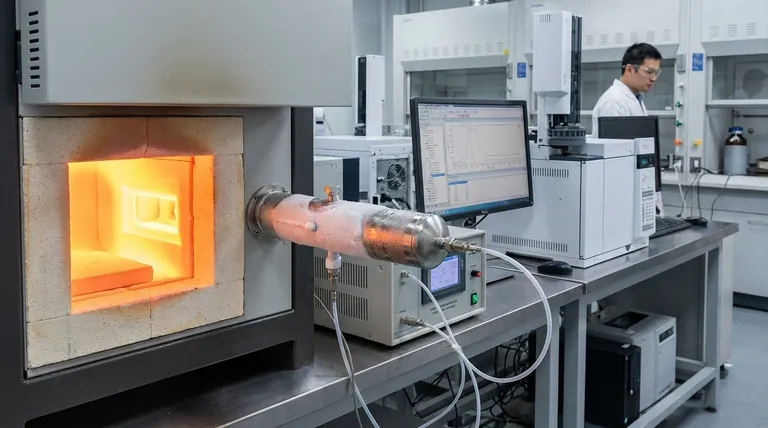
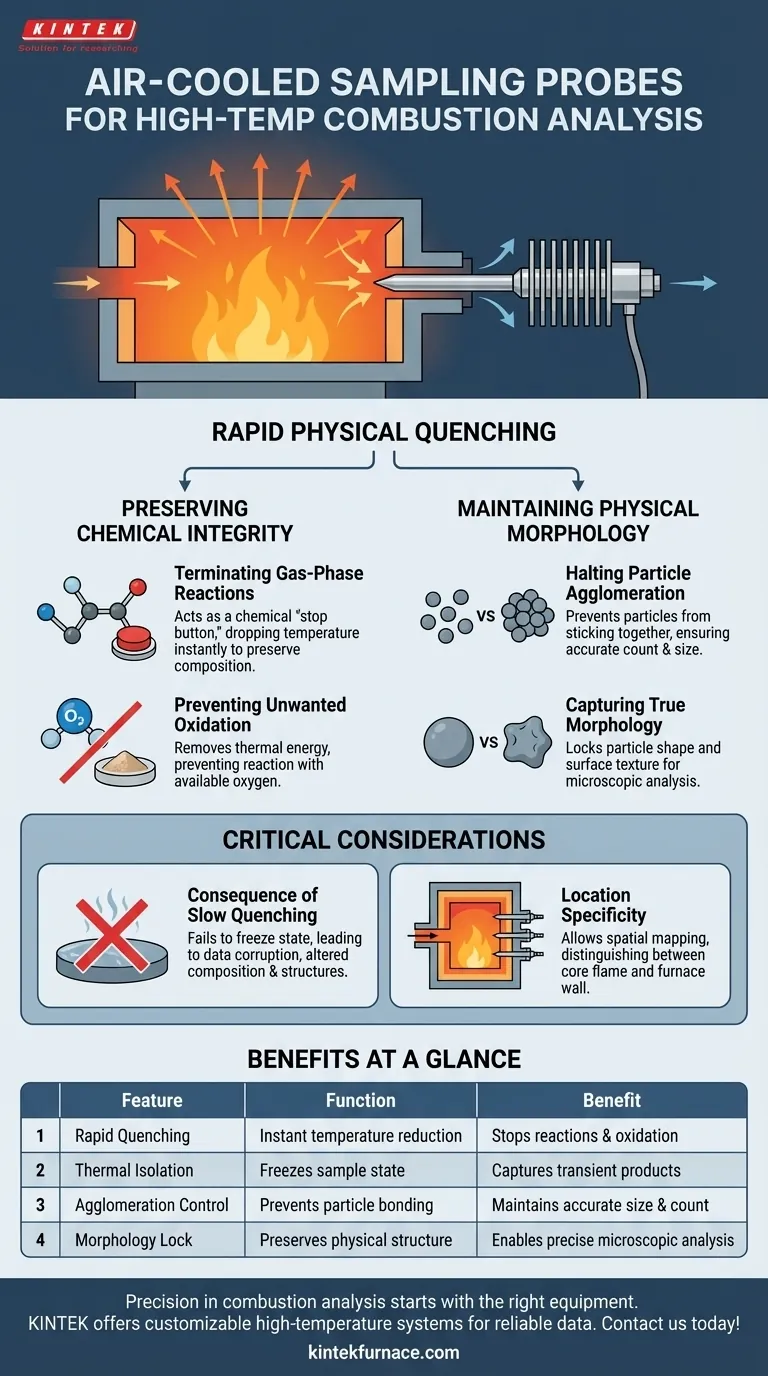
Rapid physical quenching is the primary objective. An air-cooled stainless steel sampling probe is utilized to immediately and drastically lower the temperature of gases and particles the moment they are extracted from the high-temperature reaction zone. This instantaneous cooling is the only way to capture the combustion products in their true, transient state.
By effectively freezing the sample in time, the probe prevents the data corruption that occurs when high-temperature reactions are allowed to continue outside the furnace, ensuring laboratory results reflect the actual conditions inside the reaction zone.

Preserving Chemical Integrity
To understand the necessity of this probe, one must understand the volatile nature of combustion environments. Without intervention, a sample changes character simply by moving from the furnace to the collection vessel.
Terminating Gas-Phase Reactions
Combustion is a continuous chain of chemical events. If hot gases are extracted slowly or without cooling, these reactions continue inside the sampling line.
The air-cooled probe acts as a chemical "stop button." By dropping the temperature instantly, it terminates gas-phase reactions, preserving the specific chemical composition present at the exact point of extraction.
Preventing Unwanted Oxidation
High temperatures facilitate oxidation. As combustion products exit the main reaction zone, they are highly susceptible to reacting with available oxygen.
The probe’s rapid cooling mechanism removes the thermal energy required for these oxidation reactions to occur. This ensures the sample remains a pristine snapshot of the furnace atmosphere rather than an oxidized byproduct.
Maintaining Physical Morphology
For researchers studying particulates and nanoparticles, the physical structure of the matter is just as critical as its chemistry. Heat alters structure; cooling preserves it.
Halting Particle Agglomeration
In high-heat environments, small particles have a natural tendency to stick together, or agglomerate. This creates large clusters that do not exist in the active flame.
The air-cooled probe prevents this by removing the heat energy that facilitates bonding. This allows for the collection of discrete nanoparticles, providing an accurate count and size distribution.
Capturing True Morphology
The shape and surface texture (morphology) of a particle tell the story of its formation. Continued exposure to heat can smooth or warp these delicate structures.
By achieving rapid physical quenching, the probe locks the particle's morphology in place. This allows microscopic analysis to reveal the true physical state of the matter as it existed inside the furnace.
Critical Considerations for Data Accuracy
While the probe is essential, understanding the specific variables it controls is vital for interpreting your data correctly.
The Consequence of Slow Quenching
The effectiveness of the sampling relies entirely on the speed of the temperature drop. If the cooling is not sufficiently rapid, "physical quenching" fails.
In this scenario, the sample will suffer from the very artifacts the probe is designed to avoid: altered chemical composition and morphed physical structures.
Location Specificity
The primary reference highlights that this method ensures accuracy at "specific locations." The environment inside a furnace is not uniform; it varies inch by inch.
The probe allows for spatial mapping. By freezing reactions locally, you can distinguish between the reaction state at the core of the flame versus the furnace wall.
Ensuring Representative Data Collection
The ultimate goal of using an air-cooled stainless steel probe is to eliminate the variables that occur after the sample leaves the fire.
- If your primary focus is Chemical Composition: Ensure the probe provides immediate quenching to terminate gas-phase reactions and prevent post-exit oxidation.
- If your primary focus is Nanoparticle Analysis: Rely on the rapid cooling to stop agglomeration, ensuring the morphology you observe under the microscope matches the particle's state in the furnace.
This tool transforms a volatile, changing gas stream into a stable, analyzable record of combustion performance.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in Sampling | Benefit to Research |
|---|---|---|
| Rapid Quenching | Instant temperature reduction | Stops gas-phase reactions and oxidation |
| Thermal Isolation | Freezes sample state | Captures transient combustion products |
| Agglomeration Control | Prevents particle bonding | Maintains accurate particle size and count |
| Morphology Lock | Preserves physical structure | Enables precise microscopic analysis |
Precision in combustion analysis starts with the right equipment. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers a wide range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all fully customizable for your unique lab requirements. Whether you are studying nanoparticle morphology or complex gas-phase reactions, our high-temperature solutions provide the stable environment needed for reliable data. Contact KINTEK today to discover how our advanced furnace technology can enhance your laboratory's research accuracy!
Visual Guide
References
- Di Chang, Yiannis A. Levendis. Effects of oxygen concentration on nanoparticle formation during combustion of iron powders. DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2025.135366
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is it necessary to use high-purity alumina crucibles for sintering hydroxyapatite? Ensure Chemical Phase Purity
- What is the importance of using external thermometers for lead bath monitoring? Ensure Precision in Chemical Refining
- What is the function of a laboratory electric blast drying oven in biomass pretreatment? Standardize Your Samples
- What is the primary function of a high-purity alumina crucible in PrVSb3 synthesis? Ensure Chemical Inertness & Purity
- What role does a covered alumina or aluminum alloy crucible play in g-C3N4 synthesis? Maximize Yield and Quality
- What are the typical size ranges available for quartz tubes used in laboratory furnaces? Find Your Perfect Fit for High-Temp Applications
- What precautions should be taken when using the alumina furnace tube for the first time? Ensure Safe Initial Use with Proper Conditioning
- What advantages do boron nitride (BN) crucibles offer for molten FUNaK salt? Ensure Purity & High-Temp Stability



















