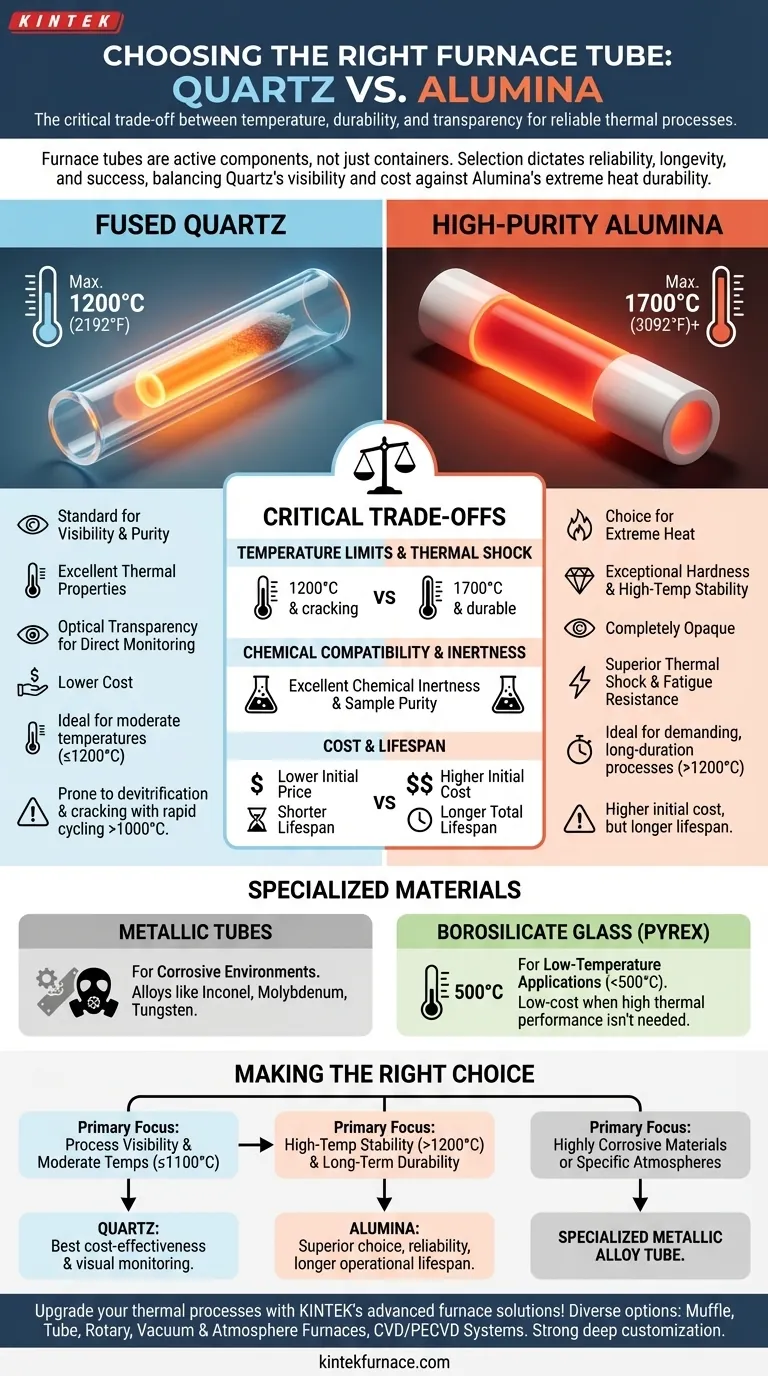
In nearly all laboratory and industrial settings, furnace tubes are made from high-purity quartz or alumina. The choice between them is not arbitrary; it is a critical decision dictated by the specific maximum temperature, thermal cycling requirements, and chemical environment of the intended process. This selection directly impacts the reliability, longevity, and success of your thermal operations.
The material of a furnace tube isn't just a container; it's an active component of your process. Your choice is a direct trade-off between quartz's transparency and cost-effectiveness at lower temperatures (up to ~1200°C) and alumina's superior thermal durability and chemical resistance at higher temperatures (up to ~1700°C).

The Two Primary Materials: Quartz vs. Alumina
The vast majority of applications are served by one of two ceramic materials. Understanding their core characteristics is the foundation for making an informed choice.
Fused Quartz: The Standard for Visibility and Purity
Fused quartz is a high-purity glass known for its excellent thermal properties and optical transparency. This allows for direct visual monitoring of the process inside the furnace, which can be invaluable.
It is the default choice for many processes due to its lower cost and excellent performance within its temperature range.
High-Purity Alumina: The Choice for Extreme Heat
Alumina (Aluminum Oxide, Al₂O₃) is an advanced ceramic prized for its exceptional hardness and high-temperature stability. It is completely opaque.
Its primary advantage is its ability to withstand significantly higher temperatures and more rigorous thermal cycling than quartz, making it the go-to material for demanding, long-duration processes.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
Selecting a tube material is an exercise in balancing performance requirements against physical limitations. The wrong choice can lead to premature failure, process contamination, and costly downtime.
Temperature Limits and Thermal Shock
A material's maximum operating temperature is its most important specification. Quartz tubes are reliably used up to 1200°C (2192°F). However, with repeated rapid heating and cooling cycles, especially above 1000°C, quartz can devitrify (become crystalline), making it brittle and prone to cracking.
Alumina tubes, by contrast, can operate at temperatures up to 1700°C (3092°F) or even higher for some grades. They are far more resistant to thermal shock and fatigue, making them much more durable for long-term use in high-temperature applications.
Chemical Compatibility and Inertness
Both quartz and alumina are valued for their chemical inertness, meaning they do not typically react with the materials being processed. This ensures the purity of the sample.
While both are highly resistant, certain aggressive chemicals at very high temperatures might slightly favor one over the other. However, for most common applications, both materials provide excellent chemical compatibility.
Cost and Lifespan
Quartz has a lower initial purchase price, making it an attractive option for budget-conscious projects or less demanding applications.
Alumina has a higher initial cost. However, in high-temperature processes that require frequent use, its superior durability and longer lifespan often result in a lower total cost of ownership due to reduced replacement frequency and less process downtime.
Specialized Materials for Unique Conditions
While quartz and alumina cover most needs, certain extreme conditions demand specialized materials.
Metallic Tubes: For Corrosive Environments
Alloys like Inconel or refractory metals such as molybdenum and tungsten are used in specific, niche applications. They are chosen when processing highly corrosive materials or when a particular gaseous atmosphere would react with a ceramic tube.
Borosilicate Glass (Pyrex): For Low-Temperature Applications
For very low-temperature work, typically below 500°C (932°F), borosilicate glass tubes like Pyrex can be used. They are a low-cost option when high thermal performance and shock resistance are not required.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
To select the correct tube material, you must align its properties with your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is process visibility and moderate temperatures (below 1100°C): Quartz offers the best combination of cost-effectiveness and visual monitoring.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature stability (above 1200°C) and long-term durability: Alumina is the superior choice, providing reliability and a longer operational lifespan despite a higher initial cost.
- If your primary focus is handling highly corrosive materials or specific atmospheres: A specialized metallic alloy tube like Inconel or molybdenum may be required.
Selecting the right furnace tube is the first step in ensuring a reliable, repeatable, and safe thermal process.
Summary Table:
| Material | Max Temperature | Key Advantages | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quartz | Up to 1200°C | Optical transparency, lower cost, high purity | Moderate temps, visual monitoring, budget projects |
| Alumina | Up to 1700°C | High thermal durability, chemical resistance, long lifespan | High-temp processes, frequent thermal cycling |
| Specialized Metals (e.g., Inconel) | Varies | Corrosion resistance, specific atmosphere handling | Highly corrosive environments |
Upgrade your thermal processes with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace options like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored furnace tubes can enhance your lab's reliability and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety



















