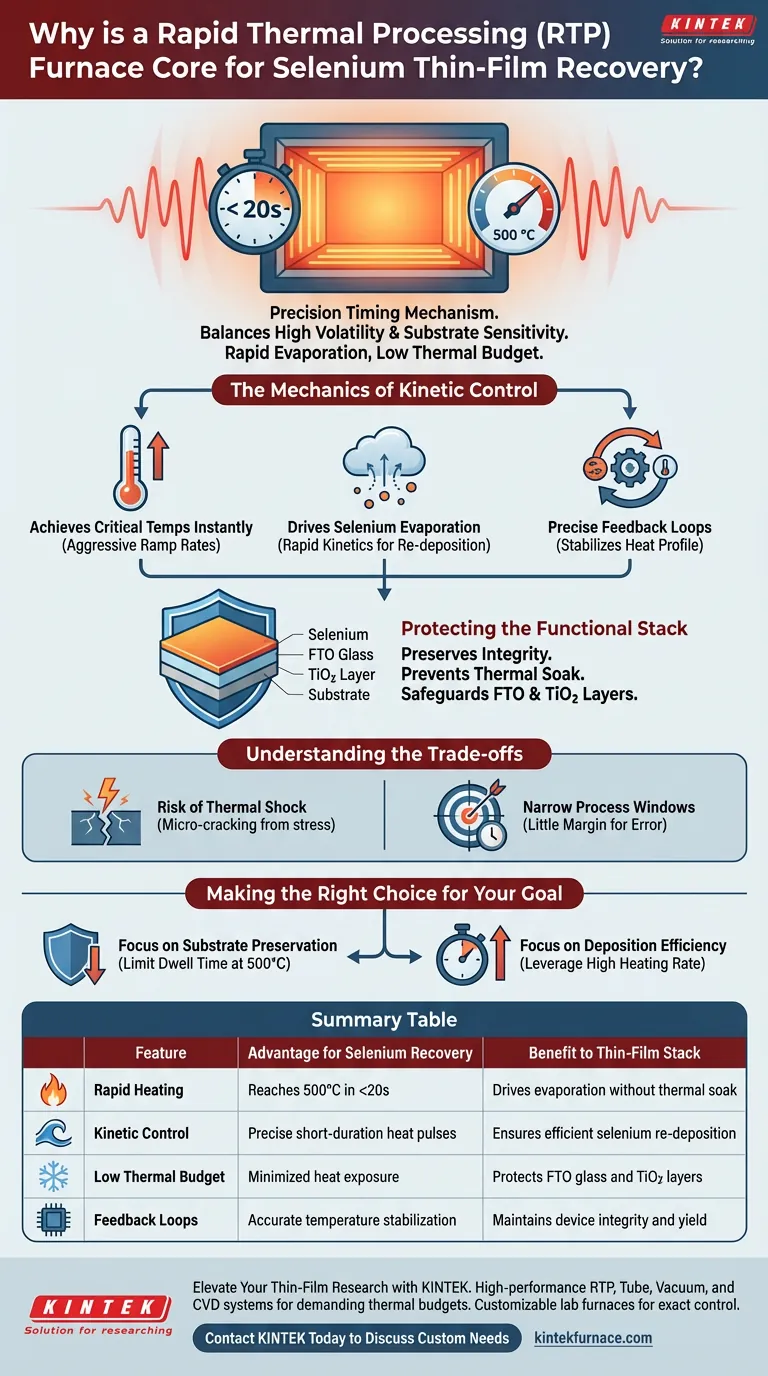
The Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) furnace acts as a precision timing mechanism for the delicate process of selenium recovery and re-deposition. It is considered a core piece of equipment because it can elevate source temperatures to 500 °C in under 20 seconds, allowing for the rapid evaporation of selenium while strictly limiting the thermal budget to protect sensitive underlying layers.
Core Takeaway Recovering selenium requires a delicate balance between high volatility and substrate sensitivity. The RTP furnace solves this by delivering intense, short-duration heat pulses that drive evaporation kinetics without degrading the functional stack.

The Mechanics of Kinetic Control
Achieving Critical Temperatures Instantly
The primary advantage of an RTP furnace is its ability to ramp temperature at aggressive rates. By reaching 500 °C within a 20-second window, the system bypasses the slow heating curves associated with conventional furnaces.
Driving Selenium Evaporation
Selenium requires specific thermal conditions to change states effectively. The RTP process maintains these high temperatures for short, controlled intervals to facilitate rapid evaporation kinetics. This ensures the selenium is mobilized quickly for re-deposition.
Precise Feedback Loops
Speed is dangerous without control. The RTP furnace utilizes precise temperature feedback mechanisms to stabilize the heat profile. This allows operators to maintain exact conditions during the critical evaporation window.
Protecting the Functional Stack
Preserving Substrate Integrity
In thin-film applications, the substrate often contains heat-sensitive materials. The RTP furnace prevents "thermal soak," ensuring that the total heat exposure remains low despite high peak temperatures.
Safeguarding FTO Glass
Fluorine-doped Tin Oxide (FTO) glass is a common conductive substrate that can degrade under prolonged thermal stress. The rapid cycle of the RTP furnace ensures the FTO layer retains its electrical and optical properties.
Maintaining TiO2 Layers
Similarly, titanium dioxide (TiO2) layers are often present in these stacks. The short duration of the heating phase prevents thermal damage to this functional layer, ensuring the final device structure remains intact.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Thermal Shock
While rapid heating is beneficial for kinetics, it introduces the physical stress of thermal shock. If the ramp rate is too aggressive for the specific substrate thickness, micro-cracking can occur.
Narrow Process Windows
The benefit of speed creates a challenge in timing. Because the interval at peak temperature is short, there is very little margin for error. A variance of a few seconds can result in incomplete evaporation or substrate damage.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of selenium recovery, align your equipment settings with your specific priorities:
- If your primary focus is Substrate Preservation: Prioritize the precise feedback capabilities of the RTP to limit the dwell time at 500 °C, ensuring FTO and TiO2 layers remain unaffected.
- If your primary focus is Deposition Efficiency: Leverage the high heating rate to minimize cycle times, ensuring the selenium evaporation kinetics are driven by immediate thermal energy rather than slow soaking.
Success in selenium re-deposition relies not just on reaching the right temperature, but on how quickly you get there and how fast you can cool down.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Advantage for Selenium Recovery | Benefit to Thin-Film Stack |
|---|---|---|
| Rapid Heating | Reaches 500°C in <20 seconds | Drives evaporation without thermal soak |
| Kinetic Control | Precise short-duration heat pulses | Ensures efficient selenium re-deposition |
| Low Thermal Budget | Minimized heat exposure | Protects FTO glass and TiO2 layers |
| Feedback Loops | Accurate temperature stabilization | Maintains device integrity and yield |
Elevate Your Thin-Film Research with KINTEK
Precision and speed are non-negotiable in selenium recovery. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance RTP, Tube, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to handle the most demanding thermal budgets. Whether you are safeguarding FTO substrates or optimizing evaporation kinetics, our customizable lab furnaces provide the exact control your unique processes require.
Ready to optimize your thermal processing? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom furnace needs!
Visual Guide
References
- Xia Wang, Ding‐Jiang Xue. Sustainable Recycling of Selenium‐Based Optoelectronic Devices. DOI: 10.1002/advs.202400615
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- What is the overall significance of CVD in industrial applications? Unlock Atomic-Level Surface Engineering
- What is Ultraviolet-activated Chemical Vapor Deposition (UVCVD)? Enable Low-Temp, High-Quality Coatings for Sensitive Materials
- What is the function of the 800 °C argon heat treatment in CNT prep? Mastering Roll-to-Roll Substrate Engineering
- Why is quartz commonly used in CVD chambers for graphene production? Key Benefits for High-Purity Synthesis
- What role does CVD play in nanotechnology? Essential for Precise Synthesis of Nanomaterials
- How does the CVD process work step-by-step? Master Thin Film Deposition for Your Lab
- What are the advantages of using a CVD furnace in material manufacturing? Achieve High-Purity, Uniform Thin Films
- What are the key considerations for selecting a CVD furnace for industrial applications? Optimize for Cost and Performance



















