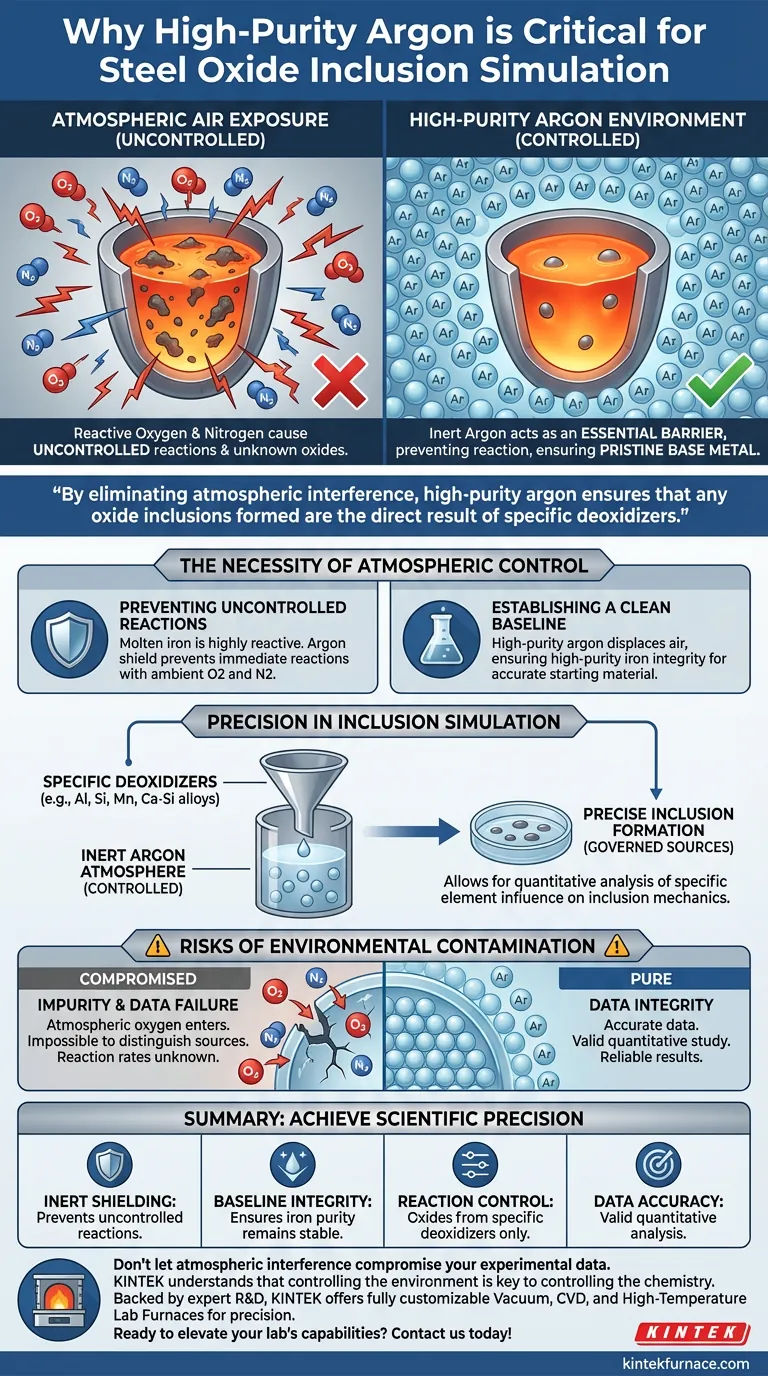
A high-purity argon environment acts as an essential isolation barrier during the melting of iron blocks. Its primary function is to prevent liquid iron from reacting chemically with oxygen or nitrogen present in the ambient atmosphere. By maintaining this inert state, researchers ensure that the base metal remains pristine until specific experimental variables are introduced.
By eliminating atmospheric interference, high-purity argon ensures that any oxide inclusions formed are the direct result of specific deoxidizers. This creates the controlled baseline necessary for the quantitative study of inclusion mechanisms.
The Necessity of Atmospheric Control
Preventing Uncontrolled Reactions
Molten iron is highly reactive when exposed to air. Without a protective shield, the liquid metal would immediately engage in uncontrolled reactions with atmospheric oxygen and nitrogen.
Establishing a Clean Baseline
To simulate steel oxide inclusions accurately, the starting material must remain chemically stable. High-purity argon displaces the air, ensuring the high-purity iron retains its integrity during the heating and melting phases.
Precision in Inclusion Simulation
Governing Inclusion Sources
The scientific objective of these simulations is to study inclusions formed by specific additives. The argon environment guarantees that oxide formation is governed exclusively by the precise addition of deoxidizers.
Validating Chemical Systems
Researchers typically use deoxidizers such as aluminum, silicon, manganese, or calcium-silicon alloys. An inert atmosphere allows for the quantitative analysis of how these specific elements influence inclusion mechanics within the system.
Risks of Environmental Contamination
The Consequence of Impurity
If the argon environment is compromised or of low purity, atmospheric oxygen will enter the melt. This contamination makes it impossible to distinguish between inclusions caused by the deoxidizers and those caused by the air.
Data Integrity Failures
In a compromised atmosphere, the "quantitative study" mentioned in technical literature becomes invalid. You cannot calculate reaction rates or formation mechanisms if the input variables (oxygen sources) are fluctuating and unknown.
Ensuring Experimental Success
To derive accurate data from your steel oxide simulations, consider the following regarding your environmental setup:
- If your primary focus is fundamental research: Prioritize the highest grade of argon purity to ensure that all observed inclusions are attributed solely to your added deoxidizers.
- If your primary focus is testing specific alloys: Use the inert environment to isolate the effects of complex deoxidizers like calcium-silicon, ensuring no atmospheric nitrogen alters the results.
Control the atmosphere to control the chemistry.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in Inclusion Simulation |
|---|---|
| Inert Shielding | Prevents uncontrolled reactions with atmospheric oxygen and nitrogen. |
| Baseline Integrity | Ensures iron purity remains stable during the heating and melting phases. |
| Reaction Control | Guarantees oxide formation results solely from specific deoxidizers. |
| Data Accuracy | Allows for valid quantitative analysis of inclusion formation mechanisms. |
Achieve Scientific Precision in Your Thermal Research
Don't let atmospheric interference compromise your experimental data. At KINTEK, we understand that controlling the environment is the key to controlling the chemistry.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers advanced Vacuum, CVD, and High-Temperature Lab Furnaces—including Muffle, Tube, and Rotary systems—all of which are fully customizable to maintain the high-purity inert environments your simulations demand.
Whether you are performing fundamental research or testing complex alloys, our systems provide the stability and precision needed for reliable results.
Ready to elevate your lab's capabilities? Contact us today to discuss your unique needs!
Visual Guide
References
- Alejandra Slagter, Andreas Mortensen. Nanoindentation Hardness and Modulus of Al2O3–SiO2–CaO and MnO–SiO2–FeO Inclusions in Iron. DOI: 10.1007/s11661-024-07330-x
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What materials can be smelted using an IGBT medium frequency induction melting furnace? Versatile Melting for Metals
- What maintenance benefits does the IGBT induction melting furnace offer? Achieve Unmatched Uptime and Reliability
- How does electromagnetic induction work in heating? Master Efficient, Non-Contact Thermal Processing
- What industries commonly use vacuum or protective atmosphere induction furnaces? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and More
- How does vacuum melting technology contribute to sustainability? Boost Durability and Recycling Efficiency
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum casting furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in Metal Processing
- What is induction shrink-fitting and how does it work? Master Precision Assembly with Induction Heating
- What are the main steps in vacuum casting? Master High-Quality Prototyping and Low-Volume Production



















