At its core, the space-saving design of a tube furnace is advantageous because it delivers high thermal efficiency and uniform heating within a minimal physical footprint. This combination of compact size and superior performance makes it an indispensable tool in research and industrial settings where both laboratory space and process precision are at a premium.
The true advantage of a tube furnace's design is not merely that it saves space. It's that its inherent compactness is directly responsible for achieving the exceptional thermal uniformity and operational efficiency required for sensitive, high-temperature processes.
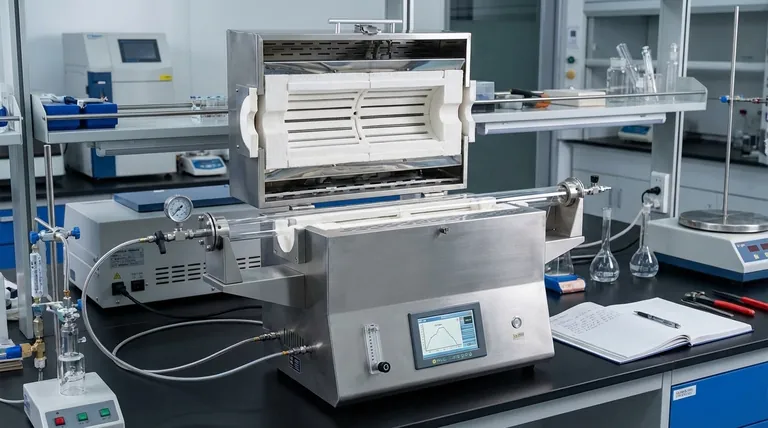

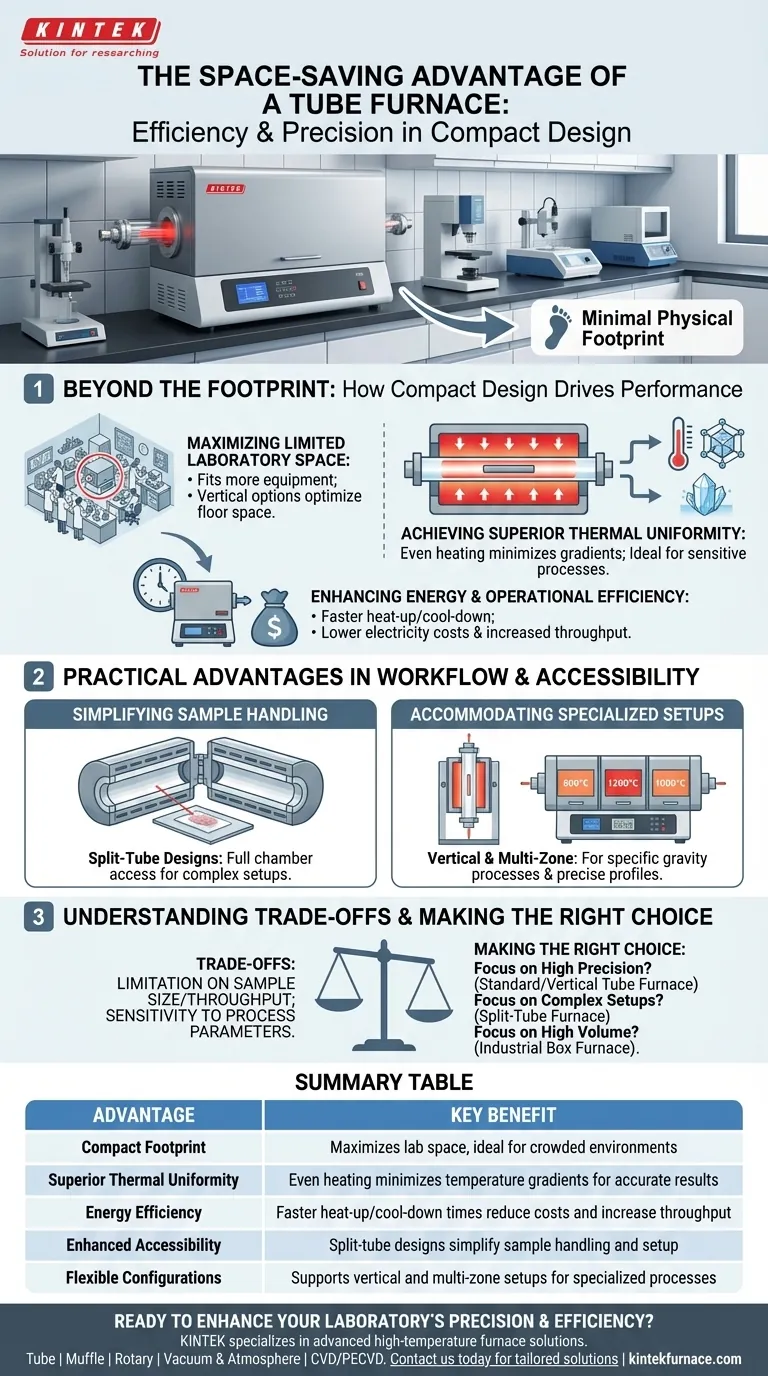
Beyond the Footprint: How Compact Design Drives Performance
The value of a tube furnace's design extends far beyond simply occupying less bench space. The physical form factor is intrinsically linked to its functional excellence, impacting everything from energy use to the integrity of experimental results.
Maximizing Limited Laboratory Space
A tube furnace’s small, linear footprint is a significant practical benefit. In crowded labs or production facilities, every square inch of counter or floor space is valuable.
Its compact nature allows for more equipment to be housed in a single area, increasing the overall capability of the facility. Some vertical models further optimize this by using vertical space, freeing up the area underneath the furnace for temporary storage or other equipment.
Achieving Superior Thermal Uniformity
This is the most critical performance advantage derived from the design. The cylindrical heating chamber ensures that the sample tube is heated evenly from all sides along its length.
This uniform heat distribution minimizes temperature gradients, which can compromise the integrity of materials processing, crystal growth, or chemical vapor deposition. Unlike larger, box-style furnaces that can struggle with hot and cold spots, the tubular design provides a naturally consistent thermal environment.
Enhancing Energy and Operational Efficiency
A smaller heating chamber requires less energy to reach and maintain a target temperature. The reduced internal volume means faster heat-up and cool-down times.
This efficiency not only lowers electricity costs but also increases throughput, as operators can complete thermal cycles more quickly.
Practical Advantages in Workflow and Accessibility
The design of a tube furnace also incorporates features that directly improve usability and streamline laboratory workflows.
Simplifying Sample Handling with Split-Tube Designs
Many tube furnaces feature a split-tube design, where the chamber is constructed in two halves joined by hinges.
This allows the furnace to be opened completely, providing immediate access to the entire process tube. This feature is invaluable for inserting or adjusting complex experimental setups, delicate samples, or substrates that cannot be easily slid in from one end.
Accommodating Vertical and Multi-Zone Setups
The modular nature of the tube furnace design makes it ideal for specialized configurations. Furnaces can be oriented vertically for specific gravity-related processes like crystal growth.
Furthermore, their compact form allows for the creation of multi-zone furnaces, where several heating units are placed in a series. This enables operators to create precise temperature profiles and gradients along the length of the tube, a level of control difficult to achieve with bulkier equipment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly advantageous, the design of a tube furnace is not universally optimal. Understanding its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Limitation on Sample Size and Throughput
The most obvious trade-off is sample volume. The diameter of the process tube inherently limits the size and shape of the materials you can process.
For applications requiring high-volume batch processing or the heating of large, bulky items, a larger chamber or industrial box furnace would be more appropriate.
Sensitivity to Process Parameters
The smaller internal volume that provides rapid heating can also make the system more sensitive to fluctuations. Precise control over gas flow rates is often necessary to maintain a stable atmosphere, as small variations can have a more pronounced effect than in a larger furnace.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the correct equipment, you must align the furnace's design benefits with your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is high-precision material synthesis in a crowded lab: The exceptional thermal uniformity and minimal footprint of a standard or vertical tube furnace are ideal.
- If your primary focus is working with complex or delicate experimental setups: The accessibility of a split-tube furnace will significantly improve your workflow and reduce the risk of sample damage.
- If your primary focus is high-volume batch processing of large components: The capacity of a box furnace or a dedicated industrial furnace will be necessary, despite its larger footprint.
Ultimately, the advantage of a tube furnace lies not just in its size, but in how its thoughtful design directly enhances the precision and efficiency of your work.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Compact Footprint | Maximizes lab space, ideal for crowded environments |
| Superior Thermal Uniformity | Even heating minimizes temperature gradients for accurate results |
| Energy Efficiency | Faster heat-up/cool-down times reduce costs and increase throughput |
| Enhanced Accessibility | Split-tube designs simplify sample handling and setup |
| Flexible Configurations | Supports vertical and multi-zone setups for specialized processes |
Ready to enhance your laboratory's precision and efficiency? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With our strong R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can benefit your research or industrial processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide



















