At its core, vacuum melting is reserved for materials whose properties would be compromised by exposure to air during processing. These include highly reactive metals like titanium, high-performance superalloys, specialty steels, and certain advanced ceramics that demand an ultra-clean environment to achieve their required strength and purity.
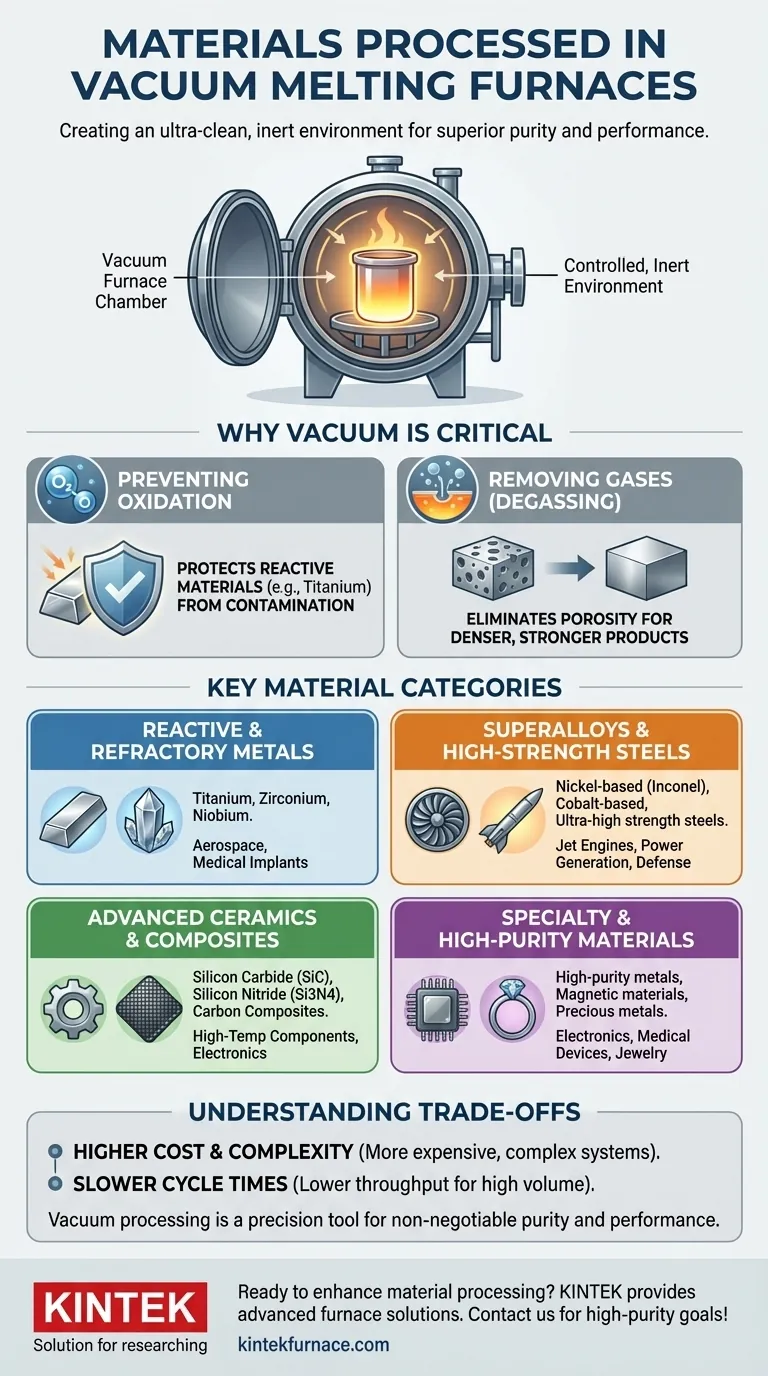
The fundamental purpose of a vacuum furnace is not just to melt material, but to create a controlled, inert environment. This prevents unwanted chemical reactions—chiefly oxidation—and removes trapped gases, resulting in finished materials with superior purity and mechanical properties.
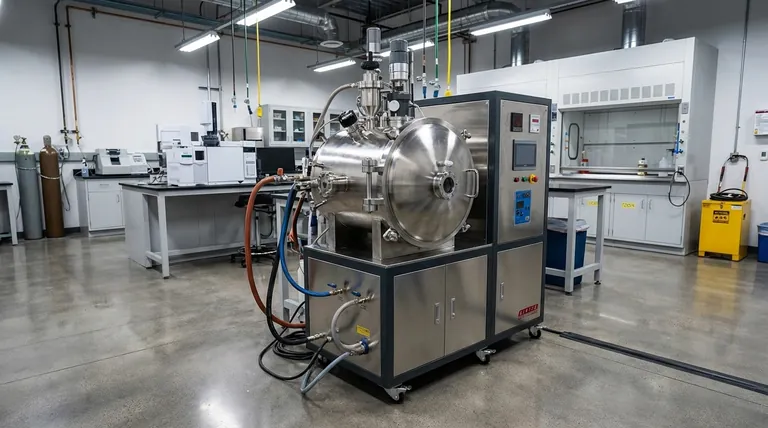

Why a Vacuum Environment is Critical
Processing materials in a vacuum is a deliberate choice driven by the need to control chemistry at a fundamental level. An open-air furnace is filled with a reactive atmosphere (21% oxygen, 78% nitrogen) that can contaminate and weaken sensitive materials.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
Many advanced metals are highly reactive, meaning they readily bond with oxygen, especially at high temperatures. A prime example is titanium, which would be severely compromised by oxidation if melted in air.
The vacuum removes oxygen and other reactive gases. This creates a chemically neutral atmosphere that protects the material's integrity throughout the melting and casting process.
Removing Dissolved Gases (Degassing)
Molten metals can hold a significant amount of dissolved gases like oxygen and hydrogen. As the metal cools and solidifies, these gases can come out of the solution, forming microscopic pores and voids.
These internal defects act as stress concentrators, drastically reducing the material's fatigue life and overall strength. The vacuum effectively pulls these dissolved gases out of the molten bath, a process known as degassing, leading to a denser, more solid final product.
A Breakdown of Key Material Categories
The need for purity and performance dictates which materials are processed in vacuum furnaces. They generally fall into several high-value categories.
Reactive and Refractory Metals
These are materials that cannot be processed in air without significant degradation. The vacuum environment is essential.
- Titanium and its alloys
- Zirconium
- Niobium
Superalloys and High-Strength Steels
These materials form the backbone of the aerospace, power generation, and defense industries. Their performance at extreme temperatures relies on a precisely controlled and incredibly pure chemical composition.
- Nickel-based superalloys (e.g., Inconel) for jet engine and gas turbine components
- Cobalt-based superalloys
- Ultra-high strength steels and specialty stainless steels for missile, rocket, and nuclear applications
Advanced Ceramics and Composites
While not always melted, these materials are often sintered or heat-treated in vacuum furnaces. The process, often called vacuum hot-pressing, uses pressure and temperature in a vacuum to fuse powders together.
- Silicon carbide (SiC) and silicon nitride (Si3N4)
- Carbon composite materials and carbon fiber
- Metal powders and metal/ceramic composites
Specialty and High-Purity Materials
This category includes materials for electronics, medical, and other niche applications where even trace impurities can cause failure.
- High-purity metals for refining electrodes
- Magnetic materials
- Precious metals for jewelry and industrial casting
- Alloys for medical implants
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum processing is not a universal solution. It involves significant trade-offs that make it unsuitable for many common applications.
Significant Cost and Complexity
Vacuum furnaces are far more expensive to purchase, operate, and maintain than their atmospheric counterparts. The systems required to create and hold a high vacuum add layers of complexity and cost.
Slower Cycle Times
The process of pumping the chamber down to a vacuum, heating, and executing a controlled cooling profile takes considerably more time than a simple air-melt. This results in lower throughput, making it less efficient for high-volume production.
It's Often Overkill
For the vast majority of metal production, such as standard structural steel or common aluminum alloys, the minor levels of oxidation and porosity from air-melting are perfectly acceptable for the intended application. Using a vacuum furnace would be economically unjustifiable.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
The decision to use vacuum processing hinges entirely on the required performance and properties of the final material.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity and performance: For materials in aerospace, medical, or nuclear applications, vacuum melting is the non-negotiable standard.
- If your primary focus is processing reactive metals: For materials like titanium that cannot survive air-melting, a vacuum environment is your only viable option.
- If your primary focus is creating dense, non-porous parts from powders: For advanced ceramics and composites, vacuum hot-pressing is the key technology to achieve superior material properties.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, high-volume production: For standard alloys where minor impurities are acceptable, conventional air furnaces remain the more economical choice.
Ultimately, vacuum processing is a tool of precision, chosen only when the material's final integrity cannot be compromised.
Summary Table:
| Material Category | Examples | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Reactive and Refractory Metals | Titanium, Zirconium, Niobium | Aerospace, Medical Implants |
| Superalloys and High-Strength Steels | Nickel-based (e.g., Inconel), Cobalt-based, Ultra-high strength steels | Jet Engines, Power Generation, Defense |
| Advanced Ceramics and Composites | Silicon Carbide (SiC), Silicon Nitride (Si3N4), Carbon Composites | High-Temperature Components, Electronics |
| Specialty and High-Purity Materials | High-purity metals, Magnetic materials, Precious metals | Electronics, Medical Devices, Jewelry |
Ready to enhance your material processing with precision and purity? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're working with reactive metals, superalloys, or ceramics, we deliver tailored solutions for superior results. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your high-purity processing goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys
- How does vacuum melting technology contribute to sustainability? Boost Durability and Recycling Efficiency



















