The primary advantages of a batch furnace are its exceptional process flexibility, precise temperature control, and cost-effectiveness for low-volume or highly varied production. Unlike a continuous furnace designed for a constant stream of identical items, a batch furnace treats a single, discrete load at a time. This allows you to perfectly customize the entire heat treatment cycle for the specific requirements of that load.
A batch furnace is the superior choice when your priority is process versatility and metallurgical precision over raw throughput. It trades the high-volume efficiency of a continuous system for the ability to flawlessly execute unique or complex thermal profiles on a case-by-case basis.
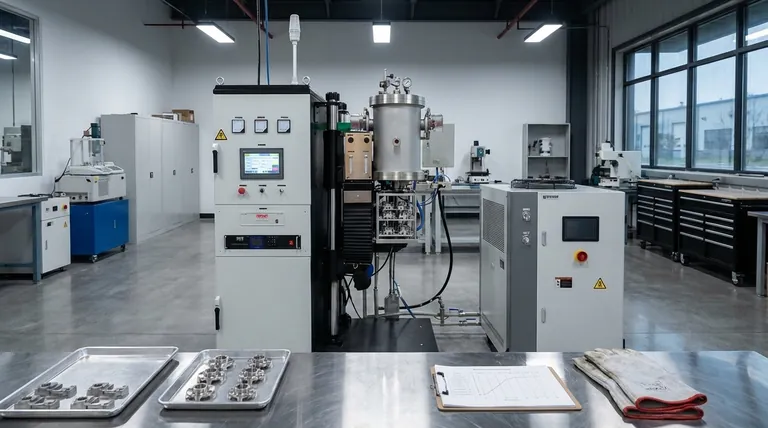

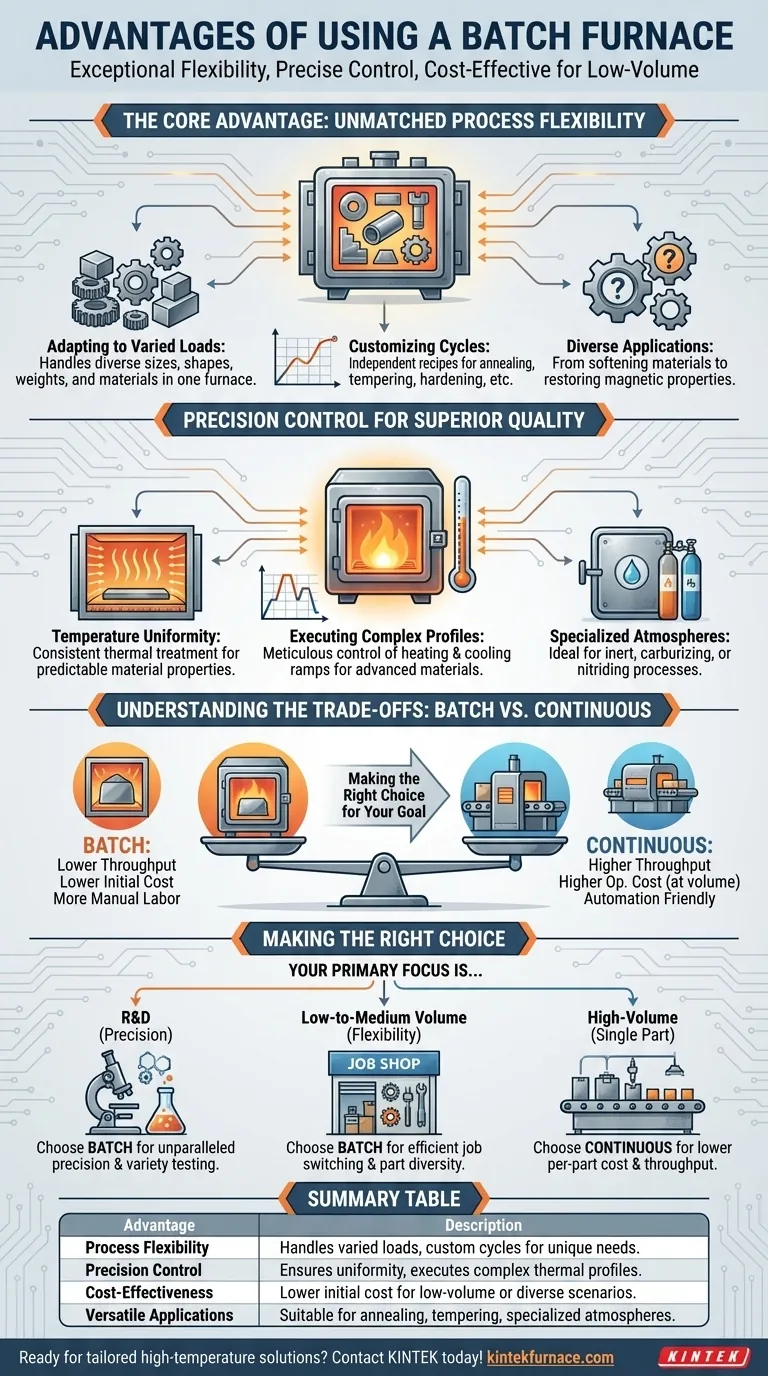
The Core Advantage: Unmatched Process Flexibility
The fundamental benefit of a batch furnace lies in its ability to treat each load as a unique event, providing a level of adaptability that continuous systems cannot match.
Adapting to Varied Loads
Batch furnaces excel at handling parts of different sizes, shapes, weights, and material grades. A single furnace can be used to process small, intricate components in one cycle and large, heavy castings in the next.
Customizing Heat Treatment Cycles
Each batch runs on its own independent process recipe. This allows operators to define unique heating rates, hold times, and cooling profiles to achieve specific outcomes like annealing, tempering, stress relief, or hardening.
Handling Diverse Applications
This versatility makes batch furnaces suitable for a vast range of industrial and laboratory applications. They can be used for everything from softening a material to increase machinability to restoring magnetic properties after other treatments.
Precision Control for Superior Quality
Because it is a closed system during operation, a batch furnace offers a controlled environment that is ideal for achieving high-quality, repeatable results.
Achieving Temperature Uniformity
A key design goal for batch furnaces is exceptional temperature uniformity. This ensures that every part within the load, regardless of its position, receives the exact same thermal treatment, leading to consistent and predictable material properties.
Executing Complex Thermal Profiles
The ability to precisely program and control heating and cooling ramps is critical for advanced materials and processes. Batch control systems allow for the meticulous execution of these complex recipes, which is vital for eliminating thermomechanical stresses or achieving specific microstructures.
Enabling Specialized Atmospheres
The sealed nature of a batch furnace makes it ideal for processes requiring a controlled atmosphere. This is essential for preventing oxidation with inert gases or for performing case hardening with carburizing or nitriding atmospheres.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Batch vs. Continuous
Choosing a batch furnace involves a clear trade-off between flexibility and production volume. Understanding these differences is critical to making the correct investment.
Throughput and Scalability
The most significant limitation of a batch furnace is its throughput. It is inherently less efficient for high-volume manufacturing of identical parts, where a continuous furnace offers far greater output per hour.
The Cost Equation
Batch furnaces typically have a lower initial capital cost, making them an excellent choice for startups, R&D labs, and job shops. However, at very high production volumes, the per-part operational cost of a continuous furnace (which remains at temperature) is often lower.
Labor and Automation
Processing in discrete batches often requires more manual labor for loading and unloading compared to a fully automated continuous furnace line. While automation is possible for batch systems, it is a more natural fit for continuous processing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific operational goal is the most important factor in selecting a furnace type.
- If your primary focus is research and development: Choose a batch furnace for its unparalleled precision and ability to test a wide variety of materials and thermal cycles.
- If your primary focus is low-to-medium volume production with diverse parts: A batch furnace provides the essential flexibility to switch between different jobs and part types efficiently.
- If your primary focus is high-volume manufacturing of a single part type: A continuous furnace will almost always provide a lower per-part cost and the necessary throughput.
Ultimately, selecting a batch furnace is a strategic decision to prioritize perfect process control and operational versatility over mass-production speed.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Process Flexibility | Handles varied loads and custom heat cycles for unique requirements. |
| Precision Control | Ensures temperature uniformity and execution of complex thermal profiles. |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Lower initial cost ideal for low-volume or diverse production scenarios. |
| Versatile Applications | Suitable for annealing, tempering, and specialized atmosphere processes. |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with tailored high-temperature solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced furnaces like Batch, Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can optimize your processes and deliver superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering and Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do vacuum sintering and annealing furnaces contribute to the densification of NdFeB magnets?
- What role does a vacuum sintering furnace play in the formation of the 'core-rim' structure in Ti(C,N)-FeCr cermets?
- Why is a vacuum environment essential for sintering Titanium? Ensure High Purity and Eliminate Brittleness
- How does the ultra-low oxygen environment of vacuum sintering affect titanium composites? Unlock Advanced Phase Control
- What is the purpose of setting a mid-temperature dwell stage? Eliminate Defects in Vacuum Sintering



















