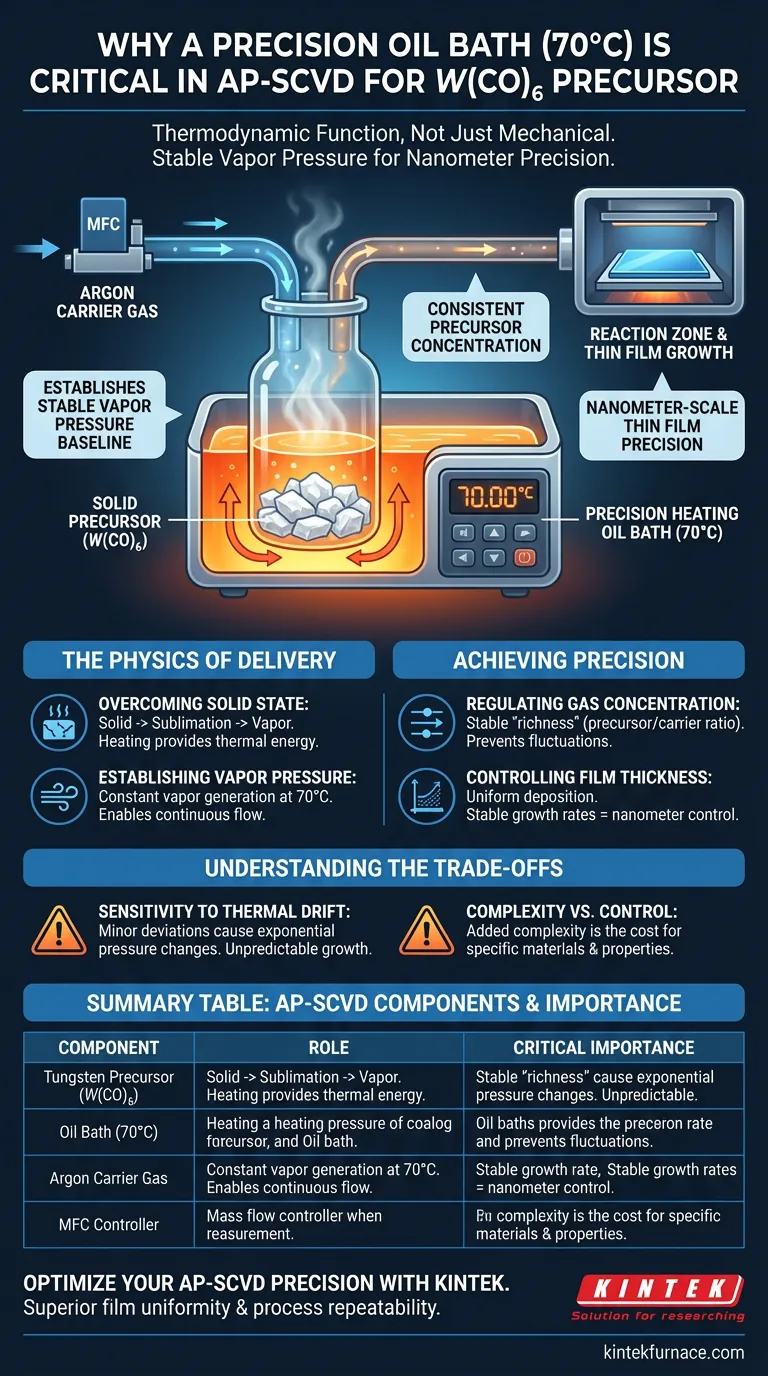
A precision temperature-controlled heating oil bath is critical in Atmospheric Pressure Spatial Chemical Vapor Deposition (AP-SCVD) because the tungsten precursor, tungsten hexacarbonyl ($W(CO)_6$), is solid at room temperature. To utilize this material, the system must maintain the precursor at exactly 70°C to generate sufficient vapor pressure, allowing the argon carrier gas to transport the necessary chemical concentration to the reaction zone.
Core Takeaway The oil bath serves a thermodynamic function, not just a mechanical one. By locking the precursor temperature at 70°C, the system establishes a stable vapor pressure baseline, which is the prerequisite for achieving consistent growth rates and nanometer-scale precision in thin film thickness.
The Physics of Precursor Delivery
Overcoming the Solid State
The primary challenge in this specific AP-SCVD process is the physical state of the source material. Tungsten hexacarbonyl ($W(CO)_6$) exists as a solid under standard room temperature conditions.
Without the introduction of thermal energy, the precursor cannot transition into a gas phase effectively. The heating oil bath provides the necessary energy to sublime the solid or generate adequate vapor, making the chemical available for transport.
Establishing Vapor Pressure
The goal of heating the bubbler is not merely to warm the material, but to generate a specific vapor pressure. At 70°C, the precursor releases a quantifiable and consistent amount of vapor.
This constant vapor generation is what allows the system to function as a continuous flow process rather than a batch process.
Achieving Nanometer-Scale Precision
Regulating Gas Concentration
Once the vapor is generated, it must be moved to the reaction zone. A high-precision mass flow controller (MFC) introduces argon as a carrier gas to sweep the tungsten vapor out of the bubbler.
The precision of the oil bath ensures that the "richness" of the gas stream (the ratio of precursor to carrier gas) remains constant. If the bath temperature were to fluctuate, the concentration of tungsten in the argon stream would vary, rendering the MFC's regulation ineffective.
Controlling Film Thickness
The ultimate metric for success in AP-SCVD is the uniformity of the deposited film. The process demands control over thickness at the nanometer scale.
Stable growth rates are impossible without a stable precursor supply. The precision oil bath eliminates temperature-induced variables, ensuring that film thickness is dictated solely by the process duration and flow rates, rather than environmental fluctuations.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Sensitivity to Thermal Drift
The reliance on sublimation or vaporization means the process is highly sensitive to thermal drift. Even minor deviations from the 70°C setpoint can cause exponential changes in vapor pressure.
If the oil bath fails to maintain precision, the precursor concentration will spike or drop. This leads to unpredictable growth rates and films that fail to meet thickness specifications.
Complexity vs. Control
Implementing a precision oil bath adds mechanical complexity and maintenance requirements to the system compared to room-temperature liquid precursors.
However, this complexity is the necessary cost of using solid precursors like $W(CO)_6$. The trade-off yields access to specific material properties (like tungsten deposition) that might otherwise be inaccessible with simpler liquid sources.
Ensuring Process Reliability
To ensure the success of your AP-SCVD process, you must view temperature control as a variable equal in importance to gas flow.
- If your primary focus is Film Uniformity: Ensure your oil bath has a tight feedback loop to prevent thermal oscillation, as temperature directly correlates to precursor concentration.
- If your primary focus is Process Repeatability: Verify that the argon carrier gas flow is calibrated specifically against the vapor pressure generated at 70°C.
True precision in chemical vapor deposition begins with the thermal stability of the source material.
Summary Table:
| Component | Role in AP-SCVD Process | Critical Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Tungsten Precursor | Solid source material ($W(CO)_6$) | Requires sublimation to transition to gas phase |
| Oil Bath (70°C) | Precision thermal regulation | Establishes stable vapor pressure for consistent supply |
| Argon Carrier Gas | Precursor transport mechanism | Maintains concentration ratio when temperature is locked |
| MFC Controller | Gas flow regulation | Ensures stable growth rates and nanometer-scale precision |
Optimize Your AP-SCVD Precision with KINTEK
Don't let thermal fluctuations compromise your nanometer-scale thin film quality. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK provides high-precision heating systems and a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems. Whether you are working with solid precursors like $W(CO)_6$ or complex gas delivery, our lab high-temp furnaces are fully customizable to meet your unique research needs.
Ready to achieve superior film uniformity and process repeatability?
Contact KINTEK Today for a Expert Consultation
Visual Guide
References
- Zhuotong Sun, Judith L. MacManus‐Driscoll. Low-temperature open-atmosphere growth of WO<sub>3</sub> thin films with tunable and high-performance photoresponse. DOI: 10.1039/d3tc02257a
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano Diamond Coating
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station CVD Machine
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using a batch furnace? Achieve Unmatched Process Flexibility and Precision
- What is the maximum temperature capability of the furnace? Find Your Perfect High-Temp Solution
- What is the objective of coordinating mechanical stirring and heating for perovskite slurries? Achieve Homogeneity
- What is the main benefit of using a benchtop industrial oven? Save Space and Boost Efficiency in Your Lab
- What is the necessity of a laboratory vacuum drying oven for photocatalytic powders? Protect Your Material Integrity
- What is the purpose of using an Argon protective atmosphere during the casting of H13 steel? Boost Purity and Strength
- What is the function of a stable heating environment and ethylene glycol in gold nanoparticle synthesis? Achieve Precision
- What is the role of carbonaceous reducing agents in copper slag treatment? Maximize Metal Recovery with Expert Insights


















