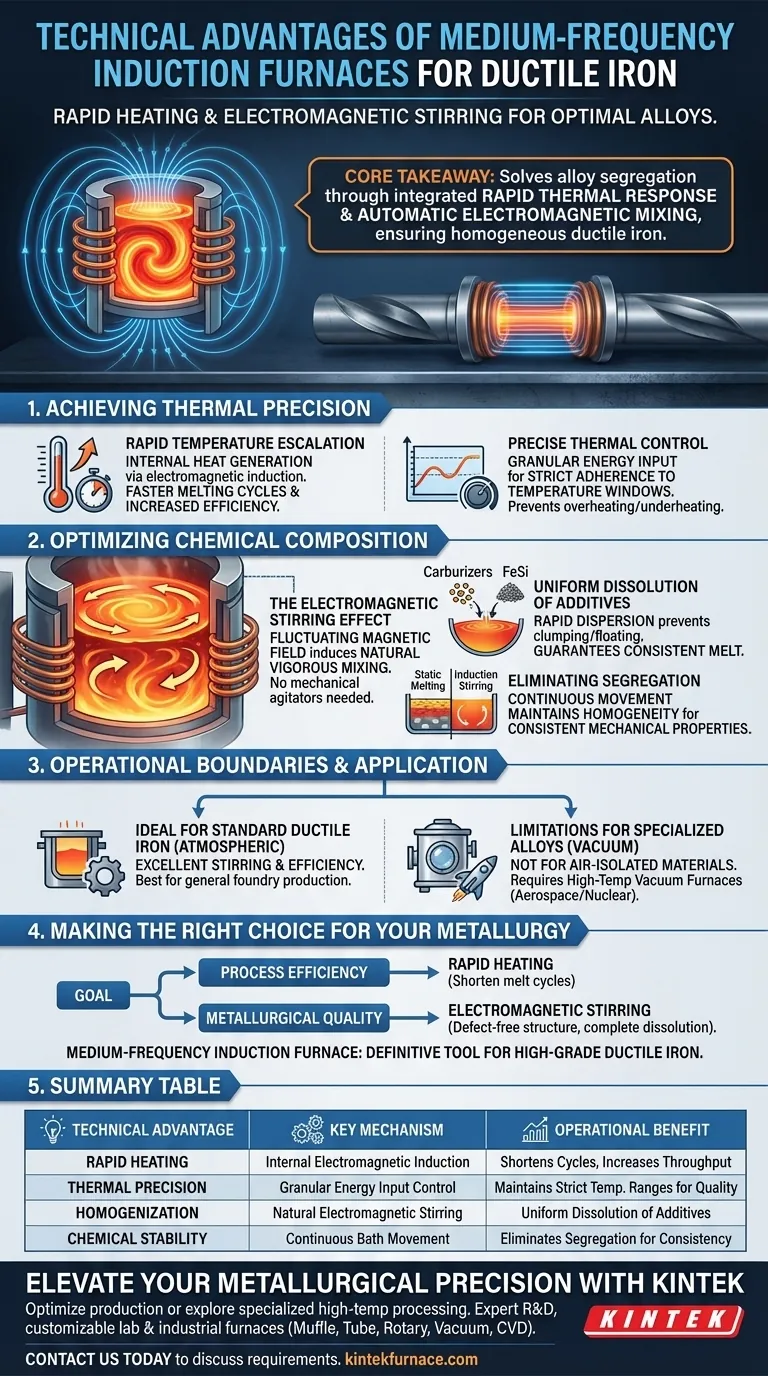
The primary technical advantage of medium-frequency induction furnaces in ductile iron production is the combination of rapid heating and inherent electromagnetic stirring. These furnaces utilize electromagnetic induction to generate heat directly within the metal, enabling fast temperature increases and precise thermal regulation. Crucially, the natural stirring effect ensures the rapid and uniform dissolution of essential additives like carburizers and ferrosilicon (FeSi), guaranteeing a chemically consistent melt.
Core Takeaway By integrating rapid thermal response with automatic electromagnetic mixing, medium-frequency induction furnaces solve the problem of alloy segregation. This technology ensures that critical additives are distributed evenly, resulting in a homogenous chemical composition essential for high-quality ductile iron.
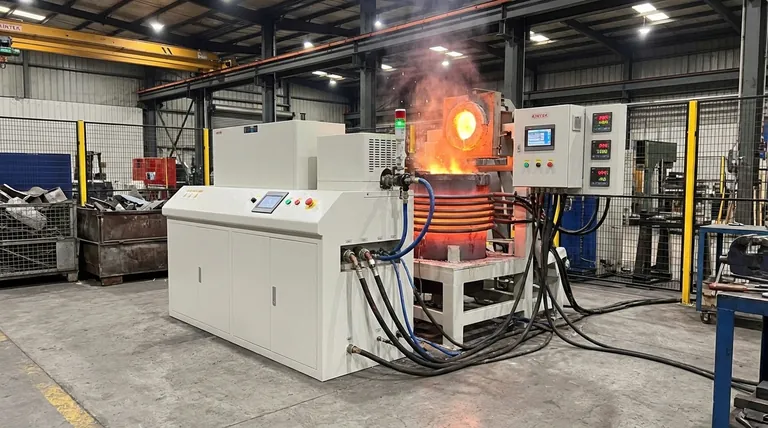

Achieving Thermal Precision
Rapid Temperature Escalation
Medium-frequency induction furnaces do not rely on external heat sources that must penetrate the charge. Instead, they use electromagnetic induction to generate heat internally.
This mechanism allows for significantly faster melting cycles. Operators can bring the iron to the required temperature quickly, improving overall production efficiency.
Precise Thermal Control
Ductile iron production requires strict adherence to specific temperature ranges to maintain metallurgical quality.
These furnaces provide granular control over energy input. This allows for precise thermal regulation, ensuring the melt stays exactly within the target window without overheating or underheating.
Optimizing Chemical Composition
The Electromagnetic Stirring Effect
One of the most distinct advantages of this technology is the electromagnetic stirring effect.
As the magnetic field fluctuates, it induces movement within the molten bath. This creates a natural, vigorous mixing action without the need for mechanical agitators or manual interference.
Uniform Dissolution of Additives
Preparing ductile iron involves the introduction of specific additives, such as carburizers and ferrosilicon (FeSi).
The inherent stirring action ensures these materials dissolve rapidly into the melt. This prevents the additives from clumping or floating, ensuring that every part of the batch has the exact same chemical makeup.
Eliminating Segregation
In static melting environments, heavier elements may sink while lighter ones float.
The continuous movement provided by the induction furnace maintains a highly uniform chemical composition. This homogeneity is critical for achieving the consistent mechanical properties required in ductile iron castings.
Understanding the Operational Boundaries
Limitations for Specialized Alloys
While medium-frequency induction furnaces are ideal for ductile iron, they typically operate under atmospheric conditions.
They are generally not suitable for alloys that require absolute isolation from air. For special alloys with unique physical and chemical properties—such as those used in aerospace and nuclear industries—high-temperature vacuum furnaces are the required standard.
The Scope of Application
It is important to select the furnace based on the end-use of the metal.
If the goal is standard ductile iron production, the induction furnace is superior due to its stirring capabilities. If the goal is ultra-pure reactive alloys, the technology discussed here (induction) is likely insufficient compared to vacuum processing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Metallurgy
To maximize the quality of your ductile iron production, align your furnace choice with your specific processing goals:
- If your primary focus is process efficiency: Leverage the rapid temperature increase capabilities to shorten melt cycles and increase throughput.
- If your primary focus is metallurgical quality: Rely on the electromagnetic stirring effect to ensure the complete dissolution of FeSi and carburizers for a defect-free structure.
Ultimately, the medium-frequency induction furnace is the definitive tool for converting raw materials into chemically precise, high-grade ductile iron.
Summary Table:
| Technical Advantage | Key Mechanism | Operational Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Rapid Heating | Internal electromagnetic induction | Shortens melt cycles and increases throughput |
| Thermal Precision | Granular energy input control | Maintains strict temperature ranges for metallurgical quality |
| Homogenization | Natural electromagnetic stirring | Ensures uniform dissolution of carburizers and ferrosilicon |
| Chemical Stability | Continuous bath movement | Eliminates alloy segregation for consistent mechanical properties |
Elevate Your Metallurgical Precision with KINTEK
Are you looking to optimize your ductile iron production or explore specialized high-temp processing? Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, as well as advanced lab high-temp furnaces—all fully customizable to meet your unique metallurgical needs.
Whether you require the rapid stirring of an induction process or the absolute purity of a vacuum environment, our technical team is ready to provide the perfect solution for your lab or foundry. Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and see how our expertise can enhance your material quality.
Visual Guide
References
- Anna Regordosa, Jacques Lacaze. Shrinkage Defect in Thermal Analysis Cups of Low and High-Silicon Spheroidal Graphite Cast Irons. DOI: 10.1007/s40962-025-01731-3
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Magnesium Extraction and Purification Condensing Tube Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering and Brazing Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the primary advantages of IGBT induction melting furnaces? Boost Efficiency & Quality
- What is the function of a cold crucible in high-entropy alloys? Ensure High Purity for Reactive Metals
- What is the function of a non-consumable vacuum arc furnace for CoCrFeNiZr0.3 alloys? High-Purity Melting Solutions
- What factors should be considered when selecting an induction melting furnace for a business? Maximize Efficiency and ROI
- What is the function of a Vacuum Arc Melting Furnace? Prepare High-Purity CoCuMoNi Alloys with Precision
- What is the function of a vacuum induction furnace with cold copper crucible in Ti-5Al-2.5Sn alloy preparation?
- What is the role of a vacuum arc furnace in the synthesis of AlCrFeNi HEAs? Achieve High-Purity Material Homogeneity
- What factors should be considered when selecting a crucible for an induction-heated vacuum furnace? Ensure High-Purity Melts and Efficiency



















