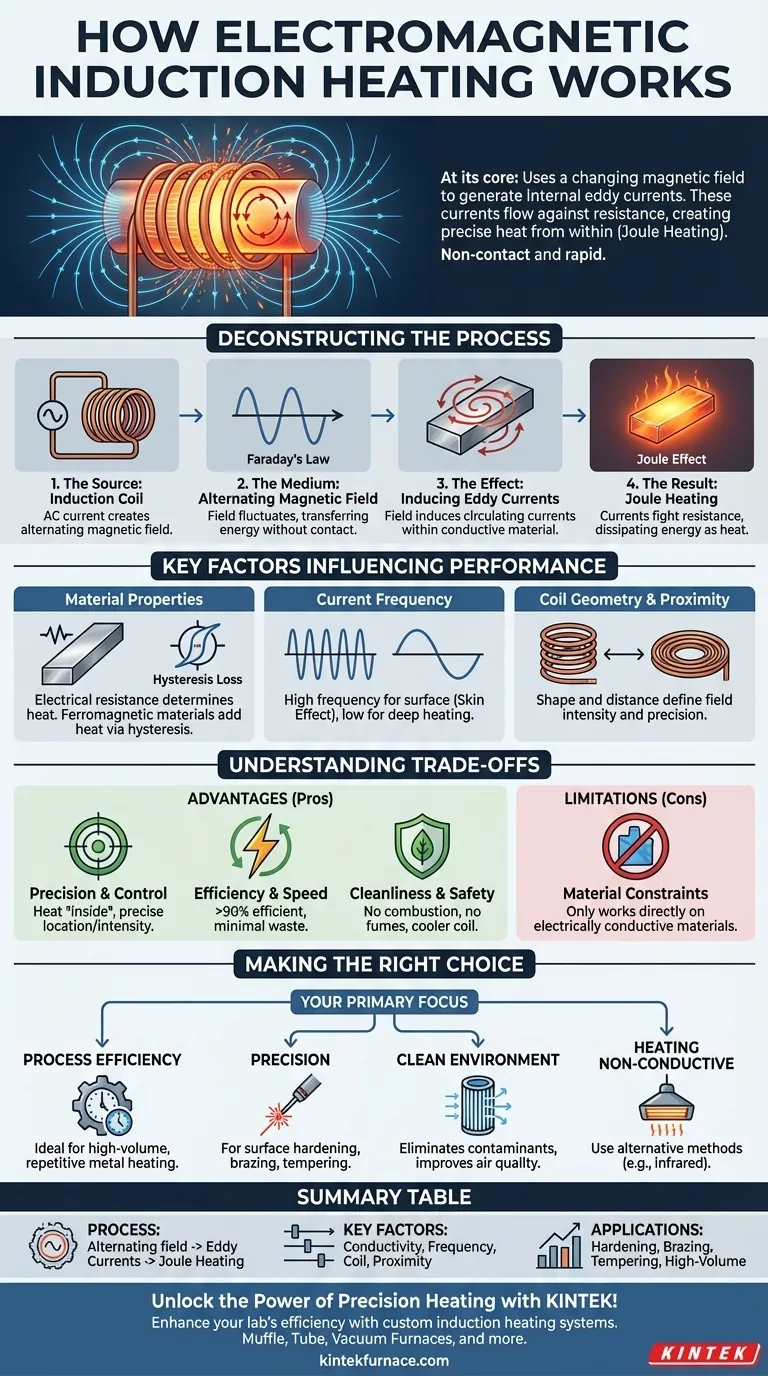
At its core, induction heating works by using a changing magnetic field to generate electrical currents directly inside a conductive object. These internal currents, known as eddy currents, flow against the material's natural electrical resistance, creating intense and precise heat through a process called Joule heating. This allows for rapid, non-contact heating of the material from within.
The central principle of induction heating is the transformation of electrical energy into a magnetic field, and then back into targeted thermal energy inside the workpiece itself. This makes it an exceptionally direct, efficient, and controllable heating method.
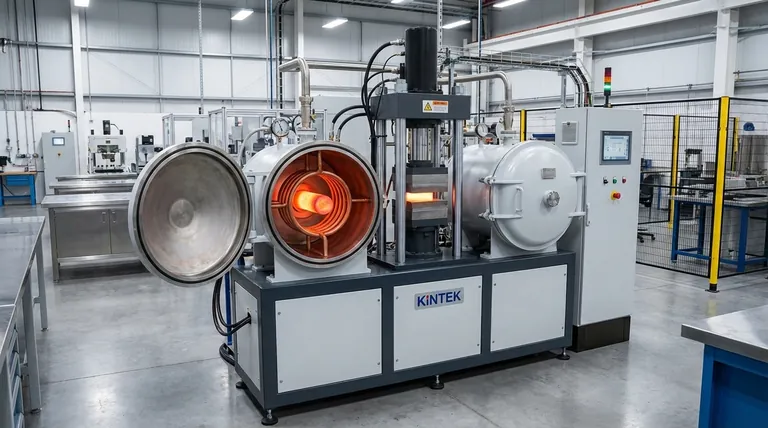

Deconstructing the Induction Heating Process
To understand how this works, we can break it down into a sequence of four fundamental physical events. These events happen almost instantaneously to transfer energy without any physical contact.
The Source: The Induction Coil
The process begins with a specially designed copper coil. A high-frequency alternating current (AC) is passed through this coil. The coil itself does not get hot but serves as the source for creating the magnetic field.
The Medium: The Alternating Magnetic Field
According to Faraday's Law of Induction, any electric current generates a magnetic field. Because the current in the coil is alternating—constantly changing direction and intensity—it produces a dynamic and fluctuating magnetic field in the space around it.
The Effect: Inducing Eddy Currents
When an electrically conductive material, such as a piece of metal, is placed within this alternating magnetic field, the field induces circulating electrical currents within the material. These are called eddy currents. They are the direct result of the magnetic field's energy being transferred to the object.
The Result: Joule Heating
These eddy currents are not flowing through a perfect conductor. The material has inherent electrical resistance. As the eddy currents flow against this resistance, they dissipate energy in the form of heat. This phenomenon is known as the Joule effect, and it is the primary source of heat in the induction process.
Key Factors Influencing Heating Performance
The effectiveness and characteristics of induction heating are not universal; they depend on several key factors that can be adjusted to achieve specific outcomes.
Material Properties
The type of material is critical. Its electrical resistance directly influences how much heat is generated. Additionally, for ferromagnetic materials like iron or steel, a secondary heating effect called hysteresis loss occurs, where the rapid switching of magnetic domains adds to the overall heat.
Frequency of the Current
The frequency of the alternating current is a crucial control parameter. Higher frequencies tend to concentrate the eddy currents on the surface of the material, a phenomenon known as the skin effect. This is ideal for applications like surface hardening. Lower frequencies allow the heat to penetrate deeper into the part.
Coil Geometry and Proximity
The shape of the induction coil and its distance from the workpiece define the shape and intensity of the magnetic field. A close-fitting coil ensures efficient energy transfer and allows for precise, localized heating of specific areas on a part.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, induction heating is not a universal solution. Understanding its advantages and limitations is key to using it effectively.
Advantage: Precision and Control
Because heat is generated inside the part, you can control its location and intensity with incredible accuracy. This is impossible with conventional furnaces, which heat the entire object from the outside in.
Advantage: Efficiency and Speed
Energy is transferred directly to the workpiece with efficiencies often exceeding 90%. Very little energy is wasted heating the surrounding air, making the process both fast and energy-efficient.
Advantage: Cleanliness and Safety
Induction heating produces no combustion byproducts, fumes, or pollutants. This creates a cleaner and safer work environment. The coil remains cool, reducing the risk of burns compared to open flames or resistive heating elements.
Limitation: Material Constraints
The single biggest limitation is that induction heating only works directly on electrically conductive materials. It cannot heat materials like plastics, ceramics, or glass unless they are paired with a conductive object (a susceptor) to transfer the heat.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ultimately, whether induction heating is the right choice depends entirely on your specific application and priorities.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency: Induction is ideal for high-volume, repetitive heating of conductive metals, as it minimizes energy waste and cycle times.
- If your primary focus is precision: Choose induction for applications like surface hardening, brazing, or tempering, where only specific zones of a part must be heated.
- If your primary focus is a clean environment: Induction is superior to any fuel-based method for eliminating airborne contaminants and improving workplace air quality.
- If your primary focus is heating non-conductive materials: You must use an alternative method like conventional or infrared heating, as induction will not work directly.
By understanding these core principles, you can effectively leverage induction heating as a powerful tool for advanced and efficient thermal processing.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Process | Uses alternating magnetic field to induce eddy currents, causing Joule heating inside the material. |
| Key Factors | Material conductivity, current frequency, coil geometry, and proximity to workpiece. |
| Advantages | High precision, efficiency (>90%), speed, cleanliness, and non-contact operation. |
| Limitations | Only heats conductive materials; not suitable for plastics, ceramics, or glass directly. |
| Applications | Surface hardening, brazing, tempering, and high-volume metal processing. |
Unlock the Power of Precision Heating with KINTEK!
Are you looking to enhance your laboratory's efficiency with advanced thermal processing? KINTEK specializes in high-temperature furnace solutions, including custom induction heating systems. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a diverse product line—such as Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—tailored to your unique experimental needs. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise, efficient, and clean heating for conductive materials, helping you achieve superior results in applications like surface hardening and brazing.
Contact us today to discuss how KINTEK can optimize your heating processes and drive innovation in your lab!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How does induction heating ensure precision in manufacturing processes? Achieve Superior Thermal Control & Repeatability
- What are the advantages of ceramic/metal composites produced using a vacuum press? Achieve Superior Strength and Durability
- What other types of furnaces are related to hot pressing? Explore Key Thermal Processing Technologies
- What are the main applications of vacuum hot pressing? Create Dense, Pure Materials for Demanding Industries
- How does the use of vacuum in hot-pressing affect the material processing? Achieve Denser, Purer, and Stronger Materials



















