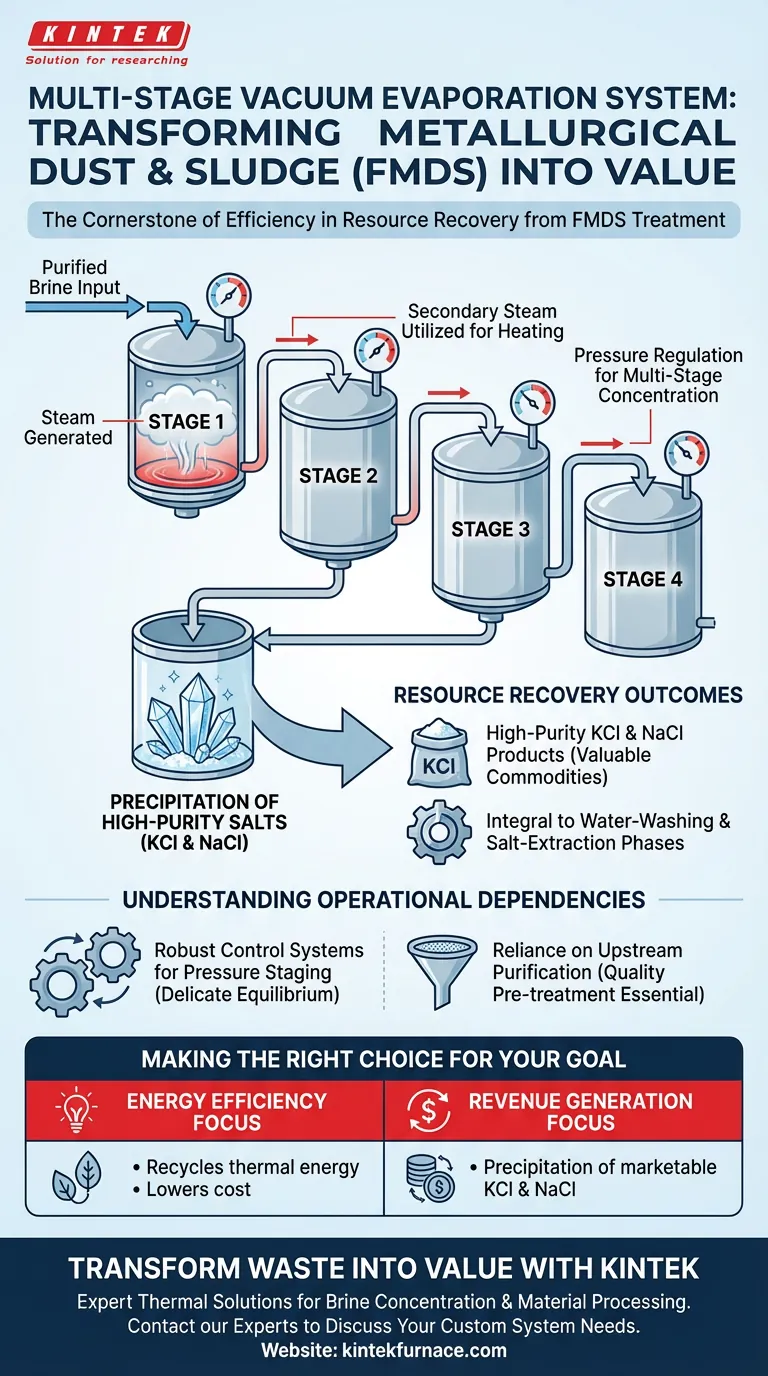
Multi-stage vacuum evaporation systems are the cornerstone of efficiency in the treatment of iron and steel metallurgical dust and sludge (FMDS). These systems primarily serve to concentrate purified brine by regulating pressures across multiple tanks, enabling the recovery of valuable resources while minimizing energy waste.
The system functions as the "core component" for resource recovery, utilizing pressure differentials and secondary steam to transform waste brine into high-purity potassium chloride (KCl) and sodium chloride (NaCl) products.
The Mechanics of Concentration
Regulating Pressure for Efficiency
The fundamental mechanism of this system involves distinct pressure regulation. By managing the pressure within different evaporation tanks, the system achieves a "multi-stage concentration" effect.
Lowering the pressure in subsequent stages allows the liquid to boil at lower temperatures. This ensures the process remains continuous and efficient across the entire equipment combination.
Harnessing Secondary Steam
A critical advantage of using a multi-effect system, such as a four-effect evaporator, is the intelligent reuse of energy. The system is designed to effectively utilize the thermal energy of secondary steam.
Instead of venting steam generated in the first stage, it is used to heat the subsequent stages. This cascading use of thermal energy drastically reduces the external power required to achieve concentration.
Resource Recovery Outcomes
Precipitating High-Purity Salts
The ultimate goal of this evaporation process is not merely volume reduction, but precise product recovery. The system concentrates the purified brine to the point of supersaturation.
This specific environment facilitates the precipitation of high-purity potassium chloride (KCl) and sodium chloride (NaCl). These are valuable byproducts that turn a waste treatment process into a resource generation process.
The Role in Water-Washing
This technology is integrated specifically into the water-washing and salt-extraction phases of FMDS treatment. It acts as the final separation engine after the initial washing steps.
By removing the water content efficiently, it ensures that the salt extraction process is commercially viable and technically effective.
Understanding the Operational Dependencies
Complexity of Pressure Staging
While highly effective, the system relies heavily on the precise balance of pressures across the tanks. If the pressure regulation fails in one stage, the thermal cascade is disrupted.
This implies that the "four-effect" configuration requires robust control systems to maintain the delicate equilibrium needed for optimal evaporation.
Reliance on Upstream Purification
The reference notes that the system concentrates "purified brine." The effectiveness of the evaporator is directly tied to the quality of the pre-treatment.
If the brine entering the vacuum system is not adequately purified first, the purity of the resulting KCl and NaCl products will be compromised, regardless of the evaporator's efficiency.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if this specific configuration suits your operational needs, consider your primary objectives:
- If your primary focus is Energy Efficiency: This system is ideal because it recycles the thermal energy of secondary steam, significantly lowering the cost per gallon of treated water.
- If your primary focus is Revenue Generation: The precise pressure regulation allows for the precipitation of high-purity KCl and NaCl, which are marketable commodities rather than waste products.
By integrating multi-stage vacuum evaporation, you convert a waste disposal challenge into a sustainable resource recovery operation.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit in FMDS Treatment |
|---|---|
| Pressure Regulation | Enables multi-stage concentration and lower boiling points for continuous operation. |
| Secondary Steam Reuse | Harnesses thermal energy from previous stages to drastically reduce external power consumption. |
| Product Recovery | Facilitates precipitation of high-purity KCl and NaCl for commercial resale. |
| Process Integration | Serves as the final separation engine in water-washing and salt-extraction phases. |
Transform Your Waste into Value with KINTEK
Are you ready to optimize your resource recovery and reduce operational costs? KINTEK provides industry-leading thermal solutions designed for the most demanding metallurgical applications.
Backed by expert R&D and precision manufacturing, we offer a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, along with specialized high-temperature lab furnaces. Whether you need a standard setup or a fully customizable system tailored to your unique brine concentration or material processing needs, our engineering team is here to help.
Maximize your efficiency today—Contact our experts at KINTEK to discuss your project requirements!
Visual Guide
References
- Jiansong Zhang, Qianqian Ren. Multi-Source Ferrous Metallurgical Dust and Sludge Recycling: Present Situation and Future Prospects. DOI: 10.3390/cryst14030273
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- MPCVD Machine System Reactor Bell-jar Resonator for Lab and Diamond Growth
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering and Brazing Furnace
- Magnesium Extraction and Purification Condensing Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why are graphite fixtures and holders important in vacuum furnaces? Unlock Precision & Durability
- What are the advantages of using a laboratory vacuum drying oven? Essential Benefits for Graphene Composite Powders
- What is the primary function of the vacuum system in the vacuum distillation process for metal purification? Achieve High-Purity Metal Separation
- What is the primary role of a vacuum melting furnace in Ti-Zr-Mo-W alloy prep? Ensure Purity and Homogeneity
- Why must humidity be controlled in aluminum alloy furnaces? Prevent Blistering & Hydrogen Damage Now
- Why use low-speed heating (600-700°C) in Al-Ti-Zr sintering? Mastering Aluminum Phase Transition for Success.
- What is the function of a flow-guiding grille in a vacuum high-pressure gas quenching furnace? Ensure Uniform Cooling
- What role does a vacuum annealing furnace play in Bi4I4 single crystals? Master Precise Fermi Level Engineering



















