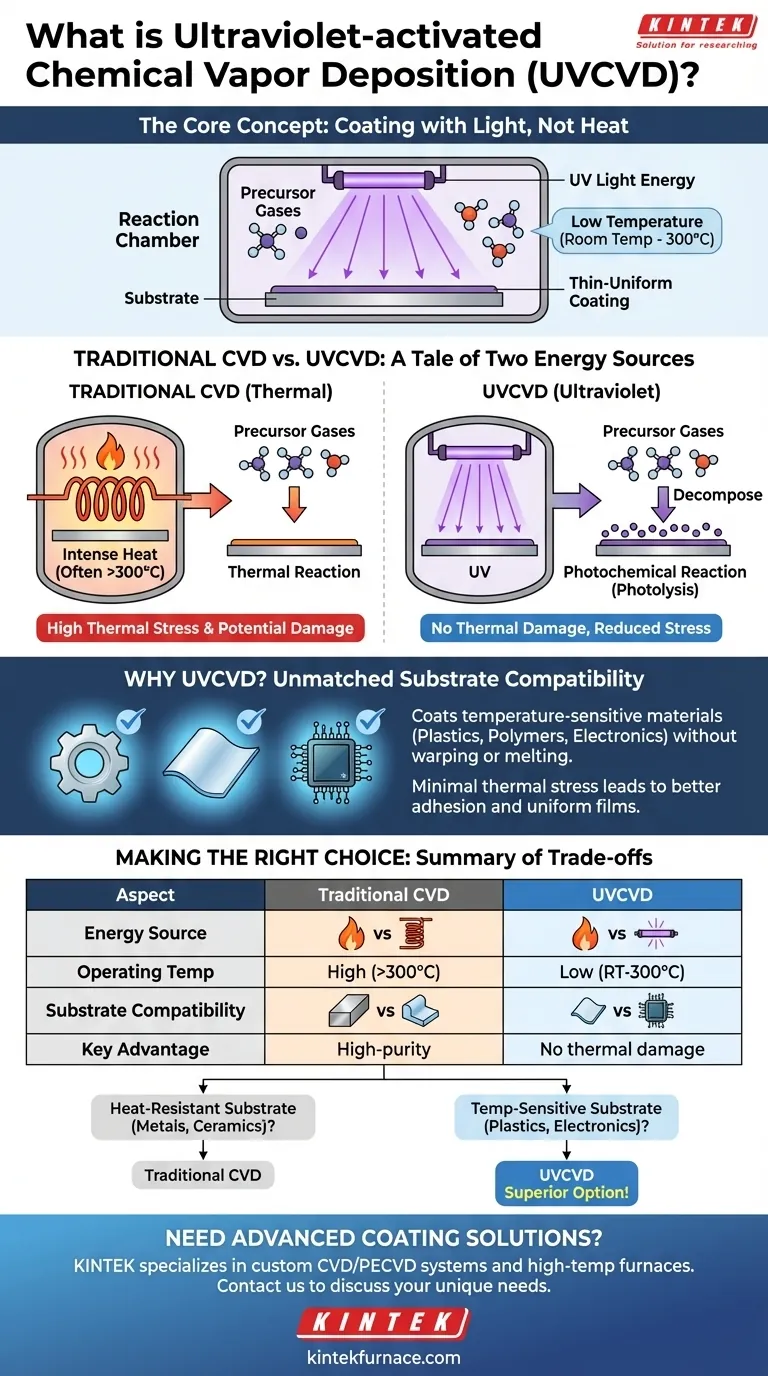
At its core, Ultraviolet-activated Chemical Vapor Deposition (UVCVD) is a method for creating thin, high-quality coatings that uses ultraviolet light as the energy source to drive the chemical reaction. Unlike traditional Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) which relies on high heat, UVCVD operates at significantly lower temperatures, often from room temperature up to 300°C. This distinction is the key to its unique applications.
The fundamental advantage of UVCVD is its ability to deposit durable, uniform films onto temperature-sensitive materials. By replacing destructive high heat with UV light, it opens up coating possibilities for substrates like plastics, polymers, and delicate electronics that traditional CVD would damage or destroy.

Deconstructing the Foundational CVD Process
To understand UVCVD, we must first understand the principles of its parent technology, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
The Core Principle: Gas to Solid
CVD is a process where a substrate (the object to be coated) is placed in a reaction chamber. Precursor gases, which contain the elements of the desired coating, are introduced into this chamber.
A chemical reaction is then initiated, causing the precursors to decompose or react. This forms a solid material that deposits onto the substrate, creating a thin, uniform film atom by atom.
The Role of Thermal Energy
In most traditional CVD processes, the energy required to trigger this chemical reaction is intense heat. The chamber and substrate are heated to very high temperatures, which gives the precursor molecules the energy they need to react and form the coating.
Key Characteristics of CVD
When performed correctly, CVD produces films that are exceptionally high-purity and uniform. It can conformally coat complex, three-dimensional shapes and is a scalable, cost-effective method for producing durable coatings that protect against corrosion and wear.
How UVCVD Changes the Equation
UVCVD follows the same basic principle as CVD but fundamentally changes the energy source, which alters the entire process.
Replacing Heat with Light
Instead of thermal energy, UVCVD uses a precise wavelength of ultraviolet (UV) light to power the reaction. The UV energy is directed into the chamber where the precursor gases and substrate are located.
The Photochemical Reaction
The photons from the UV light carry enough energy to break the chemical bonds within the precursor gas molecules directly. This process, known as photolysis, creates the reactive species needed for deposition without requiring high ambient temperatures.
The Low-Temperature Advantage
Because the reaction is driven by light instead of heat, the substrate and the chamber can remain at or near room temperature. This is the single most important feature of UVCVD, as it eliminates the thermal stress and potential damage associated with high-temperature processes.
Understanding the Trade-offs: UVCVD vs. Traditional CVD
Choosing UVCVD is a decision driven by specific needs, primarily related to the substrate material.
Benefit: Unmatched Substrate Compatibility
The low-temperature nature of UVCVD makes it the only viable option for coating materials with low melting points or high thermal sensitivity. This includes a vast range of polymers, plastics, and assembled electronic components that would warp, melt, or be destroyed by conventional CVD.
Benefit: Reduced Thermal Stress
High heat introduces stress into both the substrate and the deposited film as they expand and contract. By operating at low temperatures, UVCVD minimizes this thermal stress, reducing the risk of the coating cracking, delaminating, or altering the substrate's properties.
Limitation: Specialized Precursor Requirements
The primary constraint of UVCVD is the need for precursor gases that are photoreactive. The chosen chemicals must be specifically designed to absorb energy and decompose at the precise wavelength of the UV light being used, which can limit material selection compared to thermally-driven CVD.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The decision between UVCVD and other methods hinges almost entirely on the thermal limitations of your substrate.
- If your primary focus is coating heat-resistant materials (like metals or ceramics): Traditional thermal CVD is often a more straightforward and established choice with a wider range of available precursors.
- If your primary focus is coating temperature-sensitive materials (like plastics or electronics): UVCVD is the superior, and often only, viable option to achieve a high-quality CVD coating without causing thermal damage.
Ultimately, UVCVD empowers engineers to apply the benefits of advanced coatings to a whole new class of materials.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Traditional CVD | UVCVD |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Source | High heat | Ultraviolet (UV) light |
| Operating Temperature | High (often >300°C) | Low (room temp to 300°C) |
| Substrate Compatibility | Metals, ceramics | Plastics, polymers, delicate electronics |
| Key Advantage | High-purity, uniform films | No thermal damage, reduced stress |
| Precursor Requirement | Thermally reactive | Photoreactive |
Need advanced coating solutions for temperature-sensitive materials? KINTEK specializes in high-temperature furnaces and CVD/PECVD systems, backed by exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing. We offer deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs—whether it's Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, or Atmosphere Furnaces. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored UVCVD and furnace technologies can enhance your lab's capabilities and protect your delicate substrates!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano Diamond Coating
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System for Lab Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- What makes a CVD Tube Furnace essential for material science and nanotechnology? Unlock Precision in Material Synthesis
- What types of atmosphere control does a CVD Tube Furnace support? Master Vacuum and Gas Control for Precision
- What is the working principle of a CVD tube furnace? Achieve Precise Thin Film Deposition for Your Lab
- Why are CVD tube furnace sintering systems indispensable for 2D material research and production? Unlock Atomic-Scale Precision
- Why are advanced materials and composites important? Unlock Next-Gen Performance in Aerospace, Auto, and More



















