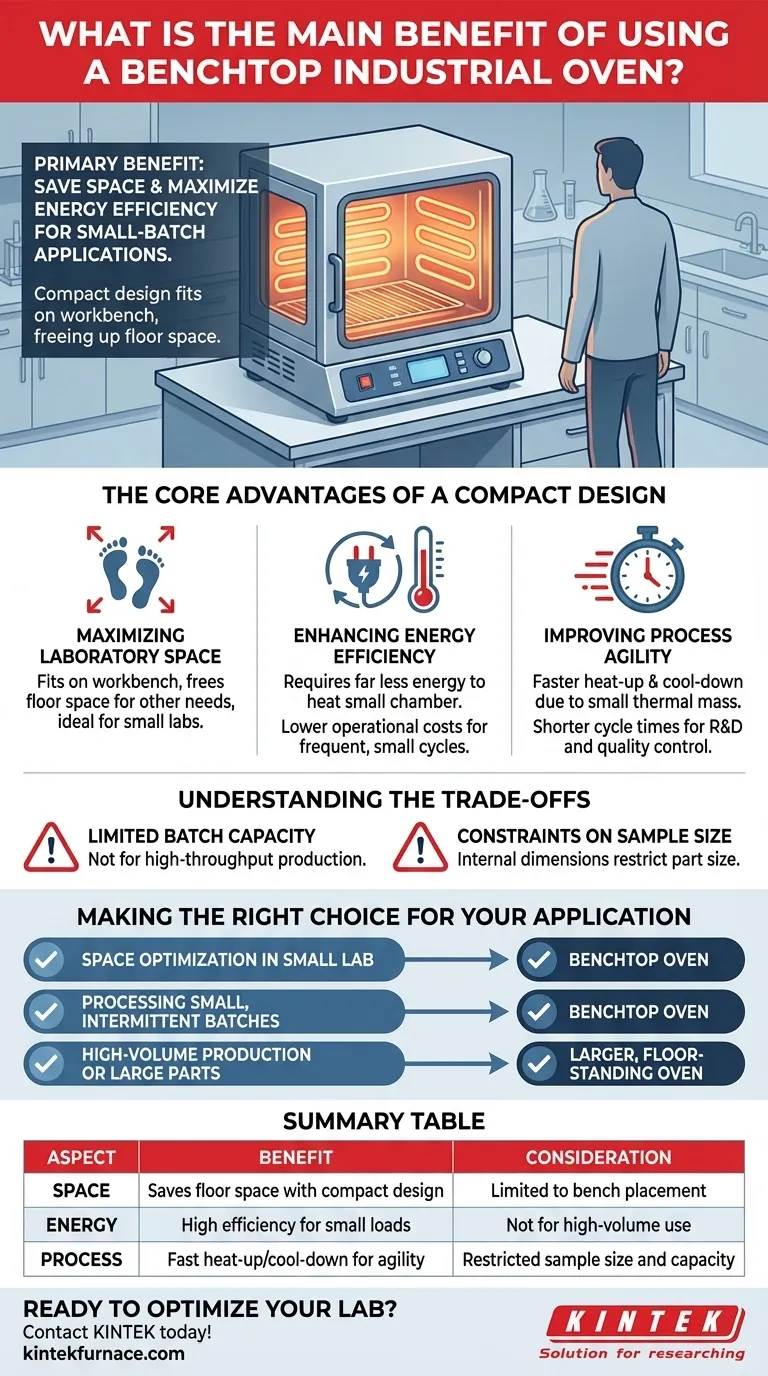
The primary benefit of a benchtop industrial oven is its ability to save significant laboratory space while providing superior energy efficiency for small-batch applications. Its compact design allows it to sit on a standard workbench, freeing up valuable floor space that larger ovens would otherwise occupy.
While benchtop ovens are defined by their space-saving design, their true value lies in aligning equipment scale with operational needs. This prevents the wasteful use of energy and space inherent in using oversized machinery for small-batch tasks.
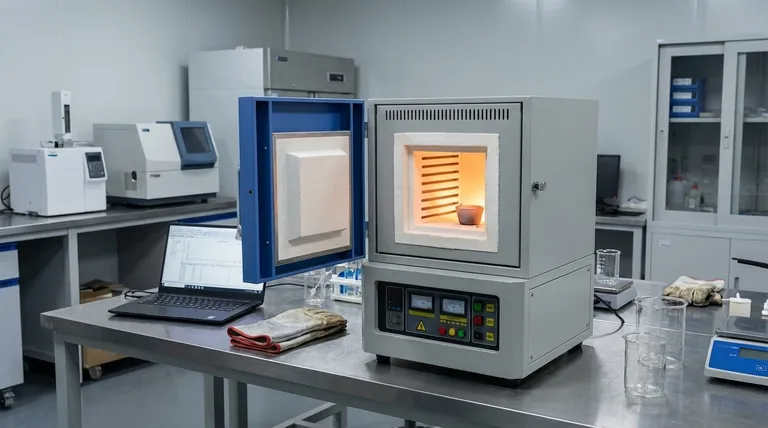

The Core Advantages of a Compact Design
The decision to use a benchtop oven is rooted in optimizing resources. The compact footprint is the most visible benefit, but the operational advantages are equally important for labs and workshops focused on efficiency.
Maximizing Laboratory Space
A benchtop oven's most obvious advantage is its small footprint. By design, it fits on a workbench, freeing up critical floor space for other equipment, storage, or workflow movement.
This is especially crucial in smaller labs or facilities where every square foot is at a premium. It allows for industrial-grade heating processes without dedicating the space required by a larger, floor-standing unit.
Enhancing Energy Efficiency
For heat-treating a small number of samples, a benchtop oven is significantly more energy-efficient. Larger ovens must heat a massive internal chamber to achieve temperature uniformity, consuming substantial energy even for a small load.
A benchtop model's smaller chamber requires far less energy to reach and maintain its target temperature. This translates directly into lower operational costs, particularly for labs that run frequent but small-scale heating cycles.
Improving Process Agility
A smaller thermal mass allows a benchtop oven to heat up and cool down more quickly than a larger unit. This results in shorter cycle times for small jobs.
This agility is ideal for research and development, quality control testing, or any application where rapid turnaround is more important than high-volume throughput.
Understanding the Trade-offs
To make an informed decision, you must recognize the inherent limitations of a smaller form factor. Objectivity requires acknowledging what a benchtop oven is not designed to do.
Limited Batch Capacity
The most significant trade-off is limited capacity. These ovens are explicitly designed for small parts or low-volume sample batches.
They are not suitable for high-throughput production environments where large quantities of material must be processed simultaneously.
Constraints on Sample Size
The physical dimensions of the internal chamber restrict the size of the parts you can process. Always verify that the oven's internal measurements can accommodate your largest expected sample with adequate clearance for airflow.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct oven depends entirely on your specific operational goals. The right equipment is a tool that fits the scale of your work.
- If your primary focus is space optimization in a small lab: A benchtop oven is the definitive choice for integrating thermal processing without sacrificing floor space.
- If your primary focus is processing small, intermittent batches: The energy savings and faster cycle times of a benchtop model offer superior cost-effectiveness.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production or large parts: You must look beyond benchtop models to larger, floor-standing ovens designed for scale.
Ultimately, choosing a benchtop oven is a strategic decision to match your equipment precisely to your workflow, ensuring maximum efficiency of both space and energy.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Benefit | Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Space | Saves floor space with compact design | Limited to bench placement |
| Energy | High efficiency for small loads | Not for high-volume use |
| Process | Fast heat-up/cool-down for agility | Restricted sample size and capacity |
Ready to optimize your lab with a tailored benchtop oven? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including benchtop models. Our product line—featuring Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to enhance efficiency and save space in your laboratory!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 9MPa Air Pressure Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a high-temperature vacuum furnace and where is it commonly used? Essential for Purity in Materials Science
- What role do high-precision laboratory ovens play in assessing the energy potential of MSW? Enhancing Biomass Accuracy
- Why is a precision furnace required after TiO2-alpha-Ga2O3 synthesis? Master Phase Transformation & Interface Bonding
- Why is dual heat treatment required for SnO2 nanoparticles? Optimize Oxidation for Superior Performance
- What is the purpose of ashing furnaces? Achieve Precise Ash Analysis for Material Quality



















