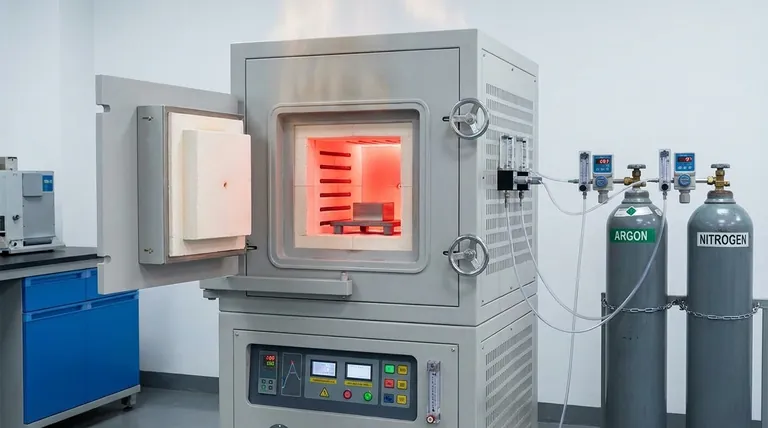
For high-temperature metallurgical processes, the most common gas used to provide an inert atmosphere is Argon (Ar). Its primary purpose is to displace oxygen and other reactive gases from the environment, thereby preventing the formation of undesirable oxides on the metal's surface. In some cases, mixtures containing hydrogen are also used to create a reducing atmosphere.
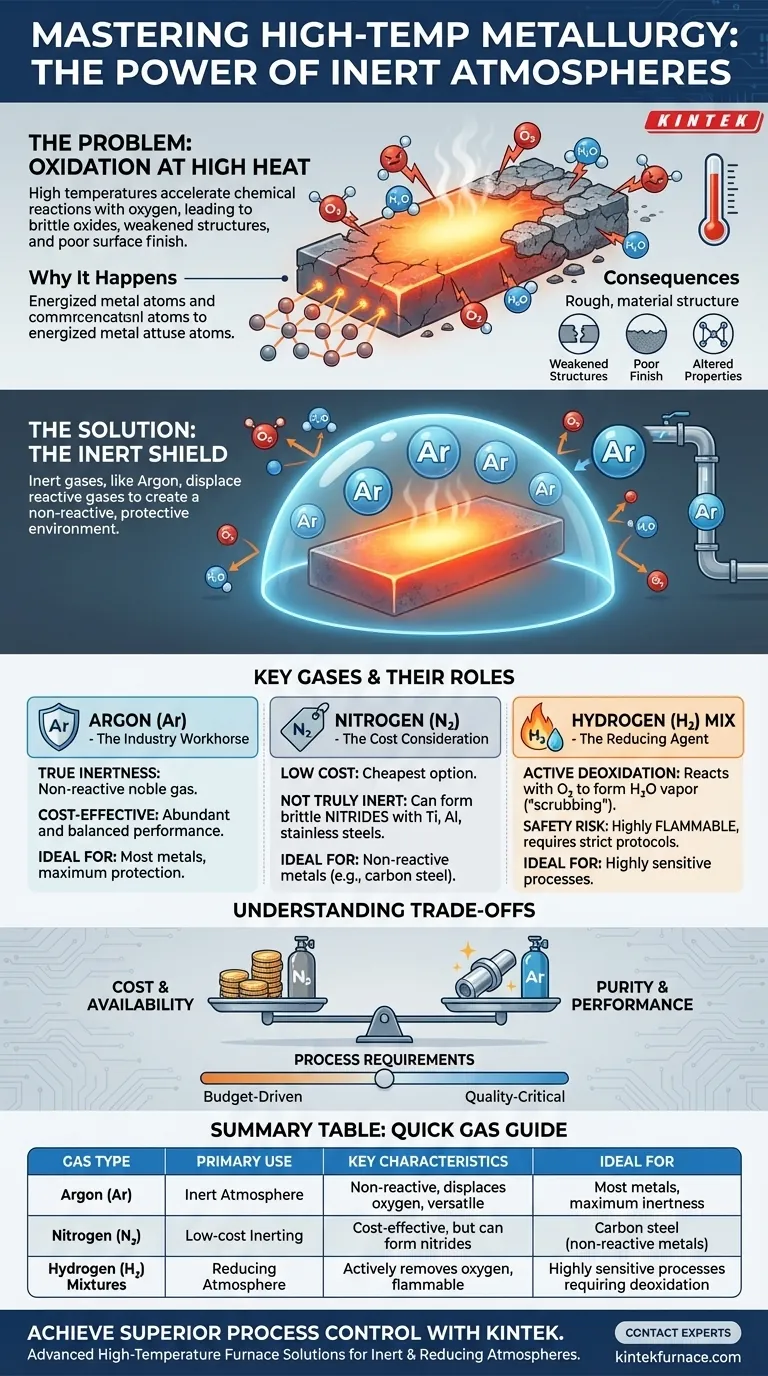
The core challenge in high-temperature metallurgy is not the heat itself, but the accelerated chemical reactions it causes, primarily with oxygen in the air. The solution is to create a protective gaseous shield that is non-reactive (inert), preventing costly defects like oxidation and ensuring the final product's integrity.

The Fundamental Problem: Oxidation at High Temperatures
Why Metals Oxidize
At room temperature, most metals are relatively stable. As temperature increases dramatically during processes like welding, casting, or heat treatment, the metal atoms become highly energized. This energy drastically accelerates their rate of reaction with oxygen present in the ambient air.
This chemical reaction results in the formation of metal oxides on the surface of the workpiece.
The Consequences of Oxidation
Oxide layers are typically brittle, flaky, and have poor mechanical properties. Their presence can lead to a host of problems:
- Weakened Structures: In welding, oxides can become trapped in the weld pool, creating inclusions that compromise the joint's strength.
- Poor Surface Finish: Oxidation leaves a discolored and rough surface, often requiring costly and time-consuming secondary cleaning processes.
- Altered Material Properties: The formation of an oxide layer consumes the parent metal and can change the chemical and physical properties of the component's surface.
Creating the Protective Shield: Inert vs. Reducing Atmospheres
To prevent oxidation, the reactive gases—primarily oxygen and water vapor—must be removed from the immediate vicinity of the hot metal. This is achieved by flooding the area with a protective gas.
The Role of an Inert Atmosphere
An inert atmosphere works on the principle of displacement. Gases like Argon are heavier than air and chemically non-reactive. When pumped into the processing zone, they physically push the lighter, oxygen-rich air away from the metal surface.
Because the inert gas will not chemically bond with the metal even at extreme temperatures, it creates a perfect, non-reactive shield.
Argon: The Industry Workhorse
Argon is the go-to choice for most inerting applications for two key reasons:
- True Inertness: As a noble gas, Argon is extremely non-reactive and will not form compounds with other elements under almost any metallurgical condition.
- Cost-Effectiveness: While more expensive than nitrogen, Argon is far more abundant and cheaper than other noble gases like Helium, making it the ideal balance of performance and cost.
An Alternative: Reducing Atmospheres
Sometimes, a purely inert atmosphere is supplemented or replaced by a reducing atmosphere, which often involves Hydrogen (H₂), typically mixed in small percentages with Argon.
Unlike Argon, which is passive, Hydrogen is chemically active. It aggressively reacts with any oxygen present in the atmosphere to form water (H₂O), which is then carried away as vapor. This process actively "scrubs" or reduces the amount of oxygen, offering an additional layer of protection against oxidation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right gas is a critical decision based on the specific metal, the process temperature, and the budget.
Cost vs. Purity
The primary trade-off is often cost. Nitrogen is the cheapest protective gas, but as discussed below, it is not always suitable. Argon is the next step up in price, offering true inertness for a wider range of applications. The required purity of the gas also significantly impacts cost; higher purity means better protection but at a premium.
The Nitrogen Consideration
Nitrogen (N₂) is often considered for inerting due to its low cost and relative lack of reactivity. However, it is not a truly inert gas.
At the high temperatures seen in many metallurgical processes, nitrogen can react with certain metals—notably titanium, aluminum, and some stainless steels—to form hard, brittle compounds called nitrides. This can be just as detrimental as oxidation, making nitrogen unsuitable for many critical applications.
Safety and Handling
While Argon and Nitrogen are safe to handle (though they are asphyxiants in confined spaces), atmospheres containing Hydrogen introduce a new risk: flammability. Hydrogen is highly flammable and requires specialized equipment, leak detection systems, and strict safety protocols to manage explosion risks.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your selection of a protective gas atmosphere must align directly with your material, budget, and quality requirements.
- If your primary focus is maximum inertness and versatility: Use high-purity Argon, as it is non-reactive with virtually all metals at any temperature.
- If your primary focus is cost-efficiency on non-reactive metals: Nitrogen can be a viable option for materials like carbon steel, but you must verify its compatibility to avoid nitride formation.
- If your primary focus is active deoxidation for a highly sensitive process: A mixture of Argon and Hydrogen is extremely effective but requires careful management of the associated flammability risks.
Ultimately, selecting the correct atmosphere is a foundational step in controlling the quality and integrity of your final metallurgical product.
Summary Table:
| Gas Type | Primary Use | Key Characteristics | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Argon (Ar) | Inert Atmosphere | Non-reactive, displaces oxygen, versatile | Most metals, maximum inertness |
| Nitrogen (N₂) | Low-cost Inerting | Cost-effective, but can form nitrides | Carbon steel (non-reactive metals) |
| Hydrogen (H₂) Mixtures | Reducing Atmosphere | Actively removes oxygen, flammable | Highly sensitive processes requiring deoxidation |
Struggling with oxidation or inconsistent results in your high-temperature processes? KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, and Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, are engineered to work seamlessly with inert and reducing atmospheres. Our deep customization capabilities ensure your furnace is perfectly configured for your specific gas requirements and metallurgical applications. Contact our experts today to achieve superior process control and product quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is nitrogen used for in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Control Heat Treatment Quality
- How does nitrogen atmosphere heat treatment improve surface strengthening? Enhance Durability and Performance
- What are the environmental benefits of using inert gases in furnaces? Reduce Waste and Emissions for a Greener Process
- What are the benefits of inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Preserve Material Integrity
- How does a chemically inert atmosphere function in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Material Purity



















