In metallurgical analysis, a rotary tube furnace provides a highly controlled environment to precisely heat, mix, and react slag samples. This capability is essential for simulating industrial conditions on a laboratory scale, allowing researchers to accurately study the slag's chemical behavior and physical properties without the variables and immense scale of a full production furnace.
Analyzing slag is challenging because its properties are highly dependent on temperature, atmosphere, and homogeneity. The rotary tube furnace's core role is to isolate these variables, enabling researchers to conduct repeatable experiments that reveal how to optimize industrial processes for better efficiency and material recovery.

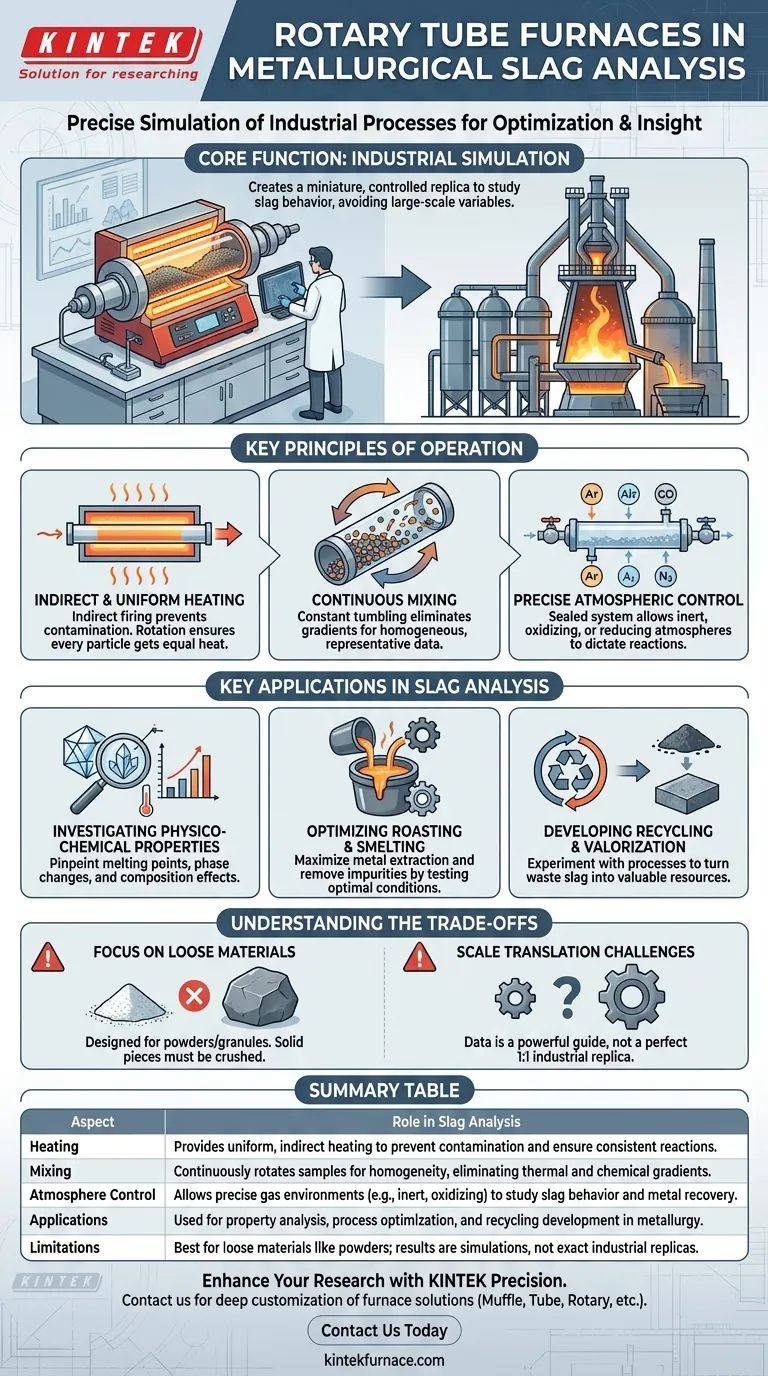
The Core Function: Simulating Industrial Processes
The primary value of a rotary tube furnace in metallurgy is its ability to create a miniature, controlled replica of a large-scale industrial environment. This is achieved through three key operational principles.
Principle of Operation: Indirect & Uniform Heating
A rotary tube furnace operates on the principle of indirect firing. The sample material is placed inside a rotating tube, which is then heated externally.
This design prevents contamination of the slag from combustion byproducts. The slow rotation continuously tumbles the material, ensuring every particle is exposed to the same temperature, which is critical for achieving uniform chemical reactions and phase changes.
The Importance of Continuous Mixing
Slags are complex and often non-homogenous mixtures. The constant rotation of the furnace tube ensures the sample is thoroughly and continuously mixed as it is heated.
This mixing prevents chemical and thermal gradients from forming within the sample, leading to data that accurately reflects the bulk properties of the material. It is fundamental for studying reaction rates and reaching chemical equilibrium.
Precise Atmospheric Control
Many critical reactions in metallurgy are dictated by the surrounding atmosphere. Rotary tube furnaces are sealed systems, allowing for complete control over the internal gas environment.
Researchers can introduce inert (e.g., argon), oxidizing (e.g., air), or reducing (e.g., carbon monoxide) atmospheres. This allows them to study how the slag will interact with metal, predict metal recovery rates, or determine how to refine the slag itself.
Key Applications in Slag Analysis
By controlling heat, mixing, and atmosphere, these furnaces enable specific and crucial types of analysis that are vital for advancing metallurgical science and industry.
Investigating Physico-Chemical Properties
The furnace's uniform heat treatment is ideal for studying the fundamental properties of slag. Researchers can pinpoint exact melting points, observe phase transformations, and test how composition changes affect the slag's behavior.
Optimizing Roasting and Smelting
The references note the use of these furnaces for roasting ores and fusing metals. By processing slag under different controlled conditions, researchers can determine the optimal temperature, residence time, and atmosphere to maximize the extraction of valuable metals or remove impurities.
Developing Recycling and Valorization Processes
As industries look to create value from waste streams, rotary tube furnaces are used to experiment with slag recycling. They help develop processes to fuse slag with other materials or extract useful substances, turning a byproduct into a valuable resource.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the rotary tube furnace is a specialized tool with specific limitations that must be understood to ensure proper application and interpretation of results.
Focus on Loose Materials
These furnaces are designed exclusively for processing powders, granules, or other loose materials. They cannot be used to analyze large, solid pieces of slag unless the sample is first crushed and milled into a fine powder.
Scale Translation Challenges
A laboratory-scale furnace provides invaluable data, but the results do not always translate perfectly to a massive industrial operation. The data serves as a powerful guide for optimization, but it is a simulation, not a perfect one-to-one replica of production conditions.
Making the Right Choice for Your Research Goal
A rotary tube furnace is a targeted instrument. Its use should align directly with your analytical objectives.
- If your primary focus is fundamental property analysis: The furnace's uniform heating and controlled environment are perfect for accurately determining the melting points, phase diagrams, and thermal behavior of slag powders.
- If your primary focus is process optimization: Use the furnace to systematically test how changes in temperature profiles and gas atmospheres impact metal recovery or slag conditioning.
- If your primary focus is recycling and valorization: The furnace is an excellent tool for simulating fusion and extraction processes to develop new methods for recovering valuable elements from waste slag.
Ultimately, the rotary tube furnace empowers metallurgists to deconstruct the complex behavior of slag, providing the clear, actionable insights needed to improve industrial efficiency and sustainability.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Role in Slag Analysis |
|---|---|
| Heating | Provides uniform, indirect heating to prevent contamination and ensure consistent reactions. |
| Mixing | Continuously rotates samples for homogeneity, eliminating thermal and chemical gradients. |
| Atmosphere Control | Allows precise gas environments (e.g., inert, oxidizing) to study slag behavior and metal recovery. |
| Applications | Used for property analysis, process optimization, and recycling development in metallurgy. |
| Limitations | Best for loose materials like powders; results are simulations, not exact industrial replicas. |
Ready to enhance your metallurgical research with precision? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our rotary tube furnaces can optimize your slag analysis and boost efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing



















