In short, precise temperature control in a rotary furnace is the most critical factor for ensuring the quality, consistency, and structural integrity of the final product. It directly prevents costly defects, minimizes material waste, and guarantees that processes like sintering, annealing, or chemical reactions produce repeatable and reliable results batch after batch.
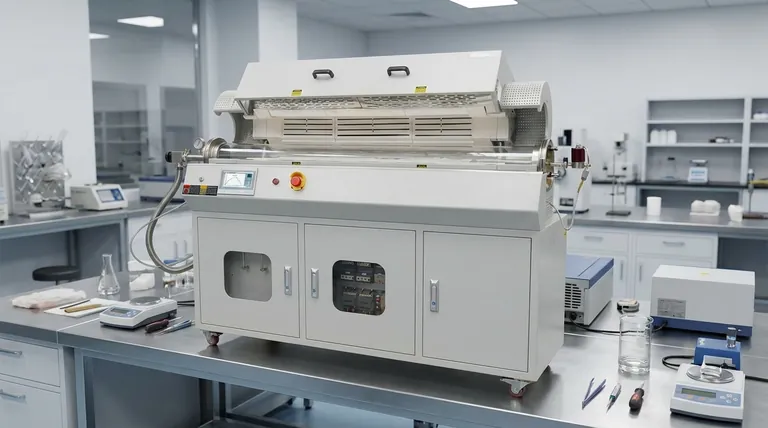
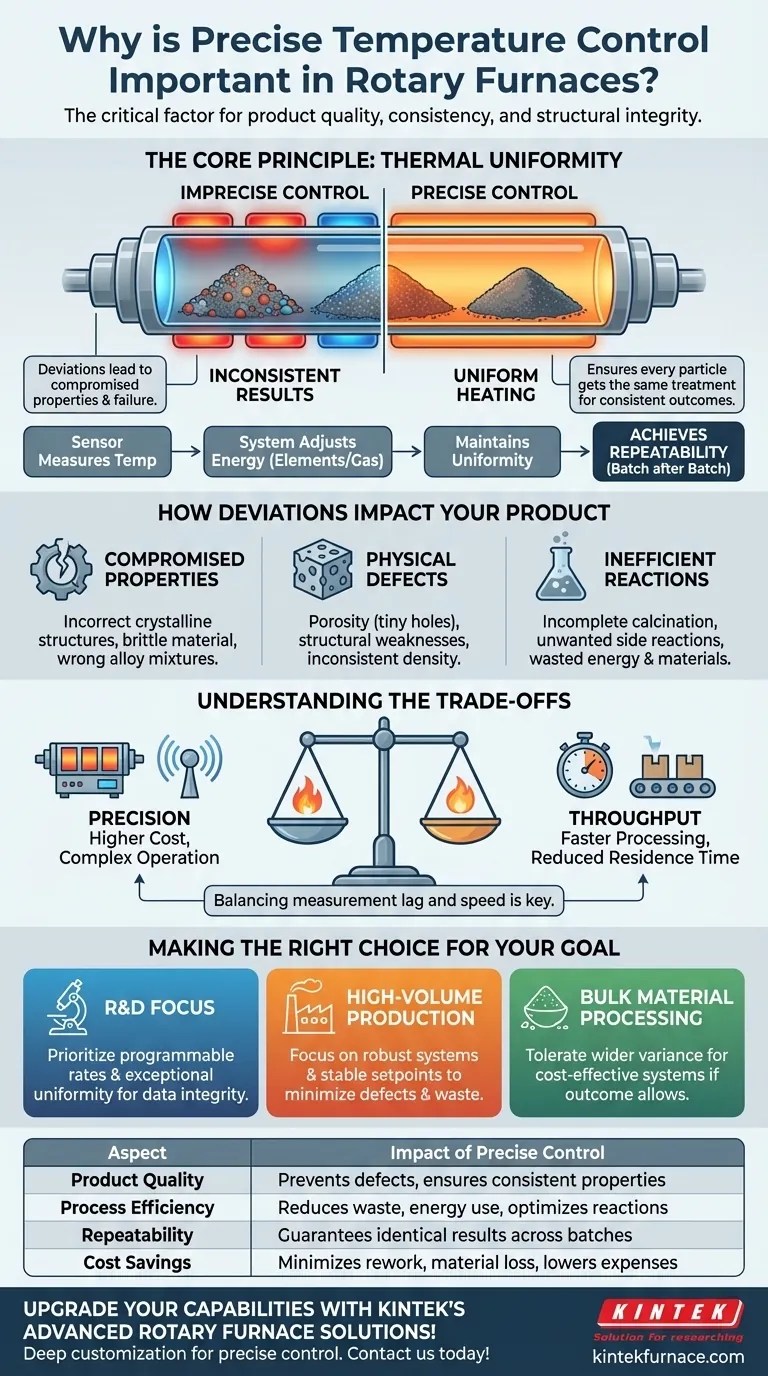
The core issue is not simply about reaching a target temperature, but about maintaining thermal uniformity throughout the entire material load as it moves. Deviations in temperature create inconsistencies that compromise the material's properties, leading to product failure and operational inefficiency.

The Core Principle: From Setpoint to Uniformity
Many assume temperature control is just about hitting a number on a display. In a dynamic environment like a rotary furnace, it's far more complex. The goal is to manage the material's entire thermal journey.
What "Precise Control" Really Means
Precise control involves a system that constantly measures temperature and automatically adjusts the energy input—be it from electrical heating elements or gas flow. This system isn't just maintaining an average; it's working to ensure the temperature is consistent across the length of the furnace tube and throughout the tumbling material bed.
Why Uniform Heating is Paramount
In a rotary furnace, the material is constantly mixing. If one part of the furnace is hotter than another, some material will be over-processed while other parts are under-processed. Uniformity ensures that every single particle receives the same thermal treatment, which is essential for consistent outcomes.
Achieving Process Repeatability
For both research labs and large-scale manufacturing, the ability to replicate a process perfectly is non-negotiable. Precise temperature control ensures that the results from a run today will be identical to the results from a run next month, guaranteeing consistent product quality and reliable experimental data.
How Temperature Deviations Impact Your Product
Even minor, transient fluctuations in temperature can have significant and detrimental effects on the final product. These issues often manifest as compromised physical properties or visible defects.
Compromised Material Properties
For processes like annealing or creating metal alloys, specific temperatures are required to achieve desired crystalline structures or chemical compositions. Poor control can result in brittle material, incorrect alloy mixtures, or incomplete chemical reactions, rendering the product useless.
Formation of Physical Defects
Inconsistent heating is a direct cause of defects. For example, in casting or sintering applications, improper temperature can lead to porosity (tiny holes) or other structural inconsistencies that weaken the final product.
Inefficient Chemical Reactions
Many rotary furnaces are used for chemical processes like calcination, where a material is heated to drive off a substance. If the temperature is too low, the reaction will be incomplete. If it's too high, you risk unwanted side reactions or material degradation, wasting both energy and raw materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Achieving perfect temperature control involves balancing competing factors. Recognizing these trade-offs is key to selecting and operating a system effectively.
The Cost of Precision
More sophisticated control systems, featuring multi-zone heating and advanced sensor arrays, deliver superior uniformity. However, this precision comes with a higher upfront investment and increased operational complexity.
The Challenge of Measurement Lag
There is an inherent delay between the heating element's output, the furnace wall temperature, and the actual temperature of the material inside. A well-designed control system anticipates this lag, but it remains a physical limitation that can be challenging in processes requiring rapid temperature changes.
Throughput vs. Control
Increasing the rate at which material moves through the furnace (throughput) reduces its residence time. This can make it more difficult for the system to achieve complete thermal uniformity. You must often choose between processing material faster and processing it with maximum precision.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The level of precision you need depends entirely on your application's sensitivity and your operational priorities.
- If your primary focus is research and development: Your goal is data integrity, so prioritize systems with programmable heating rates and exceptional uniformity to ensure reproducible results.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production: Your goal is consistency, so focus on a robust system that maintains a stable setpoint under continuous load to minimize defects and waste.
- If your primary focus is processing bulk, low-cost materials: You may be able to tolerate wider temperature variance if it doesn't critically impact the outcome, allowing for a less complex and more cost-effective system.
Ultimately, investing in the right level of temperature control is a direct investment in the reliability and value of your final product.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Impact of Precise Control |
|---|---|
| Product Quality | Prevents defects like porosity and ensures consistent material properties |
| Process Efficiency | Reduces waste and energy use by maintaining optimal reaction conditions |
| Repeatability | Guarantees identical results across batches for reliable outcomes |
| Cost Savings | Minimizes rework and material loss, lowering operational expenses |
Upgrade your laboratory's capabilities with KINTEK's advanced rotary furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide high-temperature furnaces like Rotary, Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise temperature control tailored to your unique experimental needs, enhancing product quality and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your processes and deliver reliable results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing



















