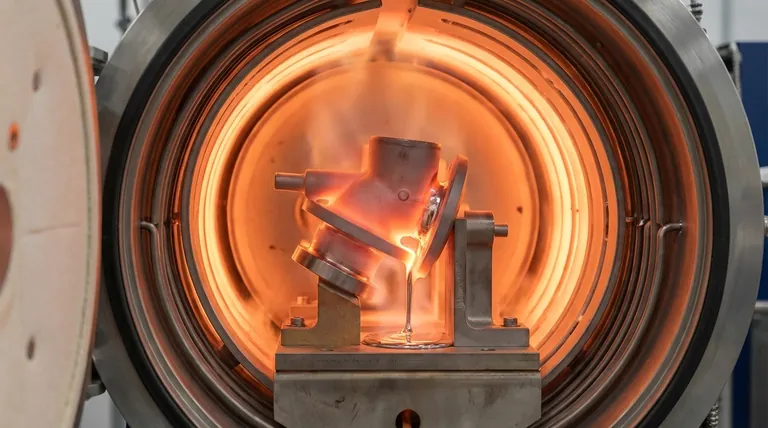
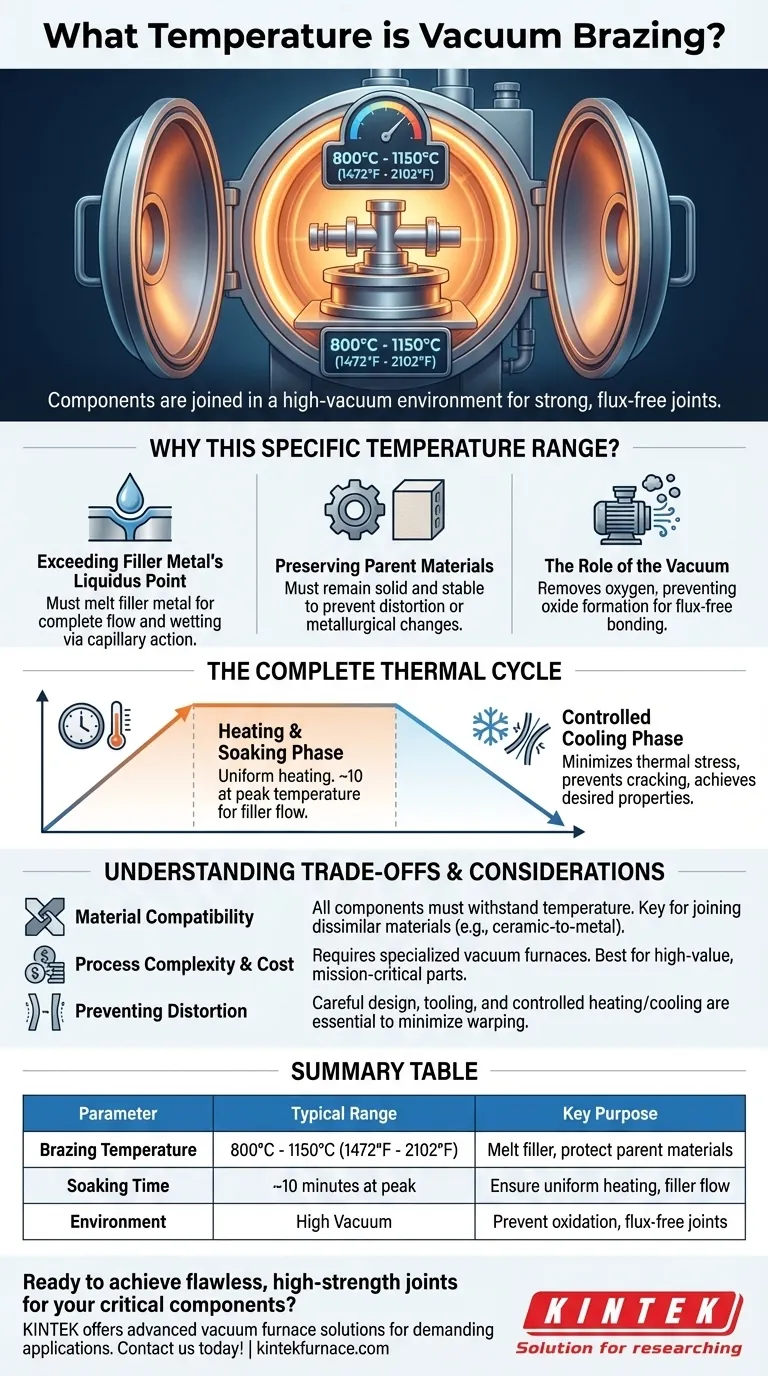
In vacuum brazing, components are joined at temperatures ranging from approximately 800°C to 1150°C (1472°F to 2102°F). This process takes place inside a high-vacuum furnace, which creates an extremely clean environment that allows for strong, flux-free joints between materials.
The specific temperature is not arbitrary; it is carefully selected to exceed the melting point of the brazing filler metal while minimizing thermal damage and unwanted metallurgical changes in the parent materials being joined.

Why This Specific Temperature Range?
The temperature is the most critical parameter in vacuum brazing, but its selection is a careful balance between the needs of the filler metal and the limitations of the parts being joined.
Exceeding the Filler Metal's Liquidus Point
For a proper braze to occur, the filler metal must melt and flow into the joint via capillary action. The chosen temperature must be above the filler's liquidus temperature—the point at which it becomes fully liquid. This ensures complete flow and wetting of the joint surfaces.
Preserving the Parent Materials
While the filler must melt, the parent materials being joined must remain solid and stable. The high end of the brazing temperature is limited by the point at which the parent metals would begin to distort, weaken, or undergo undesirable metallurgical changes. The goal is to heat the assembly just enough to activate the braze alloy without compromising the integrity of the components.
The Role of the Vacuum
Performing this process in a vacuum is essential. The vacuum removes oxygen and other reactive gases, preventing the formation of oxides on the metal surfaces. This cleanliness is what allows the molten filler metal to bond directly with the parent materials without the need for chemical fluxes, resulting in a cleaner and stronger joint.
The Complete Thermal Cycle: More Than Just Peak Temperature
Achieving a successful braze joint involves the entire heating and cooling profile, not just the peak temperature.
The Heating and Soaking Phase
Once the target temperature is reached, the assembly is "soaked" at that temperature for a specific duration, often around 10 minutes. This soaking period ensures the entire assembly reaches a uniform temperature and allows the filler metal sufficient time to flow completely throughout the joint.
The Controlled Cooling Phase
After soaking, the assembly is cooled in a highly controlled manner. The cooling rate is critical for minimizing thermal stress, preventing cracking, and achieving the desired final microstructure and mechanical properties in both the joint and the parent materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
Vacuum brazing is a powerful but demanding process. Its high-temperature nature introduces specific challenges that must be managed.
Material Compatibility
The primary limitation is that all components in the assembly must be able to withstand the required brazing temperature without damage. This is a key design consideration, especially when joining dissimilar materials like ceramics to metals, which have different rates of thermal expansion.
Process Complexity and Cost
Vacuum brazing requires specialized and expensive equipment, including high-quality vacuum furnaces and clean assembly rooms. The process is more complex and time-consuming than other joining methods like welding or soldering, making it best suited for high-value or mission-critical components.
Preventing Distortion
Although vacuum brazing is used to minimize thermal effects, the high temperatures can still cause distortion if not managed properly. This requires careful part design, appropriate tooling and fixtures to support the assembly during the thermal cycle, and precisely controlled heating and cooling rates.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting a joining process depends entirely on your project's specific requirements for performance, materials, and cost.
- If your primary focus is joining dissimilar materials (e.g., ceramic to metal): Vacuum brazing is an excellent choice due to its controlled thermal environment and flux-free process.
- If your primary focus is creating leak-tight, high-strength joints in sensitive alloys (e.g., aerospace parts): The process's ability to minimize distortion and oxidation makes it a superior and often necessary choice.
- If your primary focus is simple, low-cost assembly: Other joining methods like mechanical fastening, soldering, or conventional welding are likely more practical and economical.
Understanding the thermal principles of vacuum brazing empowers you to select the most reliable and effective joining method for your critical components.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Typical Range | Key Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Brazing Temperature | 800°C - 1150°C (1472°F - 2102°F) | Melt filler metal without damaging parent materials |
| Soaking Time | ~10 minutes at peak temperature | Ensure uniform heating and complete filler metal flow |
| Environment | High Vacuum | Prevent oxidation for flux-free, high-strength joints |
Ready to achieve flawless, high-strength joints for your critical components?
At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced vacuum furnace solutions tailored for demanding brazing applications. Whether you're joining dissimilar materials like ceramics to metals or creating leak-tight seals for aerospace parts, our expertise ensures optimal thermal cycles for superior results.
Our high-temperature furnace solutions include:
- Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces for precise, controlled brazing environments.
- Tube & Muffle Furnaces for R&D and specialized processes.
- Strong Deep Customization to meet your unique experimental and production requirements.
Contact us today to discuss how our vacuum brazing solutions can enhance your product quality and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does the ultra-low oxygen environment of vacuum sintering affect titanium composites? Unlock Advanced Phase Control
- What tasks does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace perform for PEM magnets? Achieve Peak Density
- What is the purpose of a 1400°C heat treatment for porous tungsten? Essential Steps for Structural Reinforcement
- Why is a vacuum environment essential for sintering Titanium? Ensure High Purity and Eliminate Brittleness
- What is the role of vacuum pumps in a vacuum heat treatment furnace? Unlock Superior Metallurgy with Controlled Environments



















