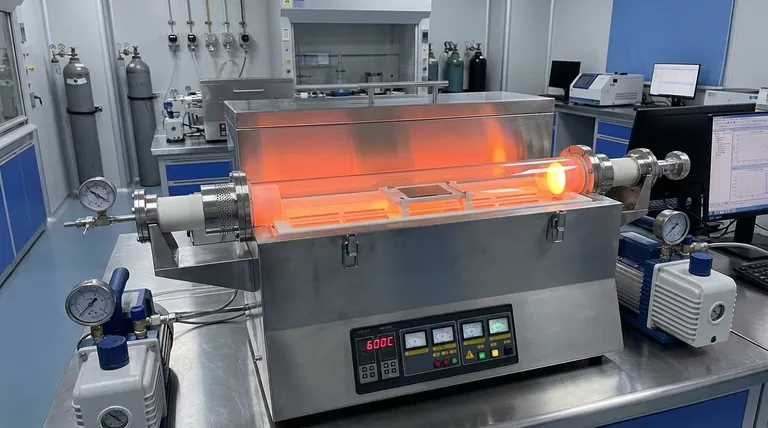
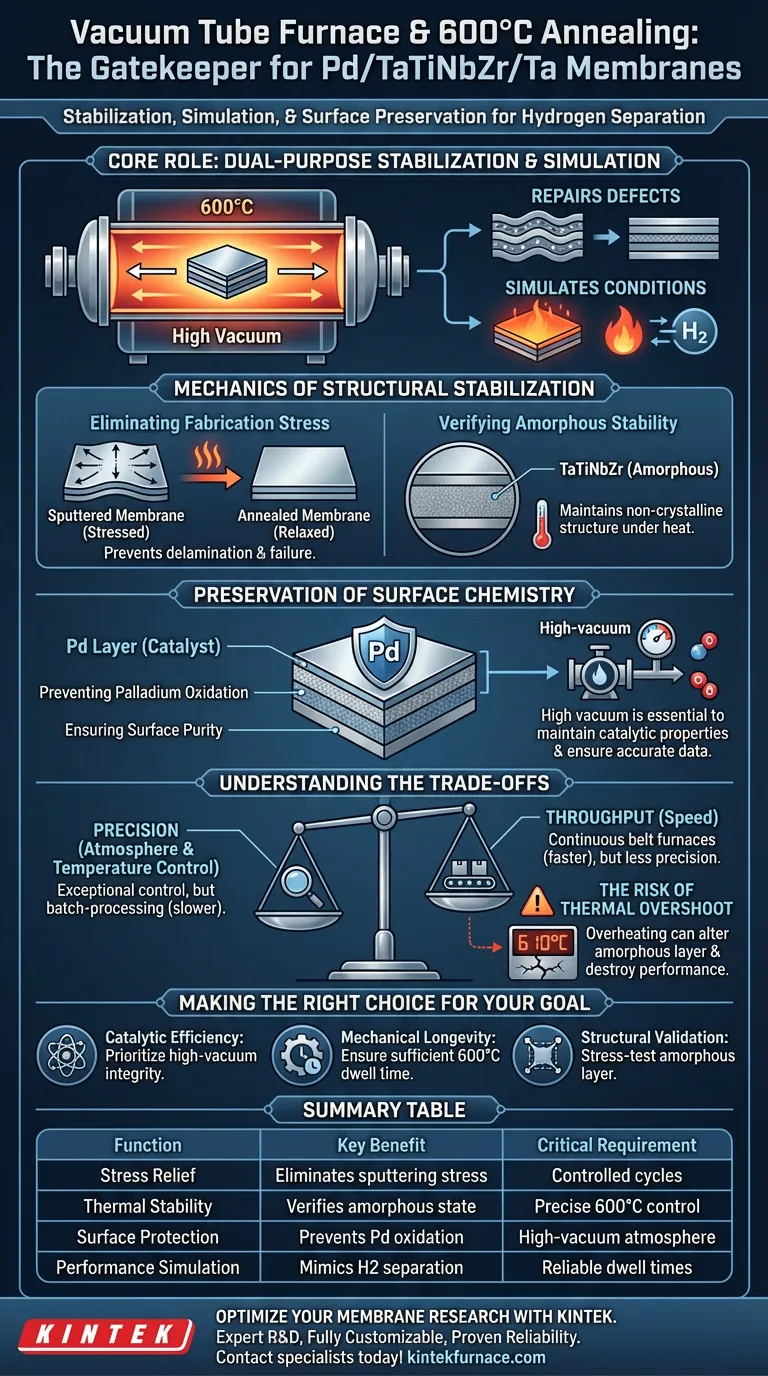
The vacuum tube furnace functions as a specialized stabilization and simulation chamber for Pd/TaTiNbZr/Ta multilayer membranes. At 600°C, its primary role is to eliminate internal stresses caused by sputtering, verify the thermal stability of the amorphous core, and protect the catalytic palladium surface from oxidation.
Core Takeaway The annealing process is a dual-purpose step that repairs mechanical defects introduced during fabrication while simulating the harsh, high-temperature conditions of hydrogen separation. Success relies on the furnace's ability to maintain a high vacuum to preserve the palladium's catalytic properties.

Mechanics of Structural Stabilization
Eliminating Fabrication Stress
During the initial manufacturing phase, processes like sputtering introduce significant internal stresses into the metal layers.
The vacuum tube furnace provides a thermal environment that allows these stresses to relax. This annealing step prevents potential delamination or mechanical failure when the membrane is later subjected to operational pressures.
Simulating Operational Conditions
Beyond simple stress relief, the furnace creates an environment that mimics the actual operating conditions of hydrogen separation membranes.
By exposing the membrane to 600°C, researchers can verify the material's performance limits before active deployment. This ensures the membrane can withstand the thermal rigors of real-world hydrogen separation without degrading.
Verifying Amorphous Stability
A critical function of this specific setup is verifying the structural stability of the TaTiNbZr layer.
This layer is amorphous (non-crystalline), and the high-temperature exposure confirms whether it can maintain this necessary structure under heat without undergoing unwanted crystallization or structural collapse.
Preservation of Surface Chemistry
Preventing Palladium Oxidation
The top layer of the membrane consists of palladium (Pd), which serves as a catalyst for hydrogen separation.
The high-vacuum environment of the tube furnace is essential to prevent oxygen from interacting with the Pd layer. Even minor oxidation at these temperatures would degrade the palladium's catalytic activity, rendering the membrane ineffective for hydrogen transport.
Ensuring Surface Purity
By maintaining a contaminant-free atmosphere, the furnace ensures the surface remains chemically active.
This pristine state is required to obtain accurate data during subsequent performance testing, ensuring that any measured limitations are due to the membrane's intrinsic properties, not surface impurities.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Precision vs. Throughput
While vacuum tube furnaces offer exceptional control over atmosphere and temperature, they are generally batch-processing tools.
The requirement for high-vacuum pumping and precise heating cycles (often requiring hours to stabilize) limits the speed of processing compared to continuous belt furnaces.
The Risk of Thermal Overshoot
Precise temperature control is paramount; if the furnace exceeds the target 600°C, it risks altering the amorphous nature of the TaTiNbZr layer.
Accidental overheating can induce unwanted phase transformations or interdiffusion between layers, destroying the membrane's specific separation characteristics.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of your annealing process, align your furnace parameters with your specific objective:
- If your primary focus is Catalytic Efficiency: Prioritize high-vacuum integrity to ensure zero oxidation of the Palladium (Pd) layer.
- If your primary focus is Mechanical Longevity: Ensure the dwell time at 600°C is sufficient to fully resolve internal sputtering stresses.
- If your primary focus is Structural Validation: Use the heating cycle to stress-test the TaTiNbZr layer, confirming it remains amorphous under operational thermal loads.
The vacuum tube furnace is the gatekeeper that transforms a delicate sputtered composite into a robust, operationally ready hydrogen separation membrane.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Benefit | Critical Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| Stress Relief | Eliminates sputtering-induced internal stress | Controlled heating/cooling cycles |
| Thermal Stability | Verifies amorphous state of TaTiNbZr core | Precise 600°C temperature control |
| Surface Protection | Prevents palladium (Pd) oxidation | High-vacuum atmosphere |
| Performance Simulation | Mimics hydrogen separation environments | Reliable thermal dwell times |
Optimize Your Membrane Research with KINTEK
Precise thermal processing is the difference between a high-performance membrane and a failed experiment. KINTEK provides industry-leading Vacuum, Tube, and CVD systems engineered for the exact requirements of material science R&D. Our lab high-temperature furnaces ensure the atmospheric purity and temperature stability necessary to protect catalytic surfaces like Palladium and maintain amorphous structural integrity.
Why choose KINTEK?
- Expert R&D & Manufacturing: Solutions tailored for advanced multilayer membrane fabrication.
- Fully Customizable: Furnaces designed to meet your specific vacuum levels and thermal profiles.
- Proven Reliability: Backed by technical expertise in high-temperature simulation.
Ready to enhance your lab's efficiency and research accuracy? Contact our specialists today to find your perfect furnace solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Haoxin Sun, Guo Pu. Improved High-Temperature Stability and Hydrogen Penetration through a Pd/Ta Composite Membrane with a TaTiNbZr Intermediate Layer. DOI: 10.3390/coatings14030370
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a tube furnace in biochar production? Transform Waste Diaper Fibers with Precision
- What role does a dual-zone tube furnace play in the synthesis of large-scale Janus RhSeCl single crystals?
- What role does a high-temperature tube furnace play in flash annealing Mg/SiOx? Precision for Advanced Anode Synthesis
- What is the specific purpose of tilting a tube resistance furnace during synthesis? Maximize Yield & Crystal Quality
- Why is a high-temperature tubular furnace required for the activation process of walnut shell activated carbon at 700°C?
- What is the role of programmed temperature control in a tube furnace? Optimize N-GC-X Catalyst Synthesis
- What is the primary purpose of using a tube reduction furnace? Achieve High-Purity Fe-Cu Sintering
- What are the common applications of a horizontal tube furnace? Unlock Precision in High-Temperature Processing



















