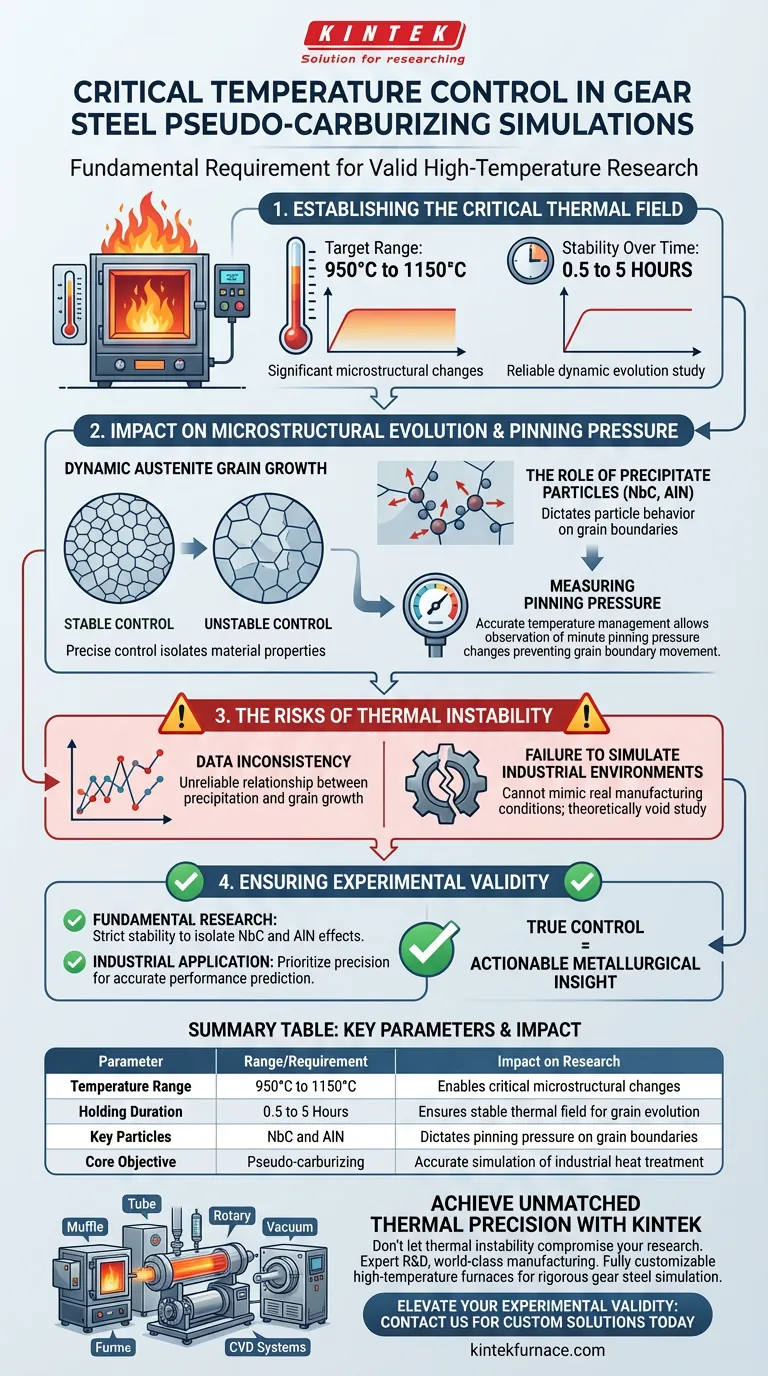
Precise temperature control is the fundamental requirement for valid pseudo-carburizing simulations. In high-temperature heat treatment furnaces, specifically within the critical range of 950°C to 1150°C, maintaining a stable thermal field is essential to accurately replicate industrial conditions. Without this precision, it is impossible to reliably study the dynamic evolution of austenite grains or the behavior of precipitate particles over holding durations of 0.5 to 5 hours.
Accurate thermal management is not just about reaching a target temperature; it is about stabilizing the environment to observe the minute pinning pressure changes caused by NbC or AlN particles. This precision ensures that experimental data accurately reflects the realities of industrial gear steel carburizing.

Establishing the Thermal Field
The Critical Temperature Range
For gear steel simulation, the furnace must maintain rigorous control between 950°C and 1150°C.
This specific high-temperature window is where the most significant microstructural changes occur in the steel.
Stability Over Time
The simulation requires this stability to be maintained for durations ranging from 0.5 to 5 hours.
Any fluctuation during this extended period can introduce variables that skew the data regarding grain evolution.
Impact on Microstructural Evolution
Dynamic Austenite Grain Growth
The primary goal of these simulations is to study how austenite grains evolve dynamically.
Grain growth is highly sensitive to thermal inputs; precise control ensures that growth patterns are a result of material properties, not furnace error.
The Role of Precipitate Particles
In gear steel, particles such as NbC (Niobium Carbide) and AlN (Aluminum Nitride) play a crucial role.
These particles reside on the grain boundaries, and their behavior is strictly dictated by the thermal environment.
Measuring Pinning Pressure
Accurate temperature management allows researchers to observe changes in pinning pressure.
This pressure is the force exerted by the precipitate particles that prevents grain boundaries from moving. Reliable observations of this mechanism are impossible without a stable thermal field.
The Risks of Thermal Instability
Data Inconsistency
If the temperature control lacks precision, the observed relationship between particle precipitation and grain growth becomes unreliable.
You cannot distinguish between effects caused by the alloy composition and effects caused by temperature spikes or drops.
Failure to Simulate Industrial Environments
The ultimate goal is to effectively simulate industrial carburizing environments.
A furnace that cannot hold a precise setpoint fails to mimic the controlled conditions of actual manufacturing, rendering the pseudo-carburizing study theoretically void.
Ensuring Experimental Validity
To maximize the value of your high-temperature simulations, align your equipment capabilities with your specific research goals.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research: Ensure your furnace can maintain strict stability to isolate the effects of NbC and AlN pinning pressures on grain boundaries.
- If your primary focus is industrial application: Prioritize thermal precision to guarantee your pseudo-carburizing cycle accurately predicts real-world gear steel performance.
True control over your thermal field is the only path to actionable metallurgical insight.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Range/Requirement | Impact on Research |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | 950°C to 1150°C | Enables critical microstructural changes |
| Holding Duration | 0.5 to 5 Hours | Ensures stable thermal field for grain evolution |
| Key Particles | NbC and AlN | Dictates pinning pressure on grain boundaries |
| Core Objective | Pseudo-carburizing | Accurate simulation of industrial heat treatment |
Achieve Unmatched Thermal Precision with KINTEK
Don't let thermal instability compromise your metallurgical research. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK provides high-precision Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to meet the rigorous demands of gear steel simulation. Whether you need to isolate pinning pressure effects or replicate complex industrial carburizing cycles, our lab high-temperature furnaces are fully customizable to your unique research specifications.
Ready to elevate your lab's experimental validity? Contact us today to find your custom solution.
Visual Guide
References
- Yingqi Zhu, Na Min. Effect of Precipitated Particles on Austenite Grain Growth of Al- and Nb-Microalloyed 20MnCr Gear Steel. DOI: 10.3390/met14040469
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the typical functions performed by laboratory furnaces? Unlock Precise Thermal Processing for Your Materials
- What is the temperature range of a lab furnace? Find Your Perfect Match
- How does an industrial vacuum drying oven affect electrode performance? Optimize Sodium-Ion Battery Stability
- What roles does a laboratory constant-temperature drying oven play in evaluating eggshell adsorbents? Key Insights
- What are some common applications of industrial furnaces? Discover Key Uses in Manufacturing and Research
- Why are graphite molds preheated to 800 °C for Invar 36 casting? Unlock High-Quality Ingot Production
- What are the benefits of adding calcium oxide in sludge thermal treatment? Boost Efficiency & Reduce Emissions
- What is the importance of a laboratory oven's programmed heating for epoxy-polyimide curing? Essential Thermal Control



















