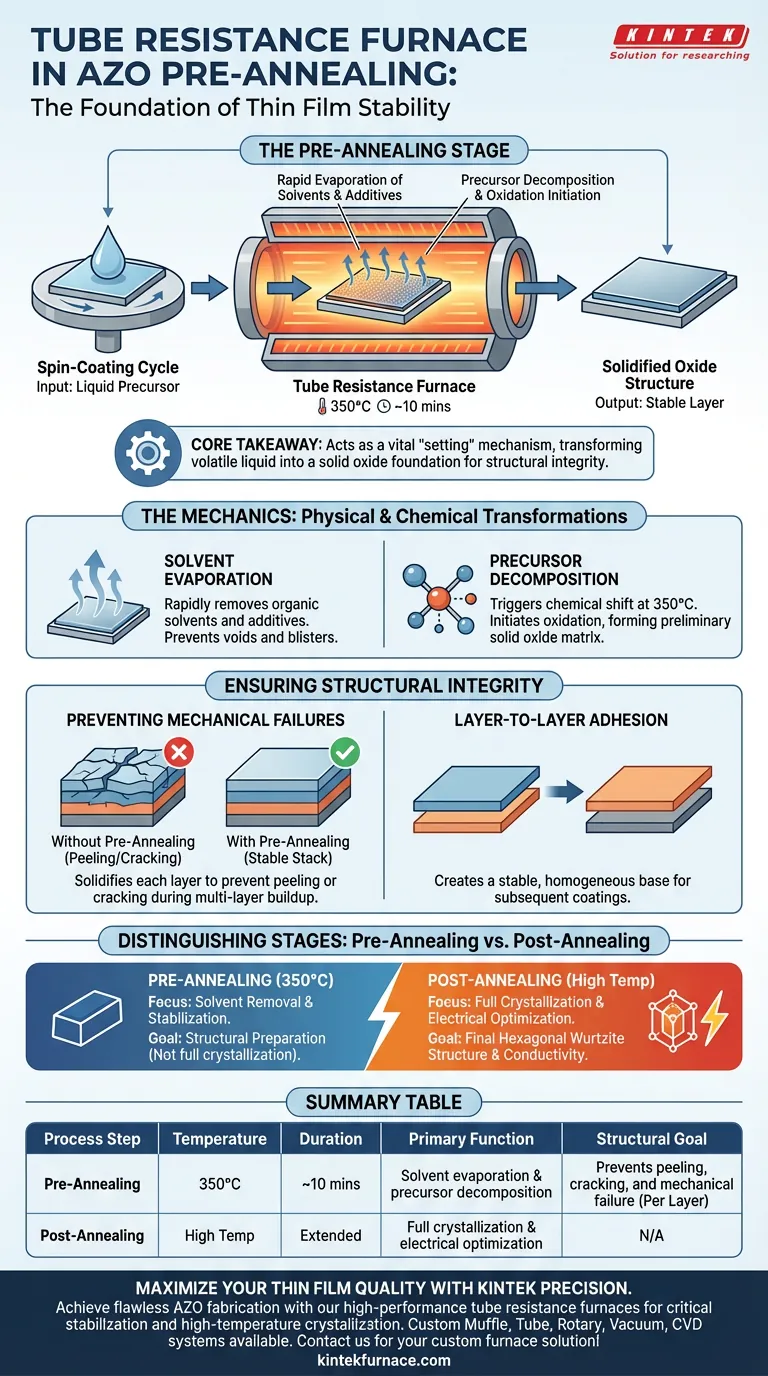
In the pre-annealing stage of Al-doped ZnO (AZO) production, a tube resistance furnace serves as a critical stabilization tool, applying a controlled thermal treatment at 350°C for approximately 10 minutes following each spin-coating cycle. Its primary function is to drive the rapid evaporation of organic solvents and additives while initiating the decomposition and oxidation of the precursor materials. By converting the film from a liquid state to a solid oxide structure, the furnace ensures the layer is mechanically stable enough to support subsequent coatings without peeling or cracking.
Core Takeaway The tube resistance furnace acts as a vital "setting" mechanism during the layering process, transforming the volatile liquid precursor into a solid oxide foundation. This step is not about final crystallization, but about ensuring structural integrity and preventing defects during multi-layer accumulation.
The Mechanics of Pre-Annealing
To understand the necessity of this equipment, one must look at the physical and chemical transformations occurring within the furnace.
Solvent Evaporation and Removal
The initial spin-coated layer is rich in organic solvents and additives. The tube resistance furnace provides a stable thermal environment that rapidly removes these volatiles.
Failure to remove these solvents effectively would result in voids or blisters in the final film.
Precursor Decomposition
Beyond simple drying, the 350°C environment triggers a chemical shift. The heat initiates the decomposition of the chemical precursors used in the AZO solution.
This begins the oxidation process, transitioning the material from a purely chemical solution into a preliminary solid oxide matrix.
Ensuring Structural Integrity
The most practical role of the tube resistance furnace is preserving the physical quality of the film during multi-step fabrication.
Preventing Mechanical Failures
AZO films are often built up through multiple spin-coating cycles to achieve the desired thickness. Without this intermediate heating stage, adding a new wet layer onto a semi-dry layer would cause stress.
The furnace solidifies the layer, effectively preventing peeling or cracking that typically occurs when stacking multiple thin films.
Layer-to-Layer Adhesion
By solidifying each layer individually, the furnace ensures a stable base for the next coating. This stepwise solidification creates a homogeneous stack rather than a mix of wet and dry interfaces.
Distinguishing Pre-Annealing from Final Annealing
It is critical to distinguish the role of the furnace in this pre-annealing stage versus its role in final post-annealing.
The Pre-Annealing Limit (350°C)
The pre-annealing process described here (at 350°C) is focused on solvent removal and stabilization. It creates a solid structure, but it does not fully maximize the crystalline quality.
The Post-Annealing Contrast (High Temperature)
While the primary focus here is pre-annealing, note that a tube furnace is also used later at higher temperatures. That separate process is responsible for full crystallization into the hexagonal wurtzite structure and eliminating oxygen vacancies.
Do not expect the pre-annealing step to achieve the final electrical conductivity or crystal quality; its job is purely structural preparation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The use of a tube resistance furnace is dictated by the specific phase of film fabrication you are currently executing.
- If your primary focus is Layer Accumulation: Prioritize stability. Use the furnace at 350°C to remove solvents and prevent cracking between spin cycles.
- If your primary focus is Electrical Performance: Understand that pre-annealing is only the preparation; you will require a subsequent high-temperature cycle to fully crystallize the AZO and optimize conductivity.
Success in AZO fabrication relies on using the furnace first to build a defect-free structure, and second to refine that structure's properties.
Summary Table:
| Process Step | Temperature | Duration | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Annealing | 350°C | ~10 mins | Solvent evaporation & precursor decomposition |
| Structural Goal | N/A | Per Layer | Prevents peeling, cracking, and mechanical failure |
| Post-Annealing | High Temp | Extended | Full crystallization & electrical optimization |
Maximize Your Thin Film Quality with KINTEK Precision
Achieve flawless AZO fabrication with KINTEK’s high-performance tube resistance furnaces. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we provide the precise thermal stability required for both critical pre-annealing stabilization and high-temperature crystallization.
Whether you need Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, or CVD systems, our lab furnaces are fully customizable to meet your unique thin-film research and production needs.
Ready to eliminate film defects and enhance structural integrity? Contact us today to find your custom furnace solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Alberto Giribaldi, Paolo Mele. Enhancing Thermoelectric Performance: The Impact of Carbon Incorporation in Spin-Coated Al-Doped ZnO Thin Films. DOI: 10.3390/coatings15010107
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How do vertical tube furnaces comply with environmental standards? A Guide to Clean, Efficient Operation
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents



















