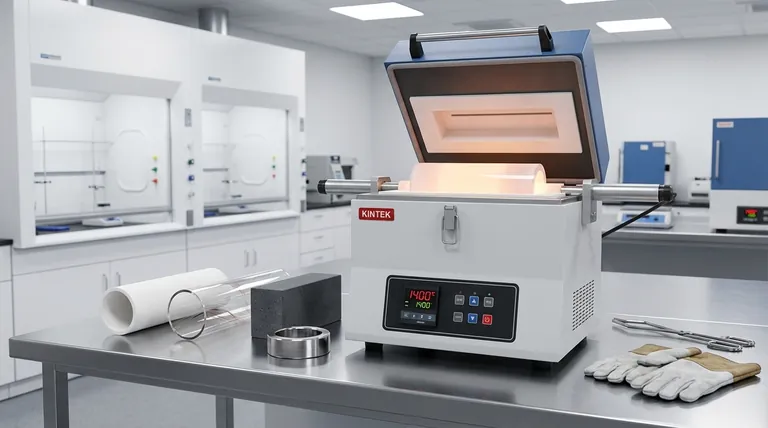
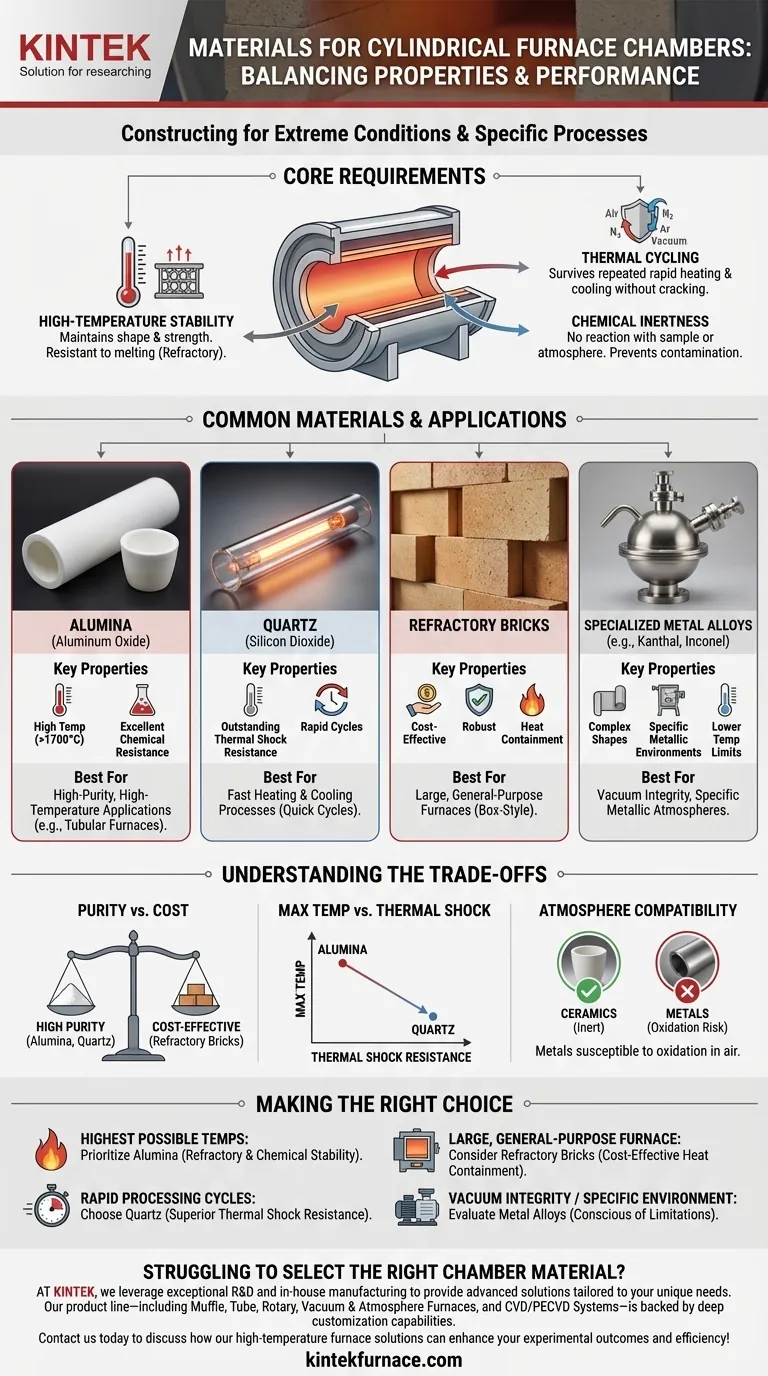
The materials used to construct a cylindrical chamber are chosen specifically for their ability to withstand extreme conditions. Common choices include high-purity ceramics like alumina and quartz, composite materials like refractory bricks, and certain specialized metal alloys. The selection depends entirely on the required operating temperature, the chemical environment, and the speed of the heating and cooling cycles.
The choice of a chamber material is a critical engineering trade-off. You are balancing the need for maximum temperature resistance against the material's ability to survive rapid temperature changes (thermal shock) and its chemical inertness, all within a specific budget.

The Core Requirements for Chamber Materials
To function reliably, any high-temperature chamber material must exhibit a few non-negotiable properties. These characteristics ensure the integrity of the chamber and the purity of the process running inside it.
High-Temperature Stability
This is the most fundamental requirement. The material must maintain its shape and strength at the furnace's maximum operating temperature without melting, sagging, or degrading. This property is often referred to as being refractory.
Resistance to Thermal Cycling
Chambers are rarely held at a constant high temperature. They are heated up and cooled down repeatedly in a process known as thermal cycling. Each cycle induces stress, and a good material must resist cracking or failing over hundreds or thousands of these cycles.
Chemical Inertness
The chamber material should not react with the sample being processed or the atmosphere inside the furnace (e.g., air, nitrogen, argon, or vacuum). Any reaction can contaminate the process and degrade the chamber itself over time.
A Closer Look at Common Materials
Each material offers a different profile of properties, making it suitable for specific applications.
Alumina (Aluminum Oxide)
Alumina is a ceramic known for its extremely high-temperature stability, often usable well above 1700°C (3092°F). It offers excellent chemical resistance and mechanical strength, making it a go-to choice for high-performance and high-purity applications, especially in tubular furnaces.
Quartz (Silicon Dioxide)
Quartz is another high-purity ceramic. While its maximum temperature limit is typically lower than alumina's, its defining feature is outstanding thermal shock resistance. It can withstand very rapid heating and cooling without cracking, which is critical for fast processing cycles.
Refractory Bricks
For larger, custom-built, or box-style furnaces, chambers are often constructed from refractory bricks. These are composite ceramic materials designed for heat containment. They are robust and cost-effective but generally offer less purity and a less controlled environment than a solid alumina or quartz tube.
Specialized Metal Alloys
Certain nickel-based or iron-chromium-aluminum alloys (like Kanthal or Inconel) can be used for chamber construction. Metals are advantageous when complex shapes are needed or when a metallic, non-ceramic surface is required. However, their maximum operating temperatures are significantly lower than ceramics, and they are more prone to reacting with the process atmosphere.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a material is never about finding a "perfect" solution. It is always an exercise in balancing competing factors.
Purity vs. Cost
High-purity alumina and quartz tubes are significantly more expensive than chambers built from refractory bricks. The level of process purity you require will be a primary driver of cost.
Maximum Temperature vs. Thermal Shock
This is a classic ceramic trade-off. Alumina will allow you to reach higher sustained temperatures, but it is more sensitive to rapid temperature changes. Quartz cannot go as high in temperature, but it excels in applications requiring quick heating and cooling.
Atmosphere Compatibility
Metals are highly susceptible to oxidation and may not be suitable for processes run in an air atmosphere at high temperatures. While ceramics are generally more inert, specific chemicals at high temperatures can still attack them, requiring careful selection.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by the primary goal of your thermal process.
- If your primary focus is reaching the highest possible temperatures: Prioritize alumina for its exceptional refractory properties and chemical stability.
- If your primary focus is rapid processing cycles: Choose quartz for its superior resistance to thermal shock, which prevents cracking during fast heating and cooling.
- If your primary focus is constructing a large, general-purpose furnace: Consider refractory bricks as a cost-effective and durable solution for heat containment.
- If your primary focus is vacuum integrity or a specific metallic environment: Evaluate specialized metal alloys, but remain conscious of their lower temperature limits and potential for oxidation.
Understanding these material properties empowers you to select a chamber that ensures both the safety and success of your high-temperature process.
Summary Table:
| Material | Key Properties | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Alumina | High-temperature stability (>1700°C), excellent chemical resistance | High-purity, high-temperature applications |
| Quartz | Outstanding thermal shock resistance, good for rapid cycles | Fast heating and cooling processes |
| Refractory Bricks | Cost-effective, robust for heat containment | Large, general-purpose furnaces |
| Metal Alloys | Complex shapes, specific metallic environments | Vacuum integrity, lower temperature uses |
Struggling to select the right chamber material for your lab's high-temperature processes? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions tailored to your unique needs. Our product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is backed by deep customization capabilities to ensure optimal performance and durability. Whether you need alumina for extreme temperatures, quartz for thermal shock resistance, or other specialized materials, we can help. Contact us today to discuss how our high-temperature furnace solutions can enhance your experimental outcomes and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What function does a tube furnace serve in the PVT growth of J-aggregate molecular crystals? Mastery of Thermal Control
- What is flash vacuum pyrolysis and how is a tube furnace utilized in this process? Unlock High-Temp Chemical Reactions
- How does a vertical tube furnace facilitate the simulation of the industrial sintering process for iron ores?



















