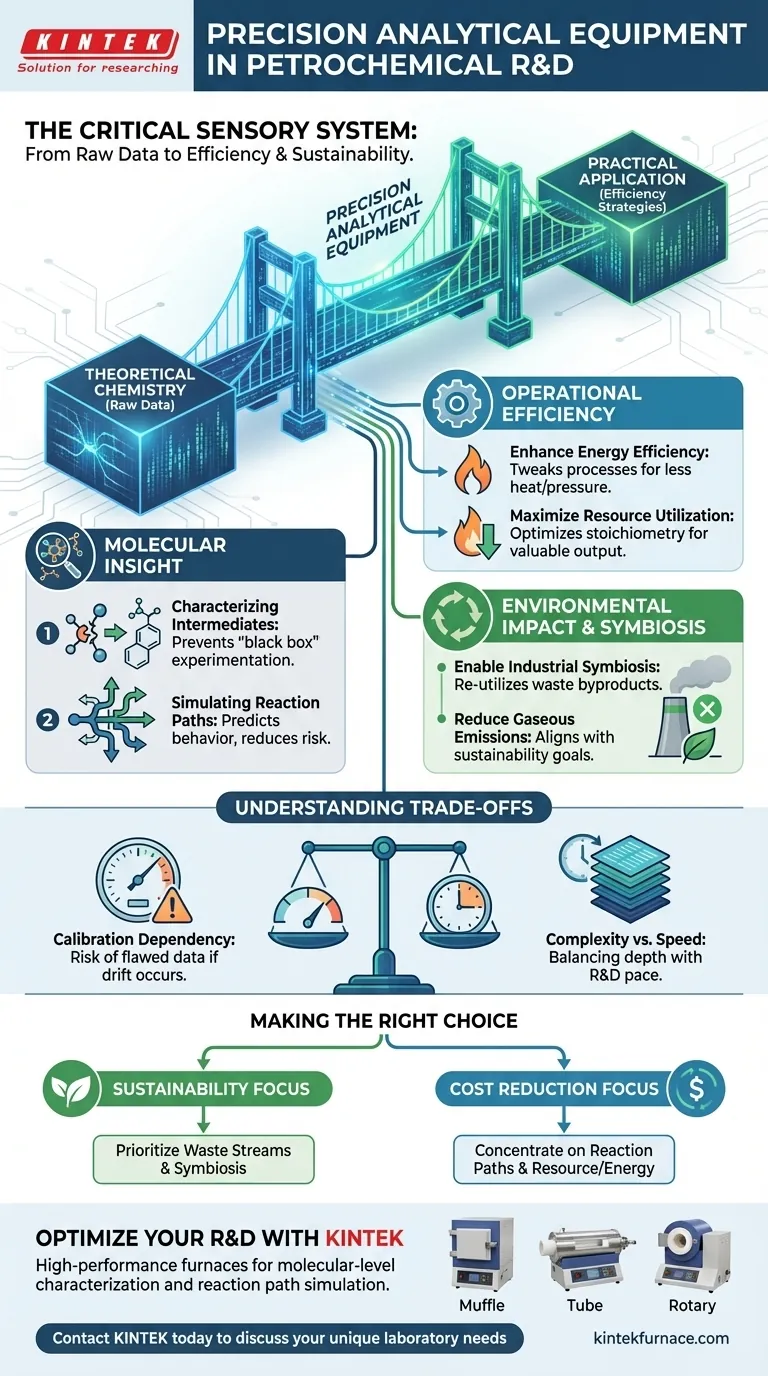
Precision analytical equipment functions as the critical sensory system for petrochemical research and development. By enabling the molecular-level characterization of chemical intermediates, these instruments allow scientists to accurately simulate complex reaction paths. This deep visibility provides the necessary experimental basis to refine processes before they are deployed at an industrial scale.
The core value of this equipment lies in transforming raw chemical data into actionable efficiency strategies. It bridges the gap between theoretical chemistry and practical application, serving as the primary driver for improved resource utilization, energy efficiency, and emission reduction.
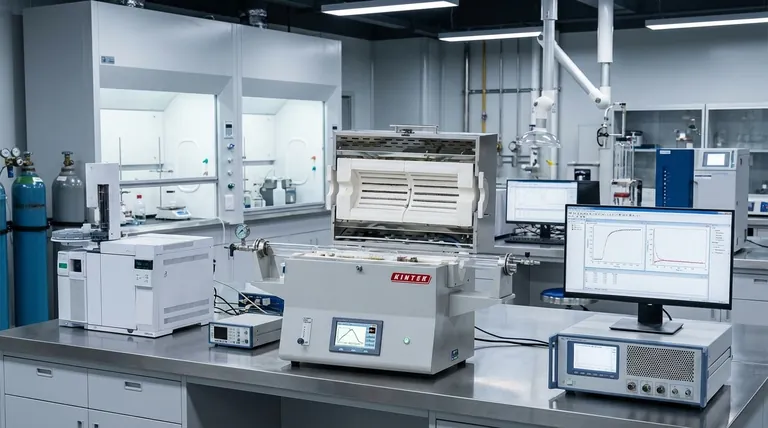

The Mechanics of Molecular Insight
Characterizing Chemical Intermediates
The primary role of precision equipment is to identify and analyze chemical intermediates—the temporary compounds formed during a reaction steps before the final product creates itself.
By characterizing these molecules at a granular level, researchers gain a complete picture of the chemical transformation. This prevents "black box" experimentation, where only inputs and outputs are understood.
Simulating Complex Reaction Paths
Modern petrochemical processes involve intricate webs of chemical interactions.
High-precision instruments allow R&D teams to simulate these complex reaction paths in a controlled environment. This modeling capability is essential for predicting how a process will behave under various conditions without the risk and cost of full-scale testing.
Driving Operational Efficiency
Enhancing Energy Efficiency
Data derived from analytical equipment reveals the precise energy requirements of specific reaction stages.
By understanding the exact molecular dynamics, engineers can tweak processes to require less heat or pressure. This directly supports the goal of enhancing energy efficiency, a critical metric for operational viability.
Maximizing Resource Utilization
Precision analysis identifies where raw materials are being wasted or converted into unwanted byproducts.
This "experimental basis" allows for the optimization of stoichiometry—the ratio of reactants—ensuring that resource utilization is maximized. The goal is to ensure every molecule of input contributes to a valuable output.
Environmental Impact and Industrial Symbiosis
Enabling Industrial Symbiosis
A key application of this technology is fostering industrial symbiosis, where the waste or byproducts of one process become the inputs for another.
Analytical equipment determines the composition of waste streams with high accuracy. This data confirms whether a byproduct is pure enough to be re-utilized elsewhere, closing the production loop.
Reducing Gaseous Emissions
Through the optimization of reaction paths and the enabling of symbiotic processes, the net result is a significant reduction in waste.
Specifically, this leads to a measurable reduction in gaseous emissions, aligning industrial petrochemical activities with stricter environmental standards and sustainability goals.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Dependency on Calibration
While precision equipment provides vital data, it introduces a heavy reliance on instrument calibration and maintenance.
If the "experimental basis" is flawed due to minor instrument drift, the resulting simulations of reaction paths will be incorrect. This can lead to process designs that work in the lab but fail to deliver efficiency at scale.
Complexity vs. Speed
There is often a tension between the depth of molecular-level characterization and the speed of R&D cycles.
Obtaining high-fidelity data on every chemical intermediate takes time and computational resources. Teams must balance the need for perfect data against the commercial pressure to move new processes to market quickly.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goals
To leverage precision analytical equipment effectively, align your analysis strategy with your primary objective:
- If your primary focus is Sustainability: Prioritize the characterization of waste streams to identify opportunities for industrial symbiosis and emission reduction.
- If your primary focus is Cost Reduction: Concentrate on simulating reaction paths to maximize resource utilization and minimize energy consumption.
Precision analysis is not just about observing chemistry; it is the fundamental tool for engineering cleaner, more efficient industrial systems.
Summary Table:
| Key Role | Impact on R&D | Strategic Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Molecular Characterization | Identifies chemical intermediates and temporary compounds. | Prevents "black box" experimentation; ensures process transparency. |
| Reaction Simulation | Models complex paths in controlled environments. | Predicts industrial-scale behavior without high-cost risks. |
| Efficiency Optimization | Maps exact heat/pressure needs and stoichiometric ratios. | Enhances energy efficiency and maximizes resource utilization. |
| Environmental Monitoring | Analyzes waste streams and byproduct purity. | Reduces gaseous emissions and enables industrial symbiosis. |
Optimize Your Petrochemical R&D with KINTEK
Precision in research requires precision in hardware. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to provide the stable thermal environments necessary for molecular-level characterization and reaction path simulation.
Whether you are a researcher focused on maximizing resource utilization or an industrial engineer targeting emission reduction, our customizable lab high-temp furnaces ensure your experimental basis is flawless.
Ready to bridge the gap between theoretical chemistry and practical efficiency? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your unique laboratory needs
Visual Guide
References
- Galymzhan Usenov, Sadilbek Akylbayevich Ussenov. The Chemical and Petrochemical Industry of Kazakhstan: History, Challenges, and Future Prospects. DOI: 10.11590/icon.2025.1.05
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of zirconia crowns? Achieve Durable, Aesthetic, and Biocompatible Dental Restorations
- What are the core advantages of using a microwave sintering furnace? Unlock Precision in Al2O3/TiC Ceramics
- What is Skin Depth and how does it affect induction heating? Master Frequency Control for Precise Heat
- What is the technical objective of preheating the extrusion cylinder and molds to 460 ℃? Optimize Quality & Flow
- How do magnesium impurities influence lithium extraction? Accelerate Production with Heterogeneous Nucleation
- What is the purpose of a safety warning system in MDR? Ensure Reactor Integrity and Laboratory Safety
- What are the two methods of temperature control of resistance furnace? Optimize for Precision or Cost
- How do surface states affect lithium carbonate crystal morphology? Controlling Nucleation for Superior Particle Shape



















