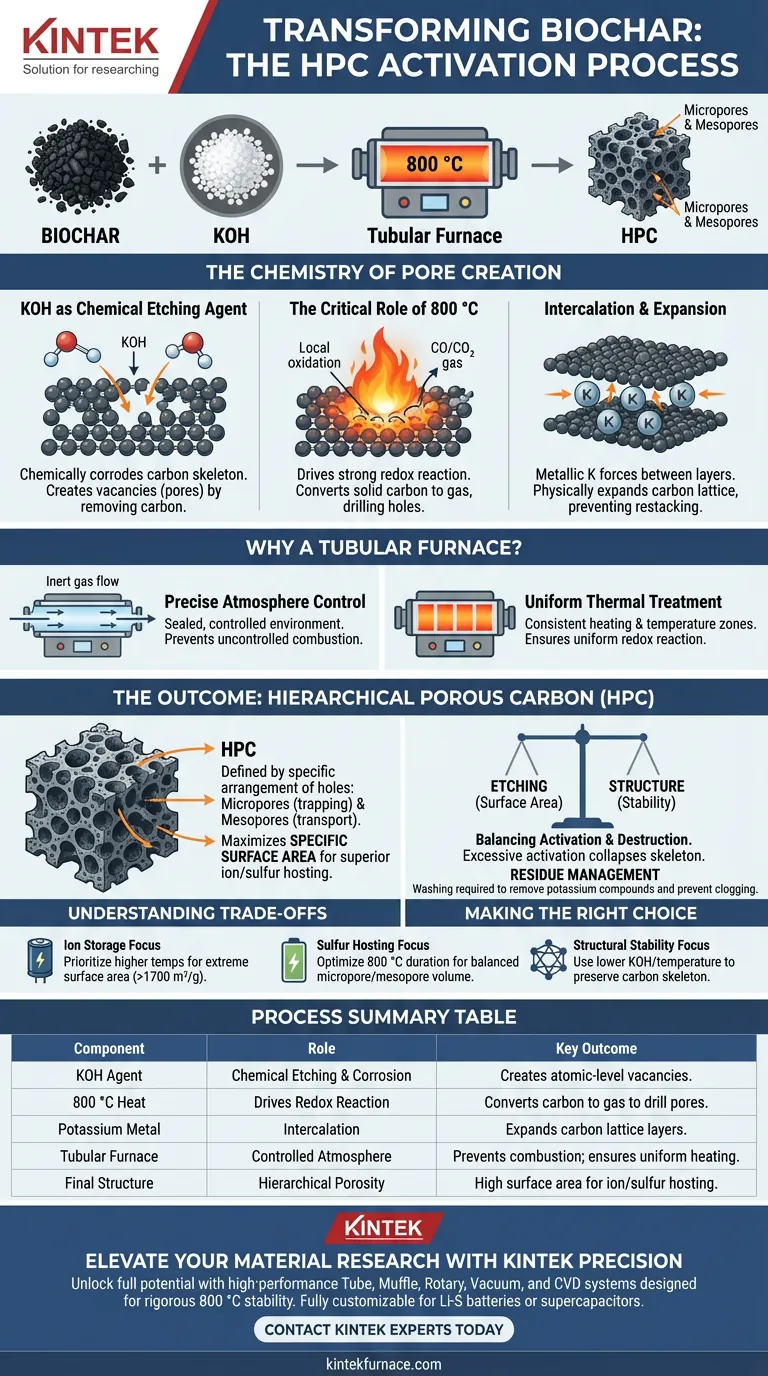
Biochar is mixed with Potassium Hydroxide (KOH) and treated at 800 °C to trigger a controlled chemical etching process known as activation. This specific combination creates a "hierarchical" pore structure—a complex network of microscopic and mesoscopic tunnels—by locally oxidizing the carbon skeleton. This significantly increases the material's specific surface area, transforming the biochar into a high-performance host capable of accommodating massive amounts of active substances, such as sulfur.
Core Takeaway: The intense heat of the tubular furnace allows KOH to act as a corrosive agent that oxidizes carbon and intercalates potassium metal between atomic layers. This dual action "exfoliates" the biochar, generating the vast surface area and porosity required for advanced energy storage applications.
The Chemistry of Pore Creation
KOH as a Chemical Etching Agent
At high temperatures, Potassium Hydroxide (KOH) does not merely coat the biochar; it actively attacks it.
KOH acts as a powerful etching agent that chemically corrodes the carbon skeleton. This reaction "eats away" specific carbon atoms, leaving behind vacancies that become pores.
The Critical Role of 800 °C
The specific temperature of 800 °C is chosen to drive a strong redox reaction between the carbon and the KOH.
At this temperature, the thermodynamic conditions trigger local oxidation. This converts the solid carbon into gas (CO/CO₂), effectively drilling holes into the material structure to create micropores and mesopores.
Intercalation and Expansion
During this process, KOH is reduced to metallic potassium.
This metallic potassium forces its way between the carbon layers (a process called intercalation). This physically expands the carbon lattice, preventing the layers from restacking and further increasing the available volume for ions or active materials.
Why Use a Tubular Furnace?
Precise Atmosphere Control
A tubular furnace is essential because it allows for a sealed, controlled environment.
This process often requires an inert atmosphere or specific reducing gases to function correctly. The tubular design prevents uncontrolled burning (combustion) of the biochar, which would happen in an open-air environment.
Uniform Thermal Treatment
Consistency is vital for pore distribution.
The tubular furnace provides accurately controlled heating rates and constant temperature zones. This ensures the redox reaction occurs uniformly throughout the sample, rather than just on the surface.
The Outcome: Hierarchical Porous Carbon (HPC)
Defining "Hierarchical" Structure
The goal is not just to create holes, but to create a specific arrangement of holes.
This process yields a mix of micropores (for trapping ions/sulfur) and mesopores (channels for transport). This multi-level structure is what makes the carbon "hierarchical."
Maximizing Specific Surface Area
The ultimate metric of success in this process is specific surface area.
By maximizing the contact area, the material creates numerous active sites. This allows the carbon to host significantly more sulfur or electrolytes, directly improving performance in batteries and supercapacitors.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Balancing Etching vs. Structure
There is a fine line between activation and destruction.
While KOH etching increases surface area, excessive activation (too much KOH or too high temperature) can collapse the carbon skeleton. This destroys the conductive pathways and mechanically weakens the material.
Residue Management
The process introduces chemical byproducts that must be managed.
After the furnace treatment, the material often requires washing to remove residual potassium compounds. Failing to clean the "etched" debris can clog the very pores you worked to create.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
This activation process is highly tunable. Adjusting your parameters in the tubular furnace dictates the final properties of your carbon.
- If your primary focus is Ion Storage (Supercapacitors): Prioritize higher temperatures (up to 800–1000 °C) to maximize intercalation and achieve extreme surface areas (potentially >1700 m²/g).
- If your primary focus is Sulfur Hosting (Li-S Batteries): Ensure the 800 °C treatment duration is optimized to balance micropore volume for trapping sulfur with mesopores for electrolyte access.
- If your primary focus is Structural Stability: Use a lower KOH ratio or slightly reduced temperature to preserve the carbon skeleton while still achieving moderate activation.
The precision of the 800 °C tubular furnace treatment is what turns low-value biochar into a high-value, functional nanomaterial.
Summary Table:
| Process Component | Role in Activation | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| KOH Agent | Chemical Etching & Corrosion | Creates atomic-level vacancies (Pores) |
| 800 °C Heat | Drives Redox Reaction | Converts carbon to gas to drill pores |
| Potassium Metal | Intercalation | Expands carbon lattice layers |
| Tubular Furnace | Controlled Atmosphere | Prevents combustion; ensures uniform heating |
| Final Structure | Hierarchical Porosity | High surface area for ion/sulfur hosting |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK Precision
Unlock the full potential of your carbon activation experiments with KINTEK’s high-performance laboratory solutions. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we provide high-precision Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to maintain the rigorous 800 °C thermal stability and inert atmospheres required for superior Hierarchical Porous Carbon (HPC) production.
Whether you are optimizing sulfur hosting for Li-S batteries or maximizing surface area for supercapacitors, our equipment is fully customizable to meet your unique research needs. Ensure uniform thermal treatment and repeatable results every time.
Ready to transform your biochar research?
Contact KINTEK Experts Today
Visual Guide
References
- Arunakumari Nulu, Keun Yong Sohn. N-doped CNTs wrapped sulfur-loaded hierarchical porous carbon cathode for Li–sulfur battery studies. DOI: 10.1039/d3ra08507d
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why Use a Programmable Tube Furnace for Ni-WOx/SAPO-11 Calcination? Ensure Catalyst Purity & Performance
- What factors should be considered when purchasing an alumina tube furnace? Key Tips for High-Temp Precision
- How does a dual-temperature zone tube furnace control crystal quality? Master PVT for Organic Single Crystals
- What Role Does a Tube Reactor Play in Food Waste Pyrolysis? Control Carbonization for High-Quality Biochar
- What is the purpose of using a high-temperature tube furnace with an argon atmosphere during carbonization?
- What is the significance of the calcination process using a high-temperature tube furnace? Enhance Bi2S3/BiOBr@In2S3 Performance
- What are the primary functions of a precision gas filtration device? Maximize Data Integrity in Drop Tube Furnaces
- What are the key applications of tube furnaces in materials research and chemistry? Unlock Precise High-Temperature Processing



















