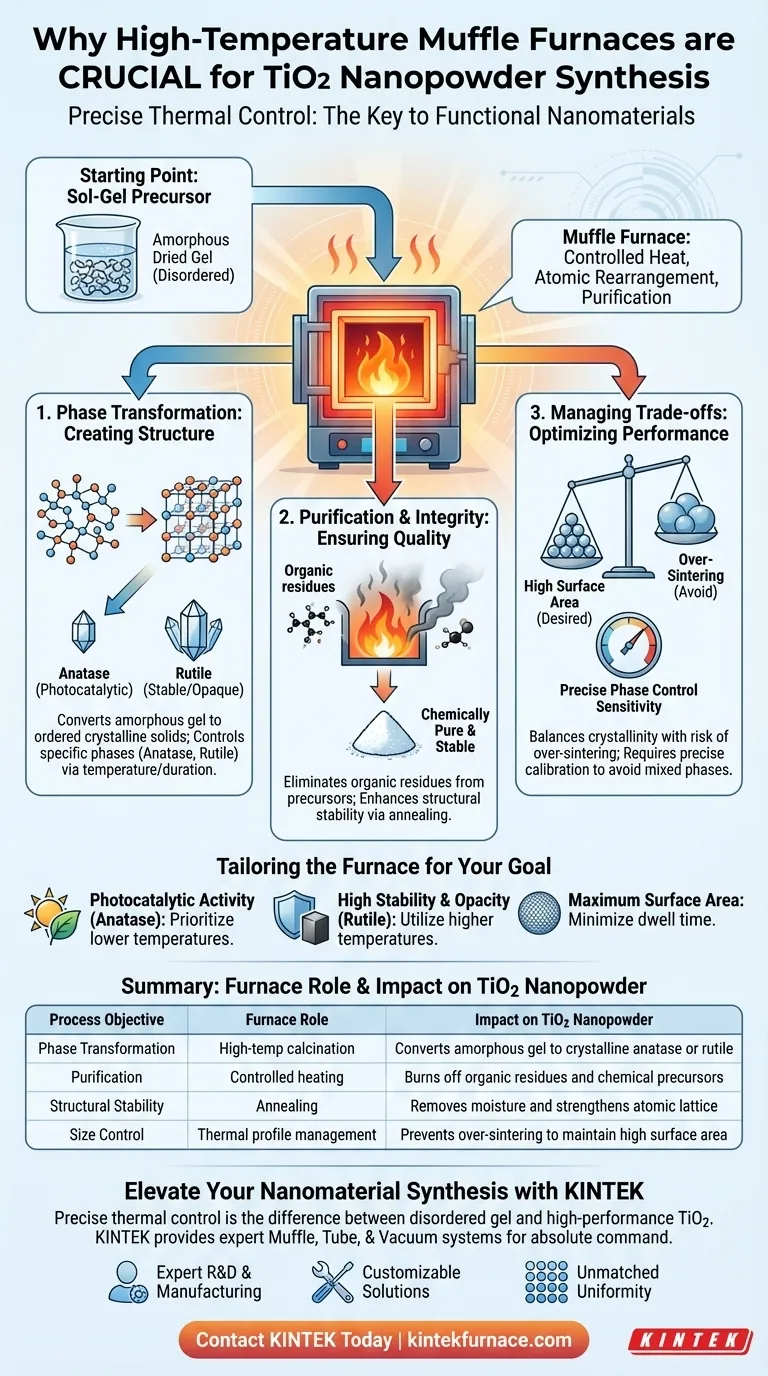
Precise thermal control is the determining factor in successfully converting raw chemical mixtures into functional nanomaterials. In the sol-gel preparation of Titanium Dioxide (TiO2) nanopowders, a high-temperature muffle furnace is necessary to perform calcination, a critical step that transforms amorphous dried gels into stable crystalline structures while simultaneously purifying the material.
The muffle furnace provides the specific thermal environment required to drive atomic rearrangement, converting disordered precursors into defined crystal phases like anatase or rutile and eliminating organic impurities.

The Critical Role of Phase Transformation
The primary function of the muffle furnace in this context is to dictate the physical structure of the material. Without this high-temperature treatment, the product of the sol-gel process is merely a dried, disordered gel rather than a functional nanopowder.
Converting Amorphous Gels to Crystalline Solids
The sol-gel process initially produces a precursor that is amorphous, meaning its atomic structure lacks long-range order.
The muffle furnace applies controlled heat to provide the energy necessary for atomic rearrangement. This thermal energy forces the atoms to align into an ordered lattice, resulting in high crystallinity which is essential for the material's optical and chemical properties.
Controlling Specific Crystal Phases
Titanium Dioxide exists in different polymorphs, primarily anatase, brookite, and rutile. Each phase has distinct properties and applications.
By manipulating the temperature and duration within the furnace, you determine which phase dominates the final product. The furnace allows you to target a specific phase structure, ensuring the nanopowder performs as intended for its specific application.
Purification and Structural Integrity
Beyond crystallization, the muffle furnace acts as a purification tool. The sol-gel process relies on chemical precursors that often leave behind unwanted residues.
Eliminating Organic Residues
The chemical reactions in sol-gel synthesis often involve organic solvents or ligands. These remain trapped in the dried gel matrix.
High-temperature calcination effectively burns off these organic residues. This ensures the final TiO2 nanopowder is chemically pure and free of volatile contaminants that could degrade performance.
Enhancing Material Stability
Thermal treatment is not just about changing phases; it is about stabilizing them.
The annealing process within the furnace removes residual moisture and strengthens the structural integrity of the particles. This stabilization prevents the material from degrading or changing physically when exposed to environmental stressors later in its lifecycle.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the muffle furnace is essential, improper use can lead to diminished material quality. It is vital to balance the need for crystallinity against the risk of microstructural damage.
The Risk of Over-Sintering
High temperatures facilitate bonding between particles. If the temperature is too high or the duration too long, individual nanoparticles may fuse together.
This phenomenon, known as sintering or agglomeration, reduces the specific surface area of the powder. For nanopowders, where high surface area is often the primary goal, this can render the material less effective.
Sensitivity of Phase Control
Phase transformation is highly sensitive to thermal inputs.
Slight deviations in the furnace temperature can lead to the formation of mixed phases (e.g., a mix of anatase and rutile) when a pure phase was desired. Precise calibration of the muffle furnace is non-negotiable to avoid inconsistent material properties.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The way you utilize the muffle furnace depends heavily on the specific requirements of your end application.
- If your primary focus is Photocatalytic Activity (Anatase): Prioritize lower calcination temperatures to promote the anatase phase while preventing the transformation into the less active rutile phase.
- If your primary focus is High Stability and Opacity (Rutile): Utilize higher temperature settings to drive the complete transformation into the thermodynamically stable rutile phase.
- If your primary focus is Maximum Surface Area: Minimize the dwell time at peak temperature to achieve crystallinity without inducing excessive particle growth or sintering.
Mastering the thermal profile of your muffle furnace is the single most effective way to dictate the quality and performance of your TiO2 nanopowders.
Summary Table:
| Process Objective | Furnace Role | Impact on TiO2 Nanopowder |
|---|---|---|
| Phase Transformation | High-temp calcination | Converts amorphous gel to crystalline anatase or rutile |
| Purification | Controlled heating | Burns off organic residues and chemical precursors |
| Structural Stability | Annealing | Removes moisture and strengthens atomic lattice |
| Size Control | Thermal profile management | Prevents over-sintering to maintain high surface area |
Elevate Your Nanomaterial Synthesis with KINTEK
Precise thermal control is the difference between a disordered gel and high-performance TiO2 nanopowders. KINTEK provides industry-leading muffle, tube, and vacuum systems designed to give you absolute command over phase transformation and material purity.
Why choose KINTEK?
- Expert R&D & Manufacturing: Our systems are built for the rigorous demands of advanced chemical synthesis.
- Customizable Solutions: Whether you need specific atmosphere control or precise ramping for CVD and sol-gel processes, we tailor our equipment to your unique lab needs.
- Unmatched Uniformity: Ensure consistent crystallinity across every batch with our high-temp lab furnaces.
Contact KINTEK today to find the perfect furnace for your research and optimize your material properties with expert-grade precision.
Visual Guide
References
- Devireddy Sandhya, Vasudeva Rao Veeredhi. An exclusive review on TiO2-based nanofluids with applications to automotive industry. DOI: 10.7862/rm.2025.16
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is a key feature of box furnaces regarding temperature control? Achieve Precise and Uniform Heating for Your Lab
- What are the steps to operate a box muffle furnace? Master Safe and Efficient Heating Processes
- What is the role of muffle furnaces in incineration processes? Precision Ashing for Accurate Material Analysis
- What is the function of a laboratory muffle furnace in treating LNMO precursors? Ensure High-Purity Material Synthesis
- How are muffle furnaces utilized in high-temperature sintering within the pharmaceutical industry? Unlock Precision in Drug Delivery and Implants
- Why is precise temperature control important in crucible furnaces? Ensure Quality & Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What role do muffle furnaces play in the ceramics industry? Essential for Precision Firing and Purity
- What is the primary function of a high-temperature furnace for nanocolloid study? Expert Thermal Performance Insights



















