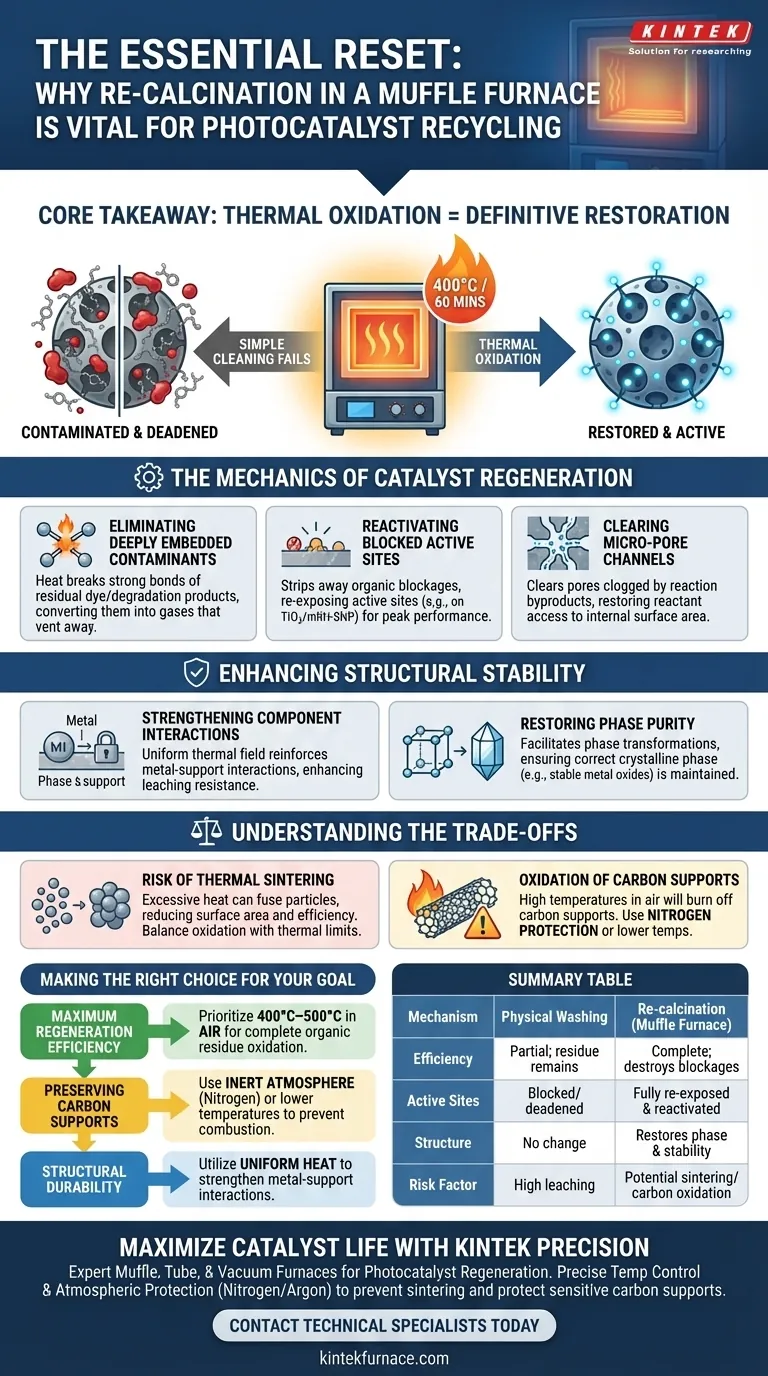
Re-calcination constitutes the definitive "reset" mechanism for photocatalysts during the recycling process. While washing removes loose surface debris, re-calcination in a muffle furnace (typically at 400°C for 60 minutes) is required to perform thermal oxidation, which chemically destroys stubborn residual dye molecules and degradation products that have bonded to the catalyst.
Core Takeaway Simple cleaning methods leave organic contaminants trapped in the catalyst's microstructure, progressively deadening its activity. Re-calcination utilizes controlled high heat to burn off these organic blockages and re-oxidize the surface, effectively restoring the material's original physicochemical properties and ensuring long-term reusability.
The Mechanics of Catalyst Regeneration
Eliminating Deeply Embedded Contaminants
During the photocatalytic process, dye molecules and their breakdown products adhere strongly to the catalyst surface.
Physical washing is often insufficient to dislodge these chemically adsorbed species.
Thermal oxidation provided by the muffle furnace breaks the chemical bonds of these organic residues, converting them into gases that vent away, leaving the catalyst surface pristine.
Reactivating Blocked Active Sites
The primary driver of photocatalytic activity is the availability of specific "active sites" on the surface (such as on TiO2/mRH-SNP).
When these sites are covered by residual pollutants, the catalyst is effectively blinded and cannot facilitate reactions.
Re-calcination strips away these blockages, re-exposing the active sites and allowing the material to function at near-original efficiency levels.
Clearing Micro-Pore Channels
Catalysts often rely on porous structures to maximize surface area.
Similar to how initial synthesis uses heat to remove organic templates (like TPAOH in zeolites), regeneration uses heat to clear pores clogged by reaction byproducts.
This ensures that reactants can once again diffuse deep into the material's structure, accessing internal surface area that was previously cut off.
Enhancing Structural Stability
Strengthening Component Interactions
Beyond cleaning, the uniform thermal field of a muffle furnace helps stabilize the catalyst structure.
Heat treatment can reinforce the interaction between the active metal phases and their support carriers.
This improved interaction enhances leaching resistance, preventing active components from detaching during subsequent liquid-phase reactions.
Restoring Phase Purity
Over repeated cycles, the crystalline structure of a catalyst can sometimes degrade or hydrate.
Re-calcination facilitates necessary phase transformations (e.g., ensuring metal hydroxides revert to stable metal oxides).
This ensures the material maintains the correct crystalline phase (such as monoclinic or hexagonal) required for peak photocatalytic activity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Thermal Sintering
While heat cleans the surface, excessive temperature or duration can cause sintering.
This is where small catalyst particles fuse together into larger clumps, drastically reducing the specific surface area and lowering efficiency.
You must balance the need for oxidation with the thermal limit of your specific material structure.
Oxidation of Carbon Supports
If your photocatalyst uses a carbon-based support (like carbon nanotubes or activated carbon), standard aerobic calcination is dangerous.
High temperatures in air will burn off the carbon support along with the contaminants.
For these materials, you must use a furnace with a nitrogen protection system or restrict temperatures to levels where the carbon framework remains stable while contaminants decompose.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When designing your regeneration protocol, consider your specific material constraints:
- If your primary focus is maximum regeneration efficiency: Prioritize temperatures around 400°C–500°C in air to ensure complete thermal oxidation of all organic residues and dye byproducts.
- If your primary focus is preserving carbon supports: Use an inert atmosphere (nitrogen) or lower temperatures to prevent the combustion of the underlying carbon framework.
- If your primary focus is structural durability: Utilize the uniform heat of the muffle furnace to strengthen metal-support interactions, which minimizes leaching during future cycles.
Re-calcination is not merely a drying step; it is a chemical restoration process that guarantees the longevity and reliability of your photocatalyst.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Physical Washing | Re-calcination (Muffle Furnace) |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | Mechanical removal of surface debris | Thermal oxidation of chemical bonds |
| Efficiency | Partial; leaves embedded residue | Complete; destroys stubborn organic blockages |
| Active Sites | Often remain blocked/deadened | Fully re-exposed and reactivated |
| Structure | No change to phase purity | Restores crystalline phase & stability |
| Risk Factor | High leaching in future cycles | Potential sintering if heat is uncontrolled |
Maximize Your Catalyst Life with KINTEK Precision
Don't let contaminated active sites compromise your research. KINTEK provides industry-leading muffle, tube, and vacuum furnace systems specifically designed for the rigorous demands of photocatalyst regeneration.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, our systems offer the precise temperature control and atmospheric protection (Nitrogen/Argon) required to prevent sintering and protect sensitive carbon supports. Whether you need standard calcination or a fully customizable high-temp furnace for unique materials, KINTEK ensures your catalysts are restored to peak performance every time.
Ready to elevate your lab's efficiency? Contact our technical specialists today to find the perfect thermal solution for your needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Lekan Taofeek Popoola, Sabitu Babatunde Olasupo. Photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue dye by magnetized TiO2-silica nanoparticles from rice husk. DOI: 10.1007/s13201-023-02052-8
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory high-temperature box furnace play in fire impact experiments for steel? | KINTEK
- What is the role of a high-temperature box furnace in coal gangue calcination? Unlock High Pozzolanic Activity
- What is the specific application of a muffle furnace in biochar characterization experiments? Optimize Ash Analysis
- How does a muffle furnace achieve high temperatures with uniformity and accuracy? Discover the Design Secrets for Precise Heat Treatment
- How does a forced convection oven facilitate the curing of flame-retardant epoxy resin? Ensure Uniform Cross-Linking
- How do muffle furnaces benefit the paint industry? Enhance Paint Testing with Precision Heat Control
- What materials are used for the cabinet of a box furnace and why? Discover Durable, Safe Steel Construction
- How does the muffle furnace ensure uniform heating? Achieve Precise, Even Heat for Your Lab



















