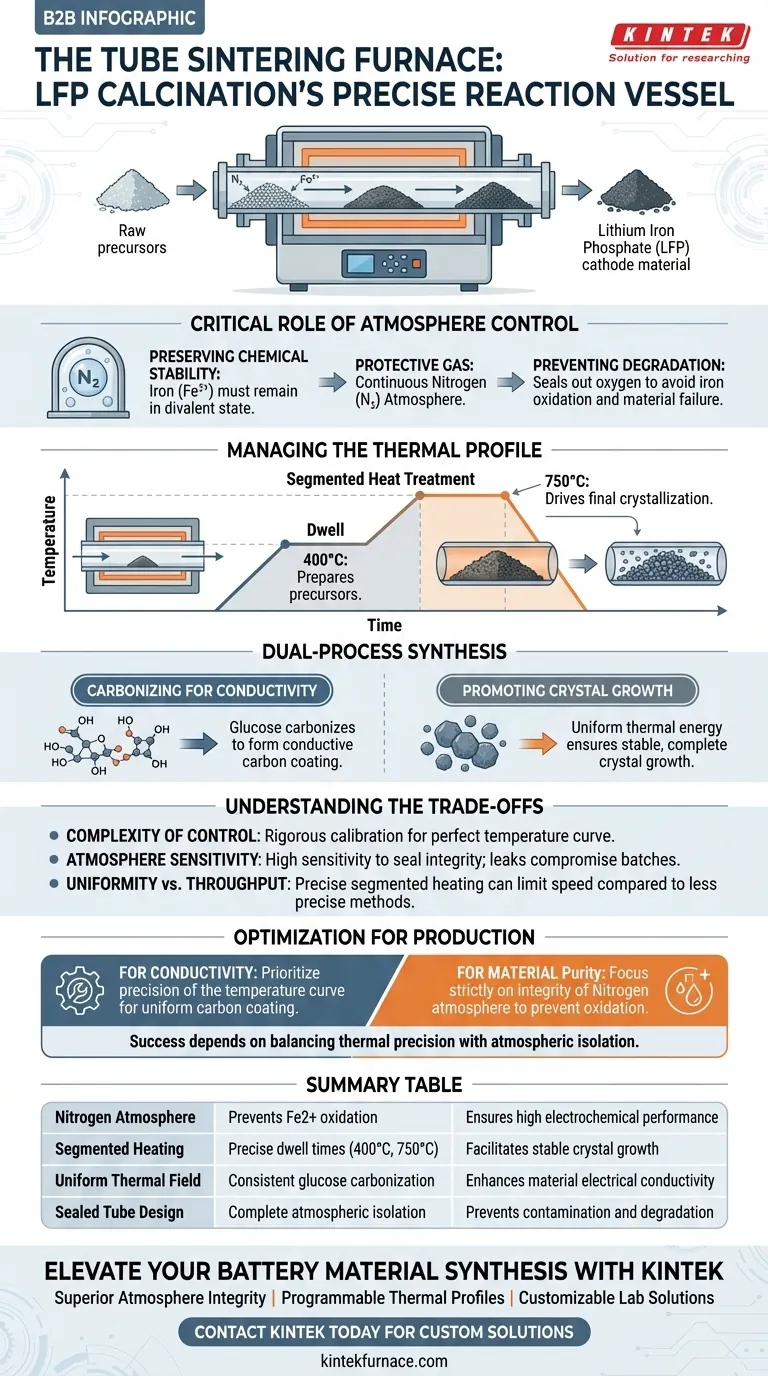
The tube sintering furnace serves as the precise reaction vessel required to transform raw precursors into stable Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) cathode material. Its role is to provide a strictly controlled thermal environment that prevents chemical degradation while simultaneously facilitating the physical restructuring of the material.
The furnace's primary function is to maintain a protective nitrogen atmosphere while executing a complex, segmented heating profile. This specific environment is non-negotiable for preventing iron oxidation and ensuring the simultaneous formation of a conductive carbon coating and a stable crystal structure.

The Critical Role of Atmosphere Control
Preserving Chemical Stability
The most significant risk during LFP calcination is the oxidation of iron. The iron component in Lithium Iron Phosphate must remain in a divalent state ($Fe^{2+}$).
Utilizing Protective Gas
To maintain this state, the tube furnace utilizes a continuous Nitrogen ($N_2$) protective atmosphere.
Preventing Degradation
Without this sealed, inert environment, oxygen would react with the iron. This would degrade the material's electrochemical performance before the battery is even built.
Managing the Thermal Profile
Segmented Heat Treatment
The calcination of LFP is not a simple linear heating process. The tube furnace enables "segmented" heat treatment, allowing the material to dwell at specific temperatures to achieve distinct chemical goals.
The Low-Temperature Stage
The process typically involves a stage around 400°C. This stage is critical for preparing the precursors for the final reaction without shocking the material.
The High-Temperature Stage
A subsequent stage occurs around 750°C. This higher temperature is necessary to drive the final crystallization of the Lithium Iron Phosphate structure.
Dual-Process Synthesis
Carbonizing for Conductivity
LFP by itself has poor electrical conductivity. To solve this, glucose is often added to the raw mix.
Creating the Carbon Coating
During the heat treatment in the furnace, this glucose carbonizes. Because the furnace creates a uniform thermal environment, the glucose forms a consistent, conductive carbon coating over the particles.
Promoting Crystal Growth
Simultaneously, the thermal energy promotes the complete growth of LFP crystals. The furnace ensures this growth is uniform, resulting in a stable and reliable cathode material.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Complexity of Control
The versatility of a tube furnace comes with increased operational complexity. Achieving the perfect "temperature curve" requires rigorous calibration.
Atmosphere Sensitivity
The system is highly sensitive to seal integrity. Even a minor failure in the Nitrogen supply or a leak in the tube can compromise the entire batch by allowing oxidation.
Uniformity vs. Throughput
While tube furnaces offer exceptional control for uniformity, managing the distinct temperature segments (400°C vs. 750°C) can limit throughput speed compared to less precise methods.
Optimization for Production
To maximize the effectiveness of your calcination process, align your furnace settings with your specific material goals:
- If your primary focus is conductivity: Prioritize the precision of the temperature curve to ensure glucose carbonizes into a perfectly uniform coating.
- If your primary focus is material purity: Focus strictly on the integrity of the Nitrogen atmosphere to prevent the oxidation of divalent iron.
Success in LFP calcination depends entirely on the furnace’s ability to balance thermal precision with atmospheric isolation.
Summary Table:
| Process Component | Role in LFP Calcination | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen Atmosphere | Prevents iron oxidation ($Fe^{2+}$ state) | Ensures high electrochemical performance |
| Segmented Heating | Precise dwell times at 400°C and 750°C | Facilitates stable crystal growth |
| Uniform Thermal Field | Consistent glucose carbonization | Enhances material electrical conductivity |
| Sealed Tube Design | Complete atmospheric isolation | Prevents batch contamination and degradation |
Elevate Your Battery Material Synthesis with KINTEK
Precise thermal processing is the backbone of high-performance Lithium Iron Phosphate production. KINTEK provides industry-leading Tube, Muffle, Rotary, and Vacuum systems designed specifically for the rigorous demands of battery research and manufacturing.
Our furnaces offer:
- Superior Atmosphere Integrity: Advanced sealing technology for perfect Nitrogen/Inert environments.
- Programmable Thermal Profiles: Easy management of complex, multi-stage calcination curves.
- Customizable Lab Solutions: Tailored configurations for CVD and high-temperature material synthesis.
Contact KINTEK Today to consult with our experts on a customizable furnace solution that ensures your materials achieve peak purity and conductivity.
Visual Guide
References
- Gongsheng Zou, Bin Wu. Crystal structure, morphology, and electrical properties of aluminum-doped LFP materials. DOI: 10.1007/s11581-024-05489-2
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What role does a horizontal tube furnace play in the carbonization of SiC-C preforms? Optimize Material Structural Yield
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- Why is a laboratory tube furnace required for the phosphidation process? Master Precision Material Synthesis
- How do vertical tube furnaces contribute to advancements in material science and industrial production? Unlock Precision in Material Innovation
- How do vacuum tube furnaces achieve energy efficiency? Maximize Thermal Performance and Cut Costs
- What role does a Vertical Tube Furnace play in ferronickel reduction smelting? Expert Process Simulation
- What are some common applications of horizontal electric furnaces? Unlock Precision in Thermal Processing
- Why is a high-temperature tube furnace required for LK-99 sintering? Achieve Precise Superconductor Phase Transformation



















