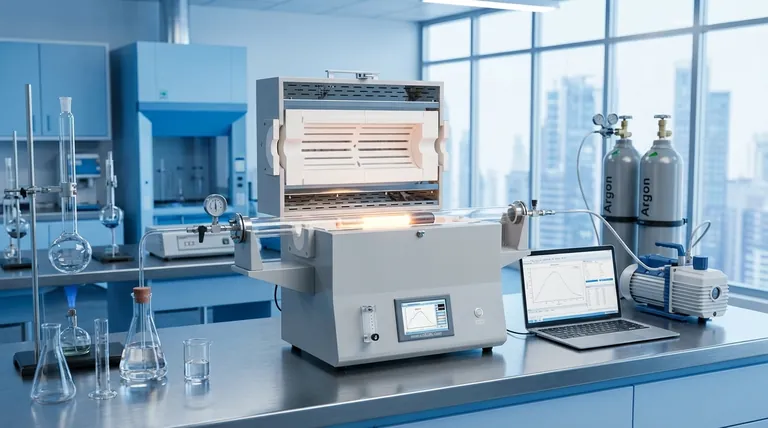

The Core Function: A Contained, Precise Environment
The design of a tubular furnace is central to its scientific utility. It moves beyond simple heating to offer researchers a tightly regulated reaction chamber.
Unmatched Atmosphere Control
The defining feature of a tubular furnace is its sealed tube, which allows for complete control over the gaseous environment. Researchers can create a vacuum, introduce specific inert gases like argon to prevent oxidation, or use reactive gases to drive chemical synthesis.
Exceptional Temperature Uniformity
The cylindrical heating chamber naturally promotes even heat distribution around the sample. This uniformity is critical for processes like annealing or crystal growth, where temperature gradients could ruin the results.
Material and Process Versatility
These furnaces are used for a wide range of thermal processes, including annealing, sintering, hardening, and coating. They can accommodate many material types, from metals and ceramics to advanced semiconductors and organic compounds.
Key Research Applications in Practice
The combination of precise temperature and atmosphere control enables groundbreaking work in several fields.
Advanced Materials Synthesis
Tubular furnaces are workhorses in materials science, particularly for creating nanomaterials like carbon nanotubes and metal oxide nanoparticles. By carefully managing temperature, gas flow, and reaction time, scientists can precisely tailor the final properties of the material.
Energy and Catalyst Research
In the development of fuel cells, these furnaces are used to test catalyst performance. They heat catalysts and reactant gases in a controlled stream, allowing for the detailed study of reaction kinetics. Similarly, they are used for the pyrolysis of biomass, breaking it down with heat in an oxygen-free environment to analyze potential biofuels.
Material Property Enhancement
Industries from aerospace to electronics rely on tubular furnaces for heat treatment. This process alters the microstructure of materials like metals and ceramics to enhance their properties, such as strength, hardness, or conductivity.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Tubular vs. Box Furnace
Choosing the right furnace depends entirely on the experimental requirements. A tubular furnace is a specialized tool, not a universal solution.
When to Choose a Tubular Furnace
A tubular furnace is the superior choice when your process is sensitive to the atmosphere. If you need to prevent oxidation, introduce a reactive gas, or operate under a vacuum, the sealed tube is non-negotiable. Its design also offers the best temperature uniformity for small or elongated samples.
When a Box Furnace May Suffice
For general-purpose heating, drying, or processing of larger or irregularly shaped samples in ambient air, a box furnace is often more practical. If strict atmosphere control is not a primary concern, a box furnace provides a larger working volume and is typically more cost-effective.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your research objective should dictate your equipment choice. Consider the following guidelines to select the appropriate tool.
- If your primary focus is synthesizing atmosphere-sensitive materials: A tubular furnace is essential for the precise environmental control required for nanomaterials, semiconductors, or reactive chemical synthesis.
- If your primary focus is analyzing reactions with gaseous components: A tubular furnace is the correct tool for studying catalysis or pyrolysis where controlling gas flow and composition is critical.
- If your primary focus is general heat treatment of non-sensitive samples: A box furnace offers greater capacity and simplicity for tasks like annealing many common metals or firing ceramics in air.
Ultimately, selecting the correct furnace is the foundational step toward achieving reliable and repeatable scientific results.
Summary Table:
| Research Application | Key Capability Demonstrated |
|---|---|
| Advanced Materials Synthesis | Precise atmosphere control for creating nanomaterials (e.g., carbon nanotubes) |
| Energy & Catalyst Research | Controlled gas flow for studying reaction kinetics and pyrolysis |
| Material Property Enhancement | Uniform heating for annealing, sintering, and hardening processes |
Ready to achieve precise, repeatable results in your research?
A lab tubular furnace is more than just a heater; it's a controlled environment essential for synthesizing sensitive materials, testing catalysts, and driving innovative energy studies. The right furnace is foundational to your success.
KINTEK's expert R&D and manufacturing team is here to help. We offer a range of customizable lab high-temperature furnaces, including Tube, Muffle, Rotary, and Vacuum systems, designed to meet your unique research requirements.
Contact us today to discuss how a KINTEK tubular furnace can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and accelerate your discoveries.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety



















