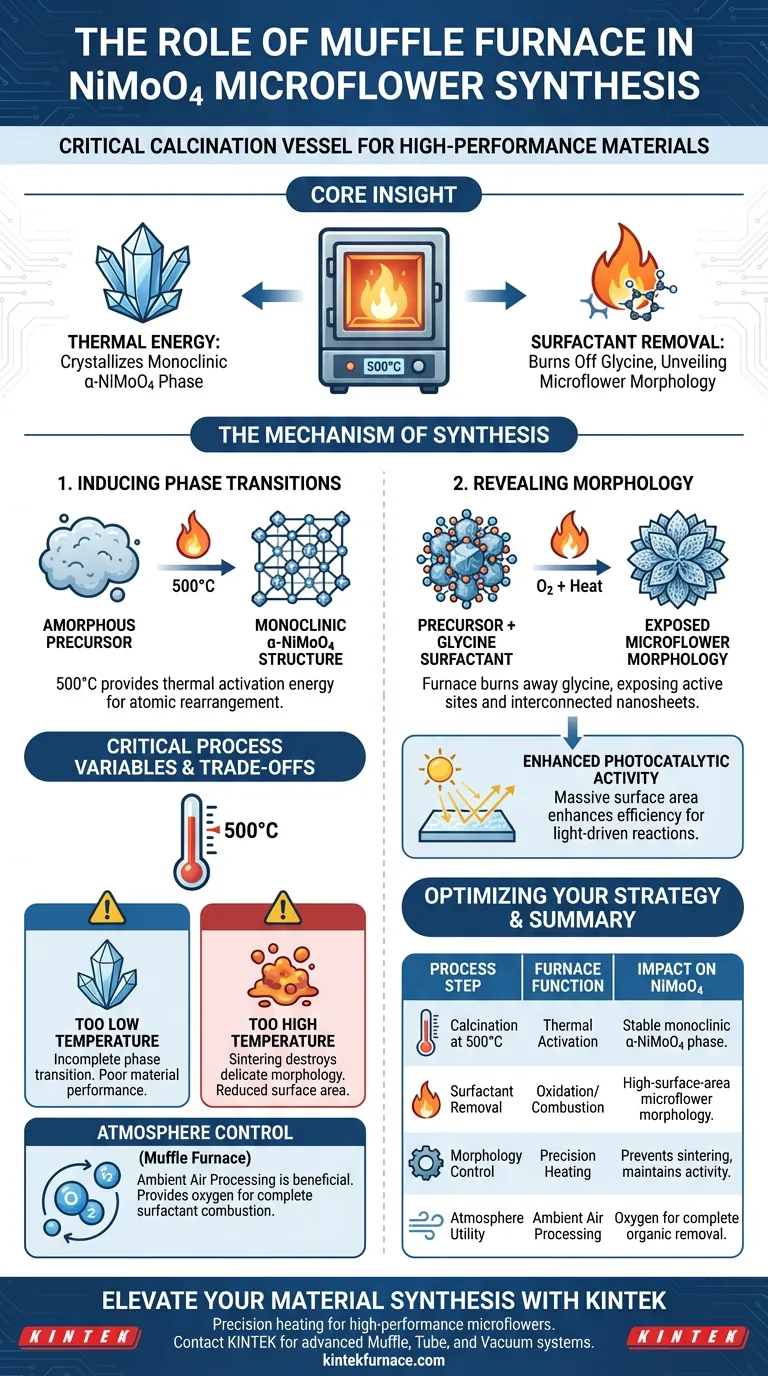
The high-temperature box-type resistance furnace (muffle furnace) serves as the critical calcination vessel in the synthesis of NiMoO4 microflowers. It subjects precursor precipitates to a controlled temperature of 500°C, a necessary step that drives the chemical conversion of the material and physically shapes its final architecture.
Core Insight: The furnace performs a dual function: it provides the thermal energy required to crystallize the material into the specific monoclinic $\alpha$-NiMoO4 phase and simultaneously burns off organic surfactants to "unveil" the high-performance microflower morphology.

The Mechanism of Synthesis
Inducing Phase Transitions
The primary function of the muffle furnace in this context is to provide the thermal activation energy necessary for crystallization.
The precursor material typically exists in an amorphous or intermediate state. By maintaining a steady temperature of 500°C, the furnace forces the atomic structure to rearrange.
This rearrangement results in a phase transition, converting the precursor into the monoclinic $\alpha$-NiMoO4 structure. This specific crystal phase is essential for the material's stability and electronic properties.
Revealing Morphology through Surfactant Removal
During the initial synthesis steps, glycine is often used as a surfactant to guide the growth of the material. However, if left in the final product, this surfactant would block active sites.
The high-temperature environment of the furnace effectively burns away (oxidizes) these glycine surfactants.
The removal of the surfactant is not just a cleaning step; it is a revealing step. Once the glycine is removed, the unique microflower morphology becomes accessible.
Enhancing Photocatalytic Activity
The structure revealed by the furnace processing consists of interconnected nanosheets that resemble flowers.
This specific architecture provides a massive surface area relative to the material's volume.
By ensuring the complete removal of organics and the formation of these nanosheets, the furnace directly enhances the material's photocatalytic activity, making it more effective for chemical reactions driven by light.
Critical Process Variables and Trade-offs
Temperature Precision
While the furnace is a robust tool, the specific temperature of 500°C is a critical parameter, not a suggestion.
If the temperature is too low: The phase transition to the monoclinic $\alpha$-NiMoO4 structure may remain incomplete, leading to poor material performance.
If the temperature is too high: You risk sintering the nanosheets together. This would destroy the delicate microflower morphology, drastically reducing the surface area and ruining the photocatalytic efficiency.
Atmosphere Control
While tube furnaces (referenced in supplementary materials) are often selected for their ability to handle complex atmospheres (vacuum or inert gas), box-type muffle furnaces generally operate in ambient air.
For NiMoO4 synthesis involving the combustion of glycine, an oxygen-rich environment (air) is actually beneficial to ensure the complete removal of the organic surfactant.
Optimizing Your Synthesis Strategy
To ensure the successful creation of NiMoO4 microflowers, align your furnace usage with your specific end-goals:
- If your primary focus is Phase Purity: Ensure your furnace is calibrated to hold exactly 500°C, as this is the precise threshold required to achieve the monoclinic $\alpha$-NiMoO4 crystal structure.
- If your primary focus is Surface Area (Morphology): Verify that the calcination duration is sufficient to fully oxidize and remove all glycine surfactants, ensuring the nanosheets are fully exposed and interconnected.
The muffle furnace is not just a heater; it is the sculptor that reveals the functional microflower structure through precise thermal processing.
Summary Table:
| Process Step | Furnace Function | Impact on NiMoO4 Microflowers |
|---|---|---|
| Calcination at 500°C | Thermal Activation | Converts precursors into stable monoclinic α-NiMoO4 phase. |
| Surfactant Removal | Oxidation/Combustion | Burns off glycine to reveal high-surface-area microflower morphology. |
| Morphology Control | Precision Heating | Prevents nanosheet sintering to maintain photocatalytic activity. |
| Atmosphere Utility | Ambient Air Processing | Provides oxygen necessary for complete organic material removal. |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK
Precision is the difference between amorphous clusters and high-performance microflowers. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK provides high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, and Vacuum systems tailored for advanced chemical synthesis. Whether you need a standard lab furnace or a fully customizable CVD system, our equipment ensures the exact temperature control and atmosphere stability your research demands.
Ready to optimize your calcination process? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your unique needs!
Visual Guide
References
- Kandasamy Sasikumar, Heongkyu Ju. Construction of Z-Scheme ZIF67/NiMoO4 Heterojunction for Enhanced Photocatalytic Degradation of Antibiotic Pollutants. DOI: 10.3390/ma17246225
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What are the latest technological advancements in muffle furnaces? Discover Precision, Efficiency, and Control Innovations
- What materials are recommended for muffle furnace construction? Optimize for High-Temp Performance and Safety
- What specific activation conditions are provided by a high-precision laboratory box furnace? Optimize Teak Carbon Pore
- What scientific processes can a muffle furnace assist with? Unlock Precise, Contaminant-Free Heat Treatment
- How does the muffle design contribute to furnace performance? Enhance Purity, Uniformity, and Efficiency
- What role does a Box Furnace play during the oxidative stabilization of nanofibers? Essential Chemical Transformation
- What options are available for temperature uniformity in Box Furnaces? Achieve Precise Heat for Your Critical Processes
- How often should a muffle furnace undergo maintenance? Ensure Longevity and Safety with Proactive Care



















