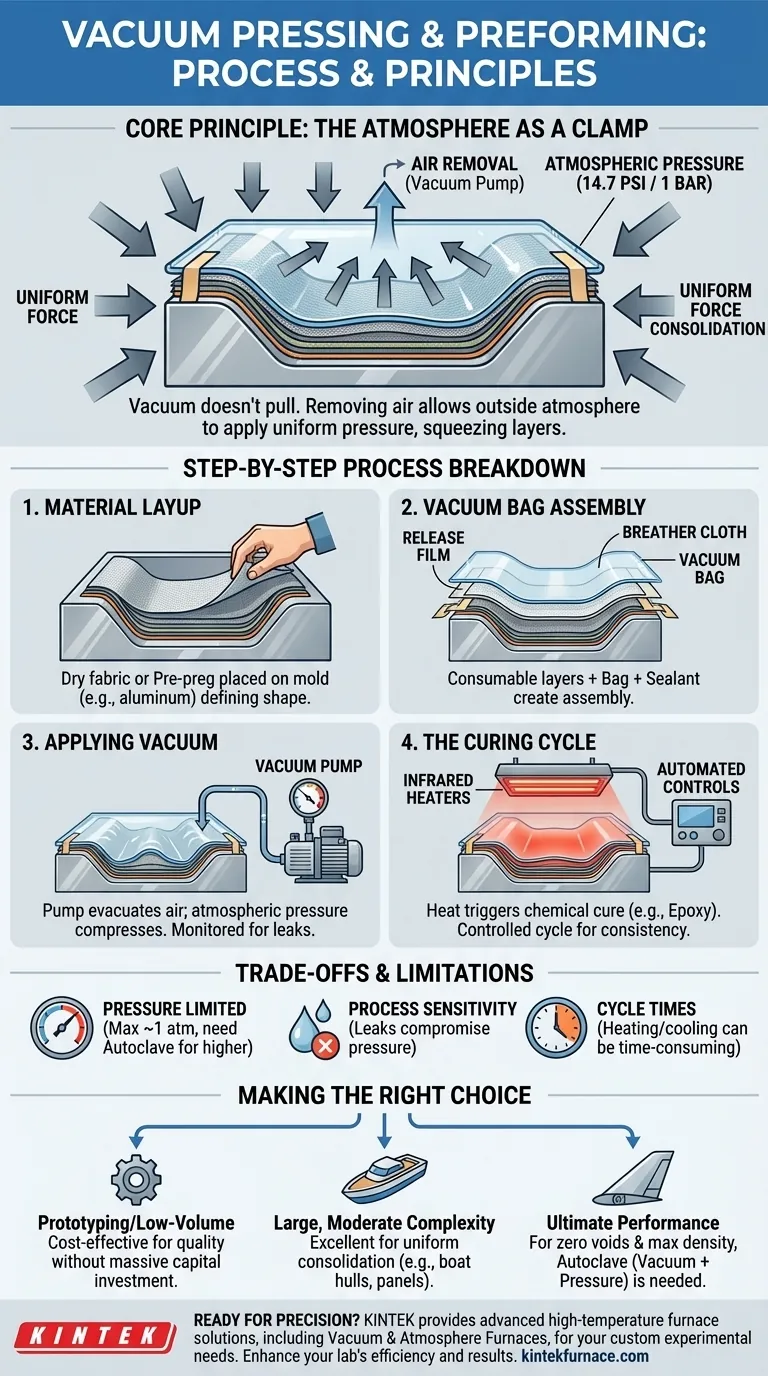
At its core, vacuum pressing and preforming are processes that use atmospheric pressure as a clamp to shape and consolidate layers of fabric or fiber, often impregnated with resin. Modern systems accomplish this with a combination of a forming tool (mold), a vacuum bag, and a precisely controlled heating system, such as infrared heaters, all managed by automated controls for consistency.
The critical insight is that "vacuum" doesn't pull the material into shape. Instead, removing the air inside a sealed bag allows the immense weight of the outside atmosphere—approximately 14.7 pounds per square inch—to apply uniform, constant pressure across the entire part, squeezing the layers together and forcing them against the mold.
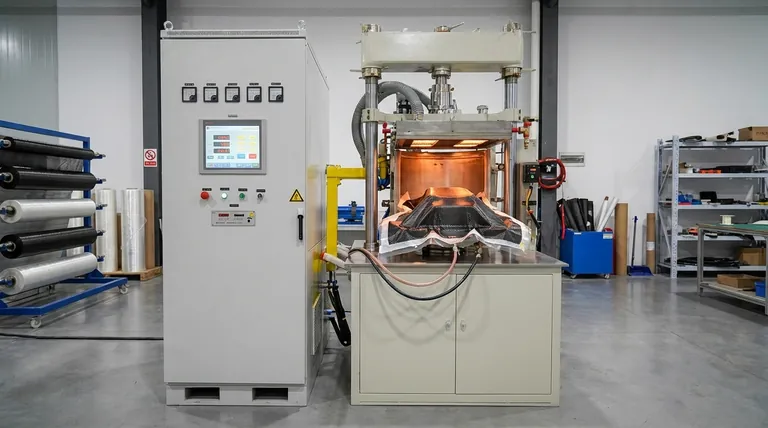

The Core Principle: Using the Atmosphere as a Clamp
What Vacuum Really Does
The term "vacuum forming" can be misleading. The process does not involve the vacuum itself exerting a pulling force on the material.
Instead, a pump removes the air from within a sealed flexible bag that covers the material and its mold. This creates a pressure differential between the inside of the bag (near zero pressure) and the outside environment (standard atmospheric pressure).
The Power of Atmospheric Pressure
This pressure difference allows the surrounding atmosphere to press down evenly on the vacuum bag. This constant, uniform force consolidates the layers of fabric, removes trapped air and excess resin, and ensures the material conforms perfectly to the contours of the forming tool.
A Step-by-Step Breakdown of the Process
The practical application of vacuum pressing follows a precise sequence of steps to ensure a high-quality, void-free composite part.
Step 1: Material Layup
First, layers of dry fabric or pre-impregnated fiber (pre-preg) are carefully placed onto the surface of a forming tool, or mold. The mold defines the final shape of the part and is often made from materials like aluminum or specialized tooling composites that can withstand the heat of the curing cycle.
Step 2: The Vacuum Bag Assembly
A series of consumable materials are placed over the laid-up part. This includes a release film to prevent sticking, a breather cloth to create a clear path for air to escape, and finally, the vacuum bag itself. The bag is sealed to the edges of the tool using specialized sealant tape.
Step 3: Applying Vacuum
A vacuum pump is connected to the sealed bag via a port. As the pump evacuates the air, the atmospheric pressure outside begins to compress the assembly. Monitoring systems track the vacuum level to ensure a proper seal and adequate pressure before moving to the next stage.
Step 4: The Curing Cycle
For thermoset materials like epoxy resin, heat is required to trigger a chemical reaction that solidifies (cures) the part. Infrared heating is a common method in sophisticated vacuum presses because it provides rapid, non-contact, and highly controllable energy to heat the part to its target temperature.
Automated production processes manage this entire cycle, controlling the rate of heating, the duration of the cure, and the vacuum level to ensure a repeatable and high-quality result.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, vacuum pressing is not the solution for every composite application. Understanding its limits is key to making the right manufacturing choice.
Pressure Limitations
The maximum pressure that can be achieved is limited to one atmosphere (~14.7 psi or 1 bar). For high-performance aerospace components requiring maximum density and minimal voids, higher-pressure systems like an autoclave are necessary.
Process Sensitivity
The success of the process is highly dependent on the quality of the vacuum bag seal. Even a microscopic leak can compromise the pressure and ruin the part, requiring skilled technicians and careful preparation.
Cycle Times
While faster than some rudimentary methods, the heating and cooling cycles required for curing can still be time-consuming, which can be a bottleneck in high-volume production compared to processes like compression molding.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right process depends entirely on your project's goals for performance, volume, and cost.
- If your primary focus is prototyping or low-volume production: Vacuum pressing is an excellent, cost-effective choice for creating high-quality parts without the massive capital investment of an autoclave.
- If your primary focus is creating large, structurally sound parts with moderate complexity: This process excels at producing things like boat hulls, automotive body panels, and architectural elements where uniform consolidation is key.
- If your primary focus is ultimate performance with zero voids (e.g., critical aerospace structures): You will likely need to use an autoclave, which combines vacuum with elevated external pressure to achieve superior material consolidation.
Ultimately, vacuum pressing is a versatile and accessible technology that bridges the gap between basic hand-layup and high-end autoclave curing.
Summary Table:
| Process Step | Key Components | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Material Layup | Fabric, Pre-preg, Mold | Define part shape and layer placement |
| Vacuum Bag Assembly | Bag, Release Film, Breather Cloth | Seal and allow air evacuation |
| Applying Vacuum | Vacuum Pump, Monitoring Systems | Create pressure differential for consolidation |
| Curing Cycle | Infrared Heaters, Automated Controls | Heat and cure thermoset materials |
Ready to enhance your composite manufacturing with precision? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental needs for processes like vacuum pressing. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your lab's efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why are precision molds and laboratory presses critical for niobium-doped TiO2 ceramics? Achieve 94% Theoretical Density
- Which process parameters must be optimized for specific materials in a vacuum hot press furnace? Achieve Optimal Density and Microstructure
- What are the advantages of vacuum hot press furnaces? Achieve Superior Material Density & Purity
- What are the advantages of using a laboratory hot press for F-MWCNT films? Boost Power Factor by 400%
- What role does a high-pressure press play in the preparation of zinc sample pellets? Optimize Carbothermic Reduction



















