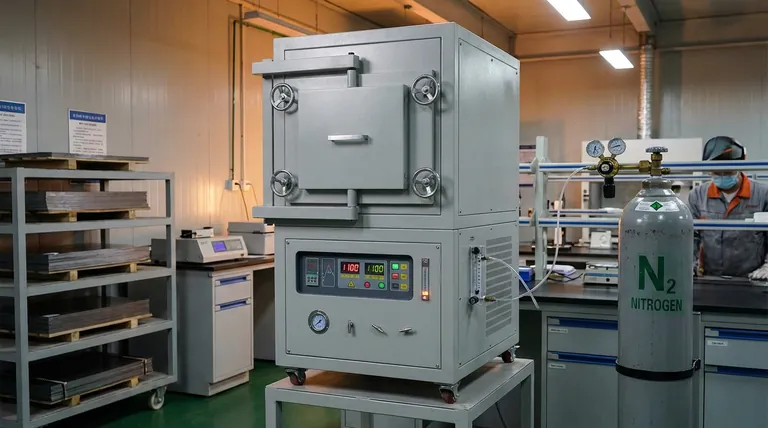
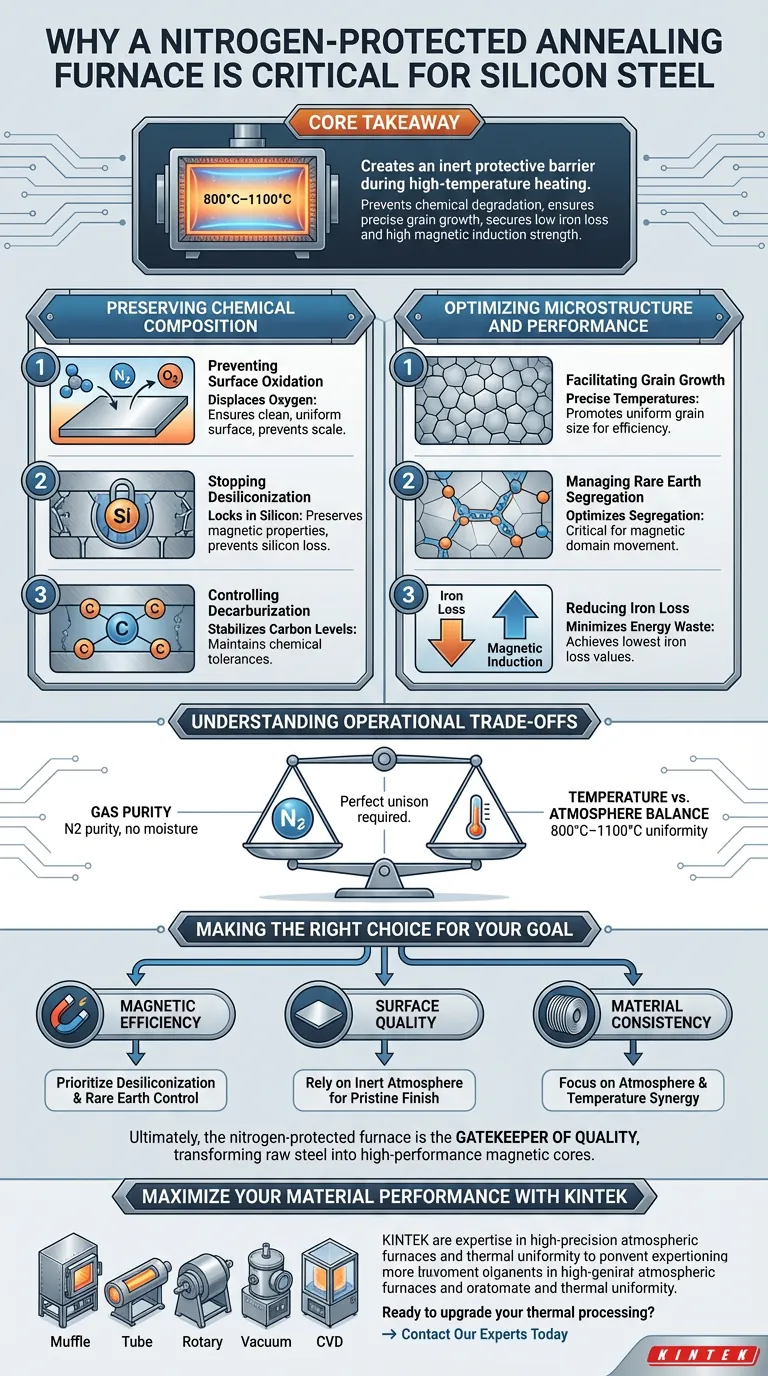
A nitrogen-protected annealing furnace is essential to preserve the chemical and structural integrity of silicon steel during its final high-temperature processing. By maintaining a strictly oxygen-free environment, nitrogen prevents the steel from reacting with the air, specifically stopping surface oxidation and the loss of silicon (desiliconization). This ensures the material retains the magnetic properties required for high-performance electrical applications.
Core Takeaway The introduction of nitrogen creates an inert protective barrier during the critical 800°C–1100°C heating phase. This atmosphere is non-negotiable for preventing chemical degradation, ensuring precise grain growth, and ultimately securing low iron loss and high magnetic induction strength in the final product.

Preserving Chemical Composition
Preventing Surface Oxidation
At the high temperatures required for annealing (800°C to 1100°C), steel is highly reactive to oxygen. Without a protective barrier, the surface would rapidly oxidize, leading to scale formation and surface defects.
Nitrogen displaces oxygen within the furnace, creating an inert environment. This ensures the surface finish of the silicon steel plates remains clean and uniform throughout the recrystallization process.
Stopping Desiliconization
Silicon is the critical alloying element that gives this steel its unique magnetic properties. An oxygen-rich atmosphere would cause the silicon near the surface to react and deplete, a process known as desiliconization.
By using a nitrogen atmosphere, manufacturers lock in the chemical stability of the steel. This preserves the intended silicon content throughout the plate's cross-section, which is vital for maintaining performance metrics.
Controlling Decarburization
Beyond oxygen control, the nitrogen atmosphere helps stabilize carbon levels. The environment prevents unwanted decarburization, ensuring the chemical composition remains within the strict tolerances required for magnetic stability.
Optimizing Microstructure and Performance
Facilitating Grain Growth
The final annealing stage is designed to recrystallize the steel's internal structure. The nitrogen atmosphere allows the furnace to maintain precise temperatures without chemical interference, promoting moderate and uniform grain growth.
The final size of these recrystallized grains is a determining factor in the steel's efficiency. Proper grain size directly correlates to reduced energy dissipation in the final core material.
Managing Rare Earth Segregation
Advanced silicon steels often utilize rare earth elements to enhance performance. The precise temperature control enabled by the protected furnace dictates the degree of rare earth element segregation at the grain boundaries.
This segregation is critical for optimizing the magnetic domain movement. It directly impacts the final magnetic induction strength, a key measure of the material's ability to conduct magnetic flux.
Reducing Iron Loss
The ultimate goal of these controls is to minimize iron loss (energy wasted as heat). By preventing surface degradation and optimizing the internal grain structure, the nitrogen-protected process ensures the lowest possible iron loss values.
Understanding the Operational Trade-offs
The Necessity of Gas Purity
The effectiveness of this process is entirely dependent on the purity of the nitrogen used. Even trace amounts of oxygen or moisture introduced into the furnace can compromise the protective "curtain," leading to localized oxidation or inconsistent magnetic properties.
Temperature vs. Atmosphere Balance
While the atmosphere is critical, it cannot compensate for poor thermal regulation. The furnace must maintain strict uniformity within the 800°C to 1100°C range.
If the temperature fluctuates outside this window, even a perfect nitrogen atmosphere will not prevent issues with grain size or rare earth distribution. The atmosphere and temperature control must work in perfect unison.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Whether you are optimizing for surface aesthetics or electromagnetic efficiency, the role of the nitrogen furnace is pivotal.
- If your primary focus is Magnetic Efficiency: Prioritize the prevention of desiliconization and rare earth segregation to maximize magnetic induction and minimize iron loss.
- If your primary focus is Surface Quality: Rely on the inert nitrogen atmosphere to prevent oxidation, ensuring a pristine finish and uniform plate thickness.
- If your primary focus is Material Consistency: Focus on the synergy between the nitrogen atmosphere and temperature control to ensure uniform grain recrystallization across the entire coil.
Ultimately, the nitrogen-protected furnace is the gatekeeper of quality, transforming raw rolled steel into a high-performance magnetic core material.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Impact of Nitrogen Protection | Benefit to Silicon Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Atmosphere | Displaces oxygen to prevent oxidation | Maintains clean surface finish & uniform thickness |
| Chemical Stability | Prevents desiliconization and decarburization | Preserves core magnetic properties and composition |
| Microstructure | Enables stable 800°C–1100°C recrystallization | Promotes uniform grain growth for higher efficiency |
| Performance | Manages rare earth element segregation | Reduces iron loss and maximizes induction strength |
Maximize Your Material Performance with KINTEK
Don't let oxidation compromise your magnetic core efficiency. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers specialized Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, including high-precision atmospheric furnaces designed specifically for silicon steel annealing. Our systems provide the strict nitrogen purity and thermal uniformity (800°C–1100°C) required to prevent desiliconization and ensure optimal grain growth.
Whether you need a standard lab furnace or a fully customizable high-temperature system for unique industrial requirements, KINTEK delivers the control you need to minimize iron loss and secure material consistency.
Ready to upgrade your thermal processing? → Contact Our Experts Today
Visual Guide
References
- The Multiple Effects of RE Element Addition in Non-Oriented Silicon Steel. DOI: 10.3390/ma18020401
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- What factors determine the amount of gas flow required for furnace inerting? Optimize Your Process for Safety and Efficiency
- Why use an air atmosphere furnace for annealing magnesium aluminum spinel? Restoring Lattice & Optical Integrity
- How does a high-temperature furnace facilitate flash pyrolysis? Unlock Superior Fe-N-C Catalyst Performance
- What are the benefits of using an atmosphere furnace in the electronics industry? Enhance Component Reliability and Performance
- Why is a tube atmosphere furnace required for sulfur-doped hard carbon? Master Precision Carbon Synthesis
- What are the commonly used inert gases in atmosphere furnaces? Optimize Your Heat Treatment Process
- What types of heat treatment processes benefit from a controlled atmosphere furnace? Enhance Material Properties with Precision
- What are the advantages of an atmosphere box furnace in the preparation and sintering of ceramic materials? Achieve Precise Control for Superior Ceramics



















