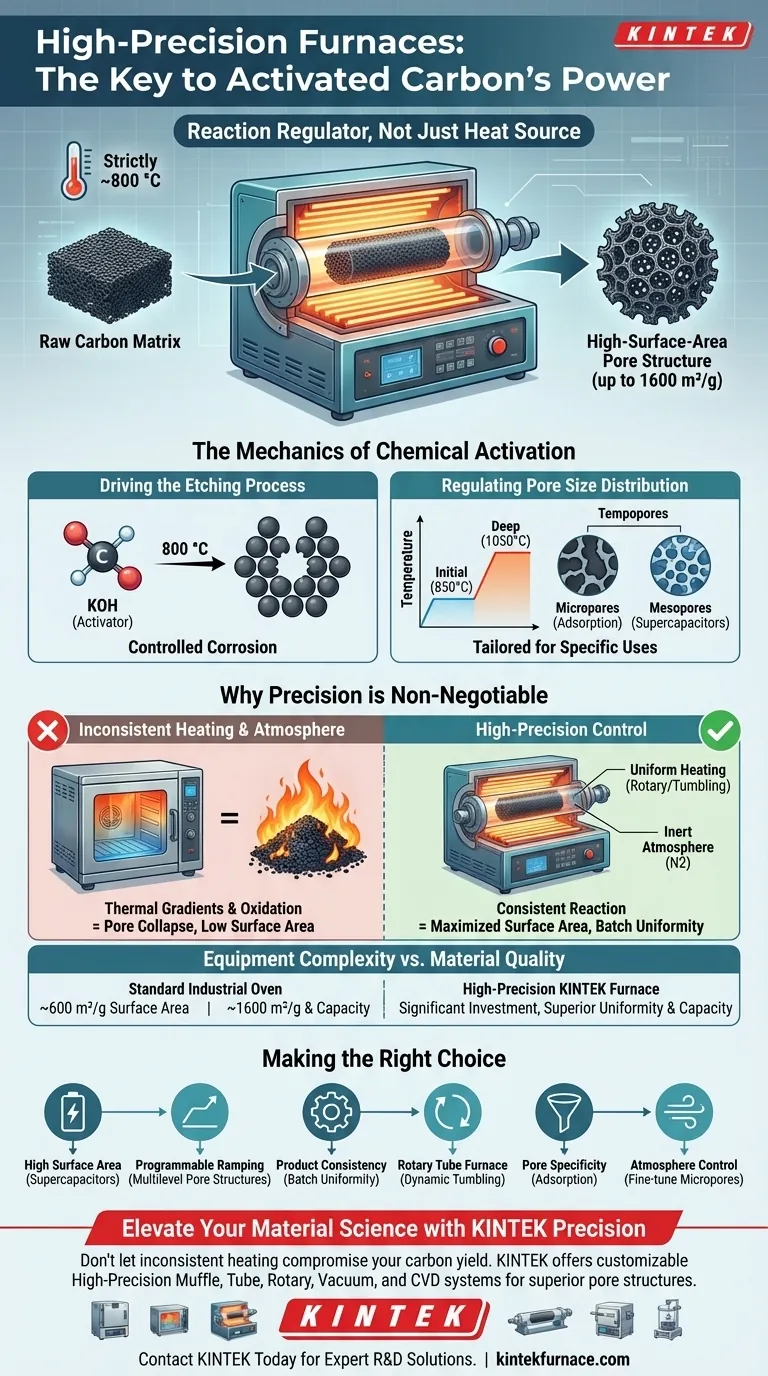
Precise thermal control is the primary determinant of success in chemical activation. A high-precision high-temperature furnace is required to strictly maintain the ~800 °C environment needed to drive the reaction between activators (such as KOH) and the carbon matrix, ensuring the creation of a high-surface-area pore structure without destroying the material.
Core Takeaway The furnace functions as a reaction regulator, not just a heat source. By enforcing accurate heating rates and constant temperatures, it controls exactly how aggressive chemical agents etch the carbon skeleton, which is the mechanism that defines the material's final micropore volume and performance capabilities.

The Mechanics of Chemical Activation
Driving the Etching Process
Chemical activation is effectively a controlled corrosion of the carbon material. At high temperatures (typically around 800 °C), activators like Potassium Hydroxide (KOH) act as powerful etching agents. The furnace provides the necessary thermal energy for these agents to attack the carbon skeleton, expanding micropore and mesopore structures to significantly increase the total surface area.
Regulating Pore Size Distribution
The specific thermal profile determines the geometry of the pores. Programmable temperature control is essential to execute segmented heating strategies—for example, stabilizing at 850 °C for initial activation before ramping to 1050 °C for deep activation. This precision allows you to dictate the ratio of micropores to mesopores, tailoring the material for specific uses like supercapacitors or mercury adsorption.
Why Precision is Non-Negotiable
Eliminating Temperature Gradients
Inconsistent heating results in a heterogeneous product where some particles are over-activated and others are under-reacted. Advanced equipment, such as rotary tube furnaces, combines precise heating with mechanical tumbling to ensure dynamic mixing. This eliminates thermal gradients within the chamber, ensuring every particle undergoes the same chemical reaction and results in consistent physical properties.
Managing the Reaction Atmosphere
At activation temperatures, the carbon matrix is highly vulnerable to uncontrolled oxidation (burning away). High-precision furnaces feature reliable atmosphere control systems to maintain an inert environment, typically using Nitrogen (N2). This isolates the chemical activation process, allowing the creation of structural defects and active sites without incinerating the carbon yield.
Understanding the Risks and Trade-offs
The Danger of Thermal Overshoot
Temperature control must be exact because the line between activation and destruction is thin. If the furnace permits local overheating, it can cause pore structures to collapse or sinter, drastically reducing the specific surface area. Conversely, insufficient heat fails to initiate the etching required to open efficient transport channels for electrolyte ions.
Equipment Complexity vs. Material Quality
High-precision furnaces represent a significant capital investment compared to standard industrial ovens. However, this equipment is necessary to achieve high-performance metrics, such as increasing specific surface area from ~600 m²/g to nearly 1600 m²/g. For advanced applications, the cost of the furnace is justified by the superior uniformity and capacity of the final activated carbon.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct thermal processing strategy depends on the desired properties of your activated carbon.
- If your primary focus is High Surface Area (Supercapacitors): Prioritize a furnace with programmable ramp rates to carefully control the etching of multilevel pore structures.
- If your primary focus is Product Consistency (Batch Uniformity): Prioritize a rotary tube furnace to ensure dynamic tumbling and eliminate thermal dead spots.
- If your primary focus is Pore Specificity (Adsorption): Prioritize atmosphere control to fine-tune the creation of micropores without uncontrolled oxidation.
Ultimately, the precision of your furnace is the limiting factor in transforming raw carbonized material into a high-value functional product.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Role in Chemical Activation | Benefit to Final Product |
|---|---|---|
| Precise Temp Control | Drives etching between activator (KOH) and carbon | Maximized specific surface area (up to 1600 m²/g) |
| Atmosphere Control | Maintains inert environment (N2) | Prevents carbon oxidation and material loss |
| Uniform Heating | Eliminates thermal gradients/hot spots | Ensures batch consistency and prevents pore collapse |
| Programmable Ramping | Executes segmented heating strategies | Tailors micropore to mesopore distribution ratios |
Elevate Your Material Science with KINTEK Precision
Don't let inconsistent heating compromise your carbon yield. At KINTEK, we understand that the furnace is the heart of your chemical activation process. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer high-precision Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet the rigorous demands of your lab.
Whether you are developing supercapacitors or high-performance adsorbents, our equipment provides the exact thermal and atmosphere control needed to achieve superior pore structures.
Ready to optimize your activation process? Contact us today to discuss your unique needs with our technical specialists.
Visual Guide
References
- João Ferreira, J. C. R. E. Oliveira. High‐Capacity Hybrid Electrode for Seawater Batteries with Bio‐Waste Electrocatalyst. DOI: 10.1002/ente.202501038
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- How does an electric laboratory furnace contribute to the glass melting process? Precision Thermal Solutions
- What are some additional options available for Box Furnaces? Enhance Your Thermal Processing Efficiency
- What advanced features are commonly found in muffle furnaces? Discover Precision Control and Safety Enhancements
- What is the primary role of a muffle furnace in the annealing process of AlCrTiVNbx alloys? Enhance Alloy Strength
- What are the uses of box type electric furnaces in chemical engineering? Unlock Precise Heat Control for Your Lab
- Why is a muffle furnace used without protective gases for molybdenum alloys? Simulate Real-World Oxidation Conditions
- What are some critical 'Don'ts' when operating a muffle furnace? Avoid Explosions and Damage



















