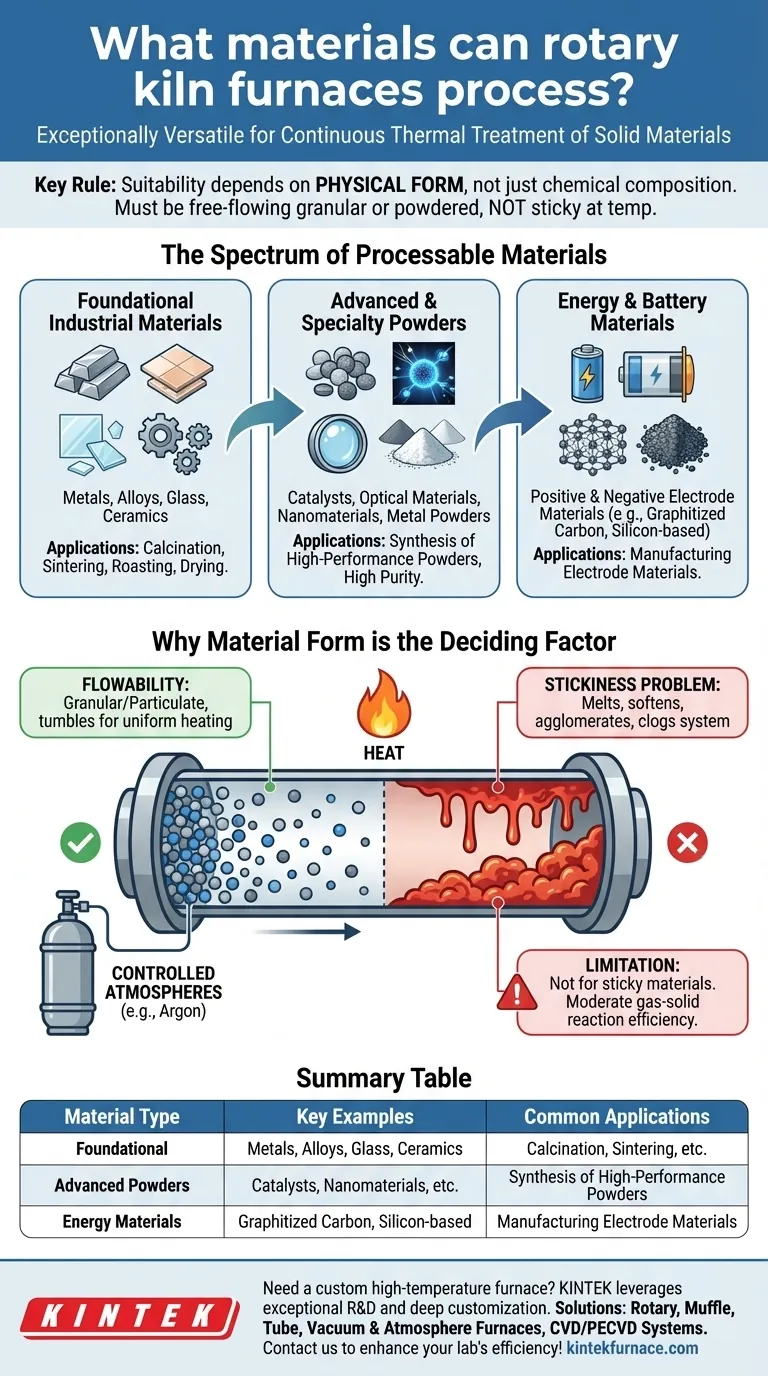
Rotary kiln furnaces are exceptionally versatile, designed to process an extensive range of solid materials through continuous thermal treatment. Their capabilities span foundational industrial compounds like metals, alloys, and ceramics, as well as advanced materials such as catalysts, battery electrode powders, and nanomaterials.
The defining characteristic for a material's suitability is not its chemical composition but its physical form. Rotary kilns excel with free-flowing granular or powdered solids that do not become sticky at processing temperatures, enabling uniform treatment under precisely controlled atmospheres.
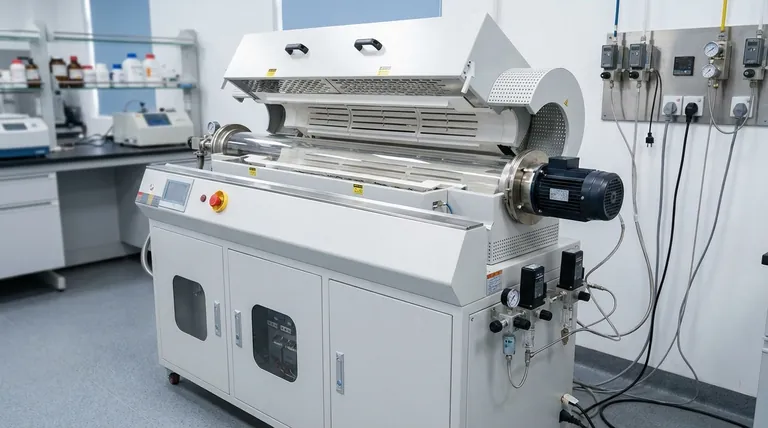

The Spectrum of Processable Materials
A rotary kiln's utility comes from its ability to handle diverse inputs for equally diverse applications, from bulk mineral processing to the synthesis of high-performance powders.
Foundational Industrial Materials
Rotary kilns are a cornerstone for processing core materials. This includes metals, alloys, glass, and ceramic compounds in powder or granular form. Common applications involve calcination, sintering, roasting, and drying.
Advanced and Specialty Powders
These furnaces are critical in creating next-generation materials. They can process catalysts, optical materials, nanomaterials, and various metal powders with high purity and specific particle characteristics. The precise temperature control is key to achieving the desired material properties.
Energy and Battery Materials
The new energy sector heavily relies on rotary kilns for synthesizing materials. This includes manufacturing positive and negative electrode materials for batteries, such as graphitized carbon and emerging silicon-based negative electrode materials.
Why Material Form is the Deciding Factor
The success of a rotary kiln process depends entirely on the physical behavior of the material inside the rotating tube. The design's effectiveness is tied to how the material moves and interacts with heat.
The Importance of Flowability
A rotary kiln functions by tumbling material, ensuring every particle is exposed to the heat source. Therefore, the material must be granular or particulate and maintain its flowability at high temperatures. This constant mixing promotes thermal uniformity throughout the batch.
The Role of Controlled Atmospheres
Many advanced processes require a specific chemical environment. Rotary kilns can be filled with inert atmospheres, such as argon gas, to prevent unwanted reactions like oxidation or nitriding of metals. Special sealing structures are used to maintain the integrity of this controlled atmosphere.
Understanding Key Limitations
While highly versatile, rotary kilns are not a universal solution. Understanding their inherent constraints is critical to avoid process failure and equipment damage.
The "Stickiness" Problem
This is the single most significant limitation. Any material that melts, softens, or becomes sticky at the target processing temperature is unsuitable for a rotary kiln. Such behavior causes material to agglomerate and coat the furnace walls, halting flow and creating a system-clogging failure.
Gas-Solid Reaction Efficiency
For processes that rely on a gas reacting with the solid material, a rotary kiln provides moderate contact efficiency. While effective for many applications, other reactor types like a fluidized bed may offer superior performance where rapid gas-solid interaction is the primary goal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Material
Selecting the correct thermal processing technology begins with a clear understanding of your material's behavior and your final goal.
- If your primary focus is bulk processing of stable solids: A rotary kiln is ideal for calcining, drying, or sintering materials like minerals, ceramics, or metal powders that remain free-flowing.
- If your primary focus is synthesizing advanced materials: The ability to control temperature and atmosphere makes it excellent for creating battery electrode materials, catalysts, or nanomaterials from precursor powders.
- If your material becomes soft or sticky at high temperatures: You must seek alternative furnace technologies, as a rotary kiln is fundamentally incompatible with this behavior.
Ultimately, a material's suitability for a rotary kiln hinges on its physical behavior at temperature—a factor even more critical than its chemical identity.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Key Examples | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Foundational Industrial Materials | Metals, Alloys, Glass, Ceramics | Calcination, Sintering, Roasting, Drying |
| Advanced and Specialty Powders | Catalysts, Nanomaterials, Optical Materials | Synthesis of High-Performance Powders |
| Energy and Battery Materials | Graphitized Carbon, Silicon-Based Electrodes | Manufacturing Electrode Materials for Batteries |
Need a custom high-temperature furnace for your material processing? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, whether you're working with bulk solids, powders, or specialty materials. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's efficiency and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating



















