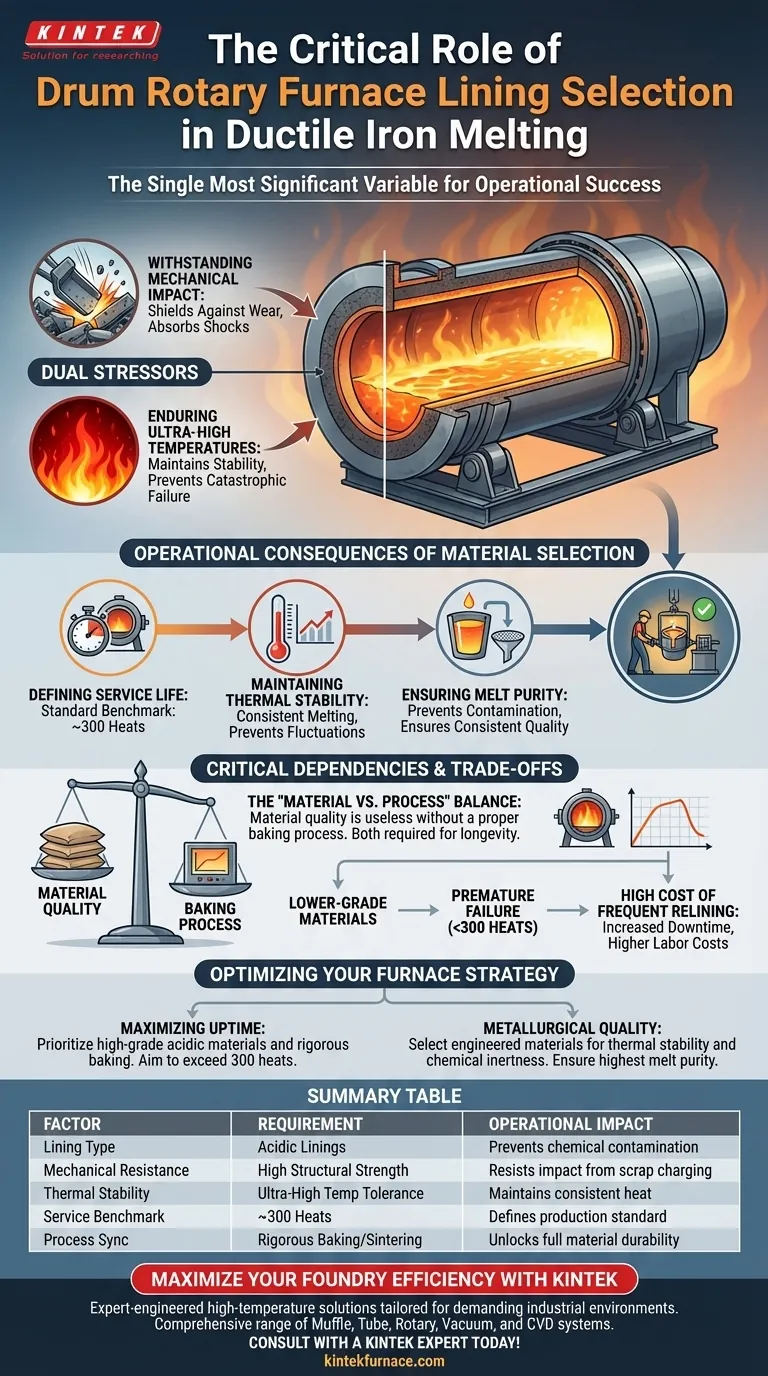
The selection of lining materials is the single most significant variable in the operational success of drum rotary furnaces. Because these furnaces typically utilize acidic linings to process ductile iron, the material must simultaneously resist the mechanical impact of charging and the thermal shock of ultra-high melting temperatures to prevent catastrophic failure.
The integrity of the furnace lining does more than just contain the melt; it directly dictates the purity of the iron and the consistency of the temperature. A compromised lining leads to reduced service life and contaminated yields, making material selection and the baking process the foundation of efficient production.

The Dual Stressors of Rotary Furnaces
Withstanding Mechanical Impact
The physical environment inside a rotary furnace is aggressive. The lining is not merely a container; it acts as a shield against mechanical wear.
During the charging process, heavy scrap material impacts the furnace walls. The lining material must possess sufficient structural strength to absorb these physical shocks without cracking or spalling.
Enduring Ultra-High Temperatures
Once melting begins, the mechanical stress is replaced by intense thermal stress. The lining must maintain stability in ultra-high temperature environments.
If the material cannot withstand these extremes, it will degrade rapidly. This degradation compromises the safety of the vessel and the efficiency of the melt cycle.
Operational Consequences of Material Selection
Defining Service Life
The lifespan of your furnace is finite, but controllable. The combination of lining quality and the baking process directly determines the service life of the unit.
A standard benchmark for a well-lined drum rotary furnace is approximately 300 heats. Falling short of this number often indicates a failure in material selection or preparation.
Maintaining Thermal Stability
A high-quality lining acts as an insulator as well as a container. It is essential for maintaining stable melting temperatures throughout the process.
Fluctuations in temperature caused by poor insulation can lead to inconsistent metallurgical properties in the ductile iron.
Ensuring Melt Purity
The chemical interaction between the melt and the lining is critical. The lining acts as a barrier to ensure the purity of the melt.
Inferior materials can degrade and introduce impurities into the molten iron. This contamination can render a batch unusable, wasting time and resources.
Critical Dependencies and Trade-offs
The "Material vs. Process" Balance
It is a common pitfall to assume that buying the most expensive lining material guarantees performance. Material quality is useless without a proper baking process.
Even premium acidic linings will fail prematurely if the initial baking does not properly sinter the material. You cannot trade process discipline for material cost; both are required for longevity.
The Cost of Frequent Relining
Choosing lower-grade materials may seem cost-effective initially. However, if the lining fails before the 300-heat benchmark, the downtime costs far outweigh the savings.
Frequent relining stops production and increases labor costs. The goal is to maximize "uptime" by selecting materials that offer predictable durability.
Optimizing Your Furnace Strategy
To ensure efficient ductile iron melting, align your lining strategy with your production goals:
- If your primary focus is maximizing uptime: Prioritize high-grade acidic materials and a rigorous baking protocol to consistently reach or exceed the 300-heat benchmark.
- If your primary focus is metallurgical quality: Select lining materials specifically engineered to maintain thermal stability and prevent chemical reactivity, ensuring the highest melt purity.
Ultimately, treating the furnace lining as a precision component rather than a simple consumable ensures the long-term viability of your melting operation.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Requirement | Operational Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Lining Type | Acidic Linings | Prevents chemical contamination in ductile iron |
| Mechanical Resistance | High Structural Strength | Resists impact from heavy scrap charging |
| Thermal Stability | Ultra-High Temp Tolerance | Maintains consistent heat and prevents vessel failure |
| Service Benchmark | ~300 Heats | Defines the standard for efficient production cycles |
| Process Sync | Rigorous Baking/Sintering | Essential to unlock the full durability of the material |
Maximize Your Foundry Efficiency with KINTEK
Don’t let lining failure disrupt your production or compromise your melt purity. KINTEK provides expert-engineered high-temperature solutions tailored for demanding industrial environments. Backed by world-class R&D and manufacturing, we offer a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all fully customizable to meet your specific metallurgical needs.
Whether you are aiming to exceed the 300-heat benchmark or seeking superior thermal insulation for specialized alloys, our technical team is ready to assist. Consult with a KINTEK expert today to optimize your melting operations!
Visual Guide
References
- Jan Bredl. Quality Prediction of Spheroidal Graphite Cast Iron for Machine Tool Parts. DOI: 10.21062/mft.2025.032
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How is a rotary kiln different from a rotary dryer? Key Differences in Thermal Processing Equipment
- How do indirect-fired rotary kilns contribute to metallurgical processes? Unlock High-Purity Material Processing
- What are the advantages of using industrial microwave heating equipment over traditional pyrolysis furnaces? Faster CFRP Recovery
- What role do rotary tube furnaces play in the analysis of metallurgical slags? Unlock Precise Slag Analysis for Better Metallurgy
- What are the key advantages of rotary furnaces? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- How does the rotating design of the rotary tube sintering furnace improve heating uniformity? Achieve Consistent Results
- How does the heating process work in rotary tube furnaces? Achieve Uniform Heat for Powders and Granules
- Why is precise temperature control important in rotary furnaces? Ensure Quality and Consistency



















