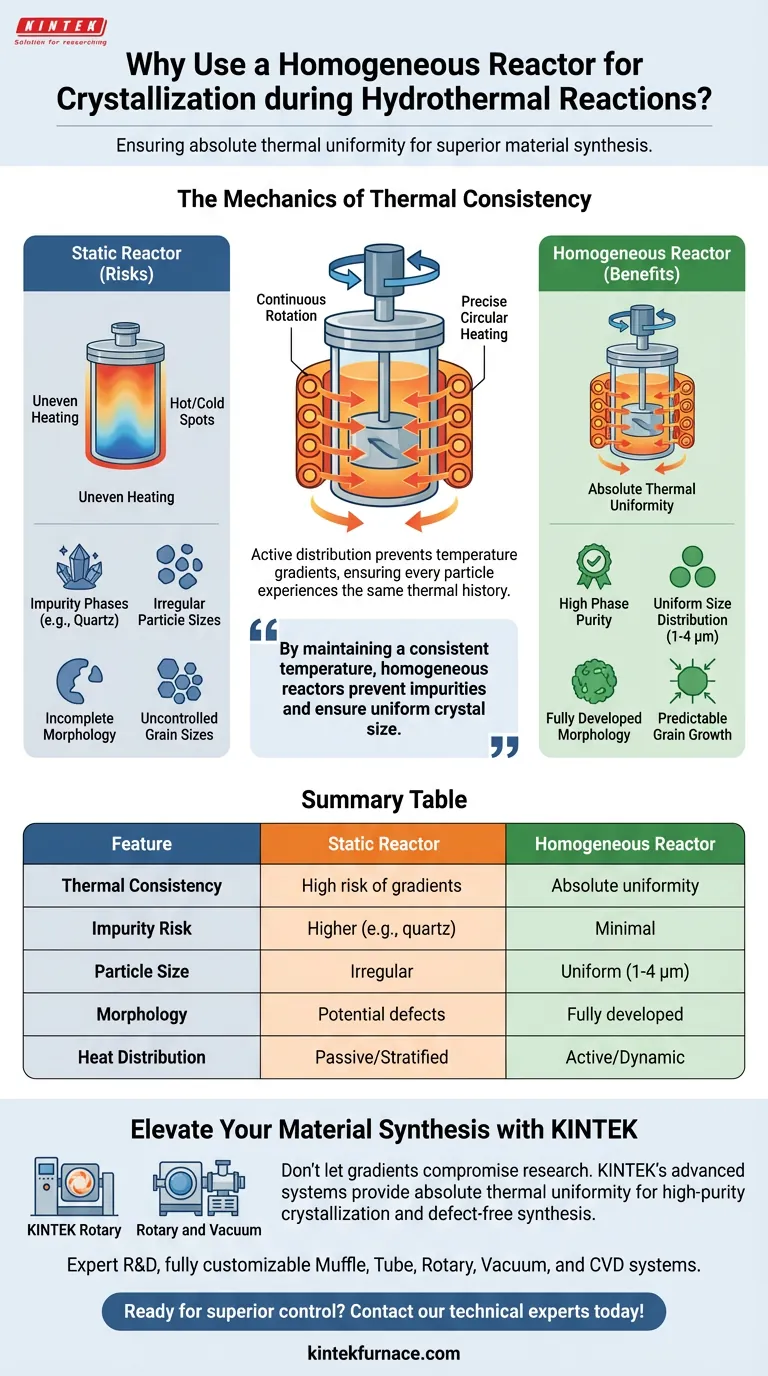
The primary role of a homogeneous reactor is to guarantee absolute thermal uniformity. By utilizing continuous rotation or precise circular heating, these reactors eliminate temperature gradients within the hydrothermal vessel. This mechanical intervention is critical for preventing the localized hot or cold spots that compromise chemical synthesis.
By maintaining a consistent temperature throughout the vessel, homogeneous reactors prevent the formation of impurities and ensure crystals grow to a specific, uniform size.
The Mechanics of Thermal Consistency
Eliminating Temperature Gradients
In a static environment, materials inside a reaction vessel often suffer from uneven heating. A homogeneous reactor addresses this by continuously turning the contents. This movement ensures that no part of the mixture is subjected to local overheating or insufficient temperatures.
The Role of Dynamic Movement
The physical rotation or circular heating mechanism actively distributes heat. This prevents the stratification of temperature zones within the fluid. It ensures every particle in the batch experiences the exact same thermal history.
Impact on Crystal Quality
Preventing Impurity Phases
Temperature variances are a leading cause of unwanted chemical byproducts. Specifically, local overheating can trigger the generation of impurity phases. In the context of synthesizing ZSM-5 zeolites, for example, failing to maintain thermal uniformity can result in the formation of quartz rather than the desired zeolite structure.
Achieving Uniform Particle Size
Consistency in temperature equates to consistency in growth rates. When the thermal environment is homogeneous, crystals grow evenly. This technology is proven to yield ZSM-5 zeolite crystals with a highly uniform particle size distribution, typically falling within the 1-4 µm range.
Risks of Non-Homogeneous Heating
Incomplete Morphology
If the heating process is uneven, the physical structure of the crystal may not form correctly. This leads to "incomplete morphology," where the crystal lattice is defective or misshapen. A homogeneous reactor ensures the crystal structure develops fully and predictably.
Uncontrolled Grain Sizes
Without the mixing action of a homogeneous reactor, grain sizes vary wildly within a single batch. Some crystals may grow too large due to hot spots, while others remain stunted. This lack of uniformity significantly degrades the performance of the final material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the quality of your hydrothermal reaction, align your equipment choice with your specific purity and sizing requirements.
- If your primary focus is Phase Purity: Use a homogeneous reactor to prevent local overheating, which is the root cause of impurities like quartz.
- If your primary focus is Size Consistency: Rely on the reactor's continuous turning to ensure all crystals grow at the same rate, achieving a narrow 1-4 µm distribution.
Precise thermal management is not a luxury; it is the fundamental requirement for synthesizing high-quality, defect-free crystalline materials.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Static Reactor (Standard) | Homogeneous Reactor (Rotary) |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Consistency | High risk of localized gradients | Absolute thermal uniformity |
| Impurity Risk | Higher (e.g., quartz formation) | Minimal (high phase purity) |
| Particle Size | Irregular and uncontrolled | Uniform distribution (1-4 µm) |
| Morphology | Potential for defects/incomplete | Fully developed crystal structures |
| Heat Distribution | Passive/Stratified | Active/Dynamic movement |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK
Don’t let temperature gradients compromise your research. KINTEK’s advanced Rotary and Vacuum systems are engineered to provide the absolute thermal uniformity required for high-purity crystallization and defect-free synthesis.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer fully customizable Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to meet the unique needs of your lab.
Ready to achieve superior grain size control and phase purity? Contact our technical experts today to find your perfect high-temperature furnace solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Zhenhua Sun, Zhaohui Huang. A Hydrothermal Synthesis Process of ZSM-5 Zeolite for VOCs Adsorption Using Desilication Solution. DOI: 10.3390/separations11020039
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the three types of dental ceramics? A Guide to Material Selection
- How does an infrared rapid thermal annealing belt furnace affect battery performance? Maximize Efficiency Today
- What is the significance of the 200 °C calcination for Fe3O4/biochar? Enhancing Stability and Magnetic Recovery
- Why is charcoal used as a susceptor material during the microwave cladding of FeCoNiMnCu? Unlock efficient heating.
- Why is a slow heating rate utilized for rice husk biochar? Optimize Pore Structure and Adsorption Performance
- Why is an equivalent diffusion combustion heat source term integrated into the furnace temperature field simulation?
- What is the primary purpose of high-temperature pyrolysis? Unlock Superior PFAS Removal with Enhanced Hydrophobicity
- How do Digital Twin and machine learning improve maintenance? Master High-Temp Equipment Reliability & Efficiency



















