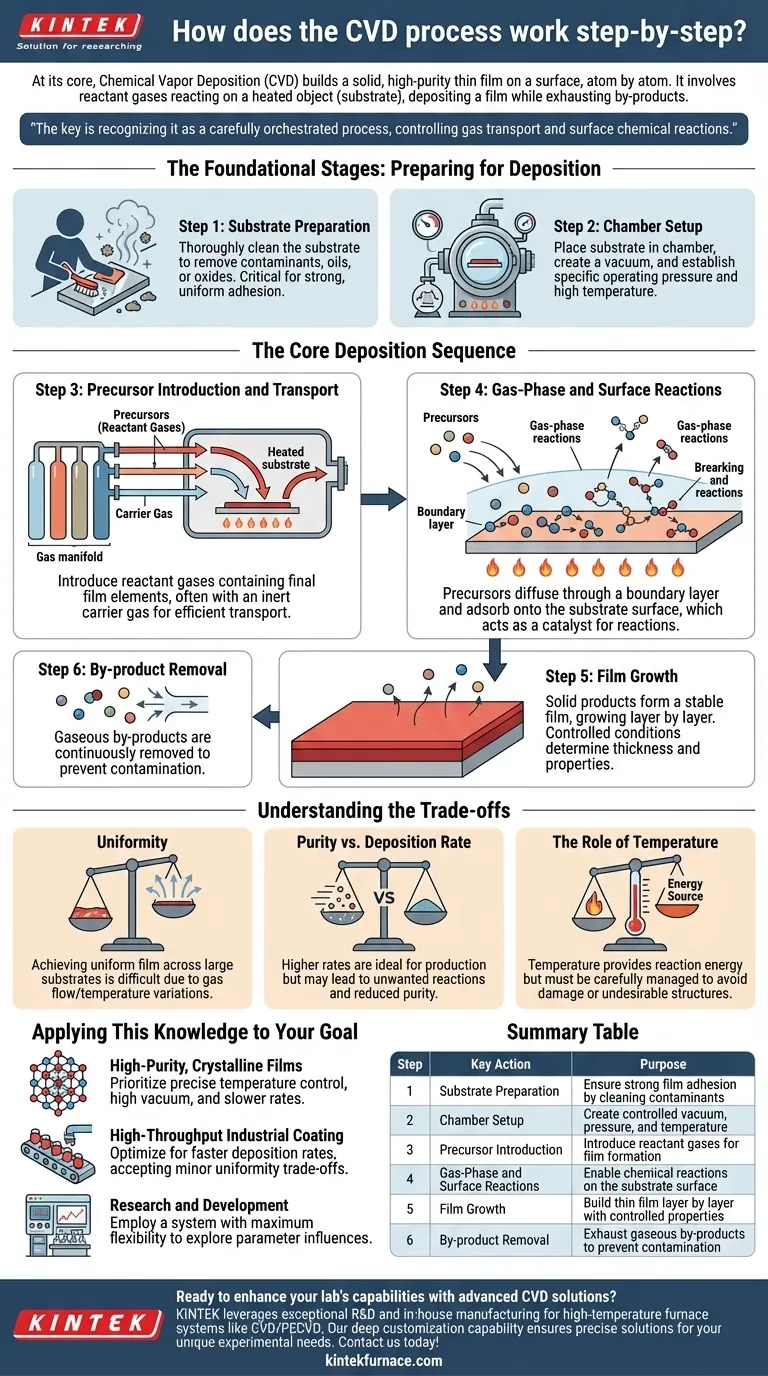
At its core, the Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) process is a sophisticated method for building a solid, high-purity thin film on a surface, atom by atom. It involves introducing specific reactant gases, or "precursors," into a controlled chamber where they chemically react on or near a heated object (the substrate). This reaction deposits a solid material as a thin coating, while gaseous by-products are exhausted.
The key to understanding CVD is not just memorizing the steps, but recognizing it as a carefully orchestrated process. Success hinges on precisely controlling the transport of gases to a surface and the chemical reactions that occur once they arrive.
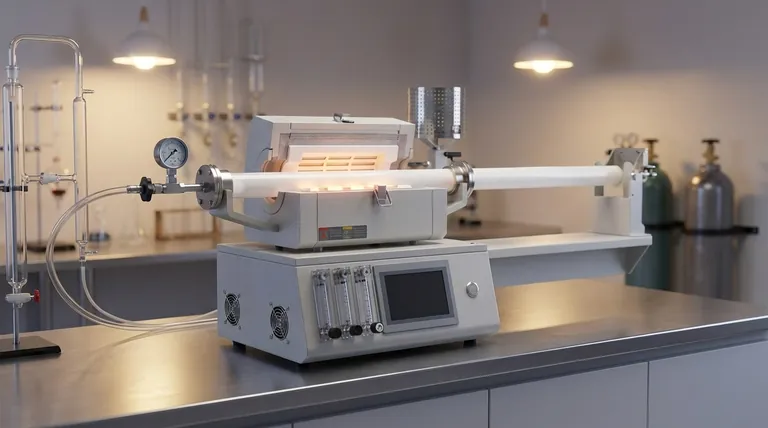

The Foundational Stages: Preparing for Deposition
Before any coating can be formed, the environment and the substrate must be meticulously prepared. These initial steps are non-negotiable for achieving a high-quality, well-adhered film.
Step 1: Substrate Preparation
The object to be coated, known as the substrate, must be thoroughly cleaned. This removes any contaminants, oils, or oxides from the surface.
Proper cleaning is critical because it ensures the deposited film will adhere strongly and uniformly to the substrate.
Step 2: Chamber Setup
The cleaned substrate is placed inside the CVD reaction chamber. The chamber is then sealed and brought to a highly controlled state.
This typically involves creating a vacuum to remove atmospheric gases and then establishing a specific operating pressure and temperature, which can be extremely high.
The Core Deposition Sequence
Once the environment is stable, the active process of film growth begins. This sequence involves a continuous flow of gas and a series of chemical and physical transformations.
Step 3: Precursor Introduction and Transport
One or more reactant gases, called precursors, are introduced into the chamber at a precise flow rate. These precursors contain the atomic elements needed for the final film.
Often, an inert carrier gas like argon or hydrogen is used to dilute the precursors and transport them efficiently towards the substrate through a process of convection.
Step 4: Gas-Phase and Surface Reactions
As the gases approach the hot substrate, a thin, slow-moving gas region called the boundary layer forms just above the surface. The precursors must diffuse through this layer.
Some chemical reactions may occur in the gas phase, but the most crucial reactions happen directly on the substrate's surface. The precursor molecules adsorb (stick) onto the surface, which acts as a catalyst, breaking them down and enabling film formation.
Step 5: Film Growth
The solid products from the surface reaction begin to form a stable film. This film grows layer by layer as more precursor molecules arrive, react, and bond to the surface.
The precise control over temperature, pressure, and gas flow rates determines the film's final thickness, composition, and properties.
Step 6: By-product Removal
The chemical reactions that form the solid film also create unwanted gaseous by-products.
These volatile by-products desorb (detach) from the surface and are continuously removed from the chamber by the gas flow and an exhaust system. Efficient removal is essential to prevent contamination of the film.
Understanding the Trade-offs
CVD is a powerful process, but it is governed by a delicate balance of competing physical and chemical factors. Understanding these trade-offs is key to mastering the technique.
The Challenge of Uniformity
Achieving a perfectly uniform film thickness across a large substrate is difficult. Variations in gas flow or temperature can cause the boundary layer thickness to change, leading to faster deposition in some areas and slower in others.
Purity vs. Deposition Rate
Running the process at higher temperatures and pressures can increase the deposition rate, which is ideal for industrial production. However, this can sometimes lead to unwanted gas-phase reactions that create particles, reducing the film's purity.
The Role of Temperature
Temperature is the primary lever for controlling CVD. It provides the energy needed to drive the chemical reactions but must be managed carefully. Too low, and the reaction won't occur; too high, and you risk damaging the substrate or creating undesirable film structures.
Applying This Knowledge to Your Goal
The optimal CVD process depends entirely on your objective. Use these principles to guide your approach.
- If your primary focus is creating high-purity, crystalline films: Prioritize precise temperature control, a high-quality vacuum, and slower deposition rates to ensure perfect atomic arrangement.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput industrial coating: Optimize for faster deposition rates by increasing precursor concentration and temperature, accepting potential minor trade-offs in film uniformity.
- If your primary focus is research and development: Employ a system with maximum flexibility over gas flows, pressure, and temperature to explore how each parameter influences the final material properties.
Mastering CVD is about orchestrating this sequence of physical transport and surface chemistry to build materials with precision from the ground up.
Summary Table:
| Step | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Substrate Preparation | Ensure strong film adhesion by cleaning contaminants |
| 2 | Chamber Setup | Create controlled vacuum, pressure, and temperature |
| 3 | Precursor Introduction | Introduce reactant gases for film formation |
| 4 | Gas-Phase and Surface Reactions | Enable chemical reactions on the substrate surface |
| 5 | Film Growth | Build thin film layer by layer with controlled properties |
| 6 | By-product Removal | Exhaust gaseous by-products to prevent contamination |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with advanced CVD solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide high-temperature furnace systems like CVD/PECVD, Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs in thin film deposition. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your CVD processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Where is a CVD Tube Furnace commonly used? Essential for High-Tech Materials and Electronics
- What temperature ranges can a CVD Tube Furnace achieve with different tube materials? Unlock High-Temp Precision for Your Lab
- Why is the tube design important in CVD furnaces? Ensure Uniform Deposition for High-Quality Films
- What role do CVD tube furnace sintering systems play in 2D material synthesis? Enabling High-Quality Atomic Layer Growth
- What is the working principle of a CVD tube furnace? Achieve Precise Thin Film Deposition for Your Lab



















