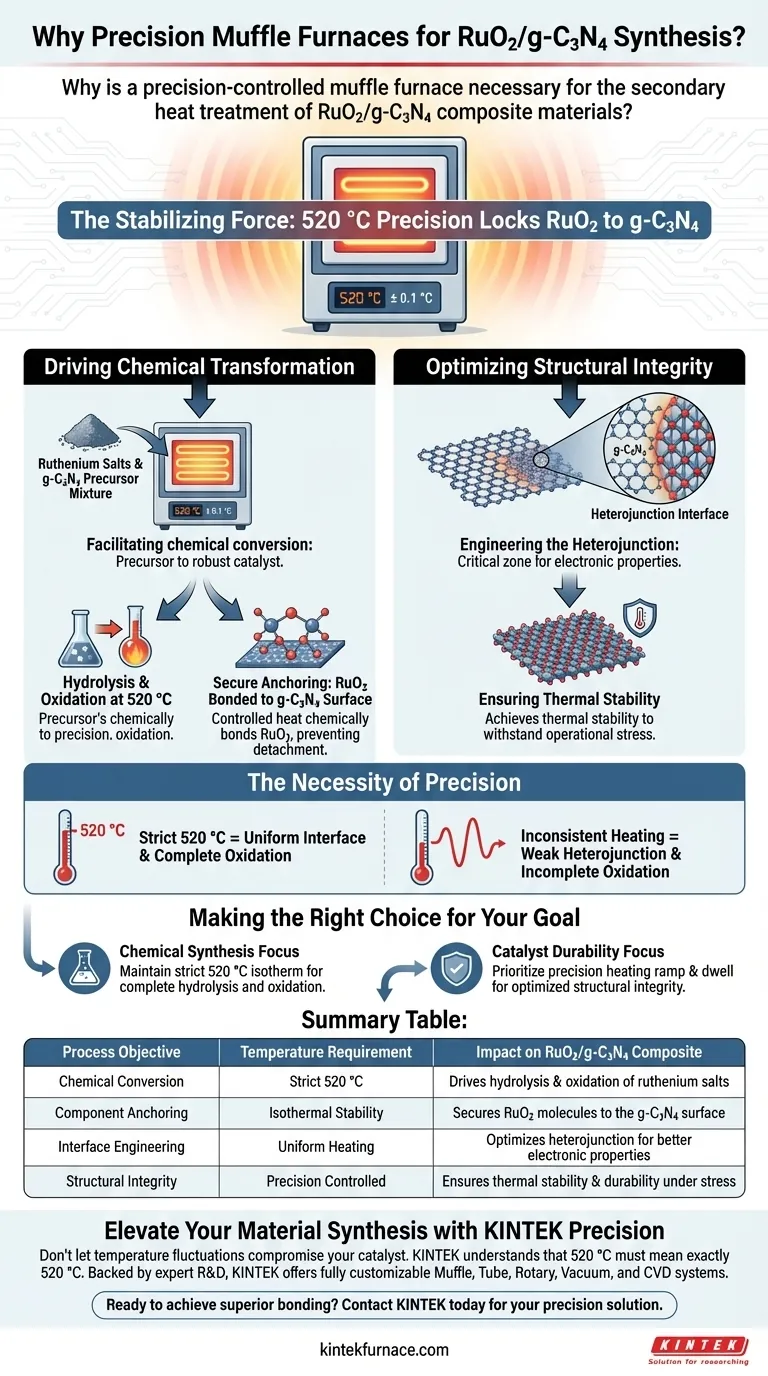
A precision-controlled muffle furnace is strictly necessary for the secondary heat treatment of RuO2/g-C3N4 composites to maintain a stable thermal environment at exactly 520 °C.
This precise temperature control drives two critical processes: the hydrolysis and oxidation of ruthenium salts into securely attached RuO2, and the structural optimization of the heterojunction interface between the ruthenium oxide and the graphitic carbon nitride support.
Core Takeaway The muffle furnace acts as the stabilizing force that locks ruthenium salts onto the g-C3N4 surface through controlled oxidation. By maintaining a uniform 520 °C environment, it transforms a loose precursor mixture into a robust, thermally stable composite catalyst with a fully optimized heterojunction.

Driving Chemical Transformation
Facilitating Hydrolysis and Oxidation
The primary function of the furnace during secondary calcination is to facilitate the chemical conversion of the precursor mixture.
At the specific temperature of 520 °C, the furnace promotes the hydrolysis and oxidation of the ruthenium salts.
Secure Anchoring of Components
This thermal process does not merely deposit material; it chemically bonds it.
The controlled heat ensures that as the ruthenium salts convert to RuO2, they become securely attached to the g-C3N4 surface, preventing detachment during future catalytic applications.
Optimizing Structural Integrity
Creating the Heterojunction Interface
Beyond simple attachment, the furnace is responsible for engineering the interface where the two materials meet.
The heat treatment optimizes the heterojunction interface of the RuO2/g-C3N4 composite, which is the critical zone where the unique electronic properties of the catalyst are defined.
Ensuring Thermal Stability
The structural integrity of the final catalyst is dependent on this secondary heating phase.
By subjecting the composite to a stable, high-temperature environment, the furnace ensures the material achieves the necessary thermal stability to withstand operational stress.
Understanding the Necessity of Precision
The Role of Temperature Stability
The term "precision-controlled" is not a suggestion; it is an operational requirement.
To achieve the specific chemical hydrolysis and oxidation described, the furnace must maintain 520 °C without significant fluctuation.
Risks of Inconsistent Heating
While not explicitly detailed in the primary data, the reliance on a muffle furnace implies that open-air heating or inconsistent heat sources would fail to produce a uniform interface.
Inaccurate temperatures could lead to incomplete oxidation of the ruthenium salts or a weak heterojunction, compromising the catalyst's structural integrity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of your RuO2/g-C3N4 synthesis, consider the following based on your specific objectives:
- If your primary focus is Chemical Synthesis: Ensure your furnace can maintain a strict 520 °C isotherm to drive the complete hydrolysis and oxidation of ruthenium salts.
- If your primary focus is Catalyst Durability: Prioritize the precision of the heating ramp and dwell time to optimize the heterojunction interface for maximum structural integrity.
The precision of your thermal treatment directly dictates the stability and bonding strength of your final composite material.
Summary Table:
| Process Objective | Temperature Requirement | Impact on RuO2/g-C3N4 Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Conversion | Strict 520 °C | Drives hydrolysis & oxidation of ruthenium salts |
| Component Anchoring | Isothermal Stability | Secures RuO2 molecules to the g-C3N4 surface |
| Interface Engineering | Uniform Heating | Optimizes heterojunction for better electronic properties |
| Structural Integrity | Precision Controlled | Ensures thermal stability & durability under stress |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK Precision
Don't let temperature fluctuations compromise your catalyst's structural integrity. At KINTEK, we understand that 520 °C must mean exactly 520 °C for your RuO2/g-C3N4 composites.
Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems. Our lab high-temp furnaces are fully customizable to meet the unique thermal stability and chemical anchoring needs of your research.
Ready to achieve superior bonding and heterojunction optimization? Contact us today to find the perfect precision-controlled solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
References
- Yongjun Liu, Zhiming Huang. Photocatalytic reduction of aqueous chromium(<scp>vi</scp>) by RuO<sub>2</sub>/g-C<sub>3</sub>N<sub>4</sub> composite under visible light irradiation. DOI: 10.1039/d5ra00883b
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a high-temperature muffle furnace in Mg-Zn-Al LDH transformation? Unlocking Adsorption Power
- What role does the air atmosphere play in a high-temperature muffle furnace? Master Ceramic Sintering Stability
- How does the calcination process in a muffle furnace facilitate the formation of pores in manganese oxide?
- What are the primary applications of muffle furnaces in laboratory settings? Unlock Precision in Material Analysis and Synthesis
- What is the significance of using a high-temperature muffle furnace for Co3O4 nanotube stabilization? Ensure Robustness & Chemical Resilience.
- What role does a muffle furnace play in material testing and analysis? Unlock Precise Heat Treatment for Accurate Results
- How is a muffle furnace applied to determine glass fiber content in GFPP? Precision Calcination Explained
- What features ensure fast heat-up and uniform temperature in the muffle furnace? Optimize Your Lab's Thermal Processing



















