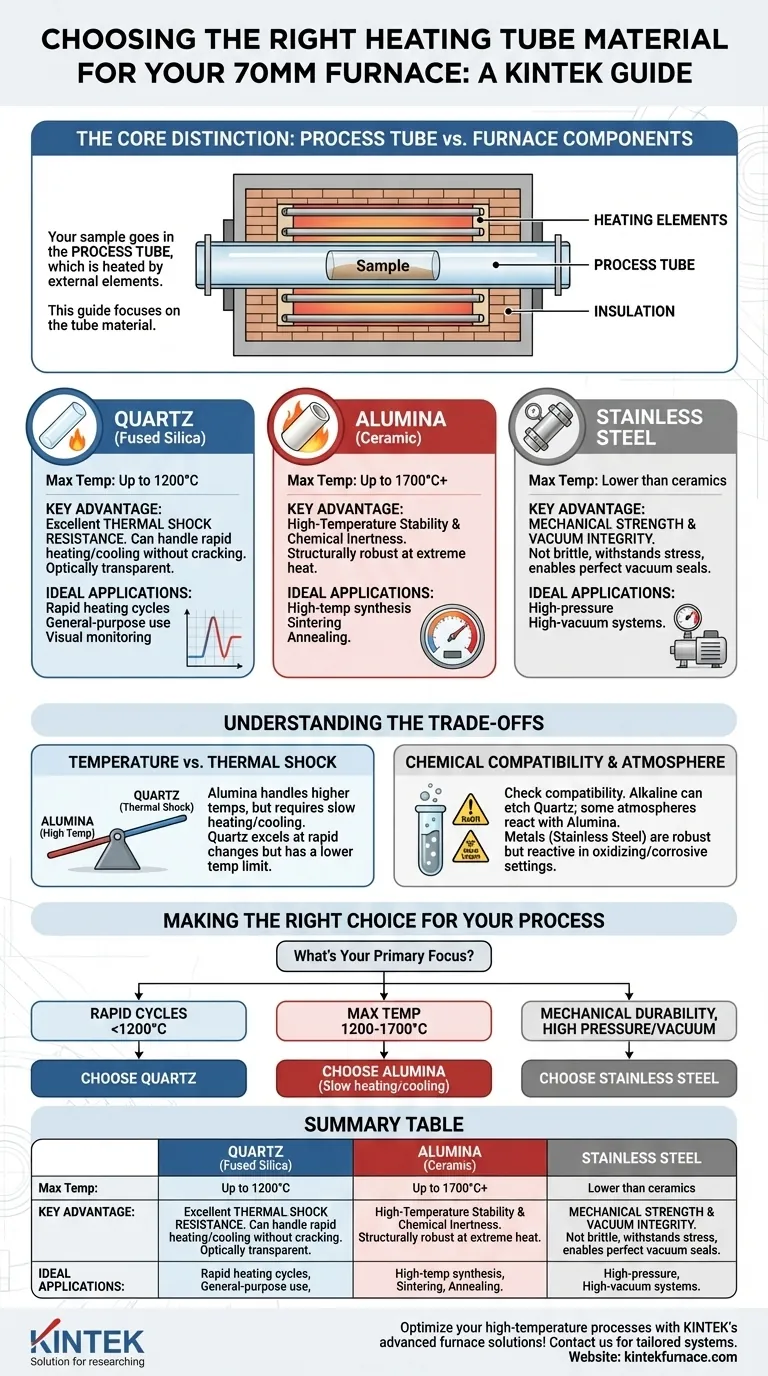
At its core, the process tube in a 70mm tube furnace is most commonly made from one of three materials: quartz, high-purity alumina (a ceramic), or stainless steel. The choice is dictated entirely by your experiment's maximum required temperature, chemical environment, and tolerance for thermal shock.
The selection of a tube material is not about the furnace itself, but a critical decision about your specific process. The right choice is a calculated trade-off between a material's maximum temperature limit, its chemical inertness, and its ability to withstand rapid temperature changes.
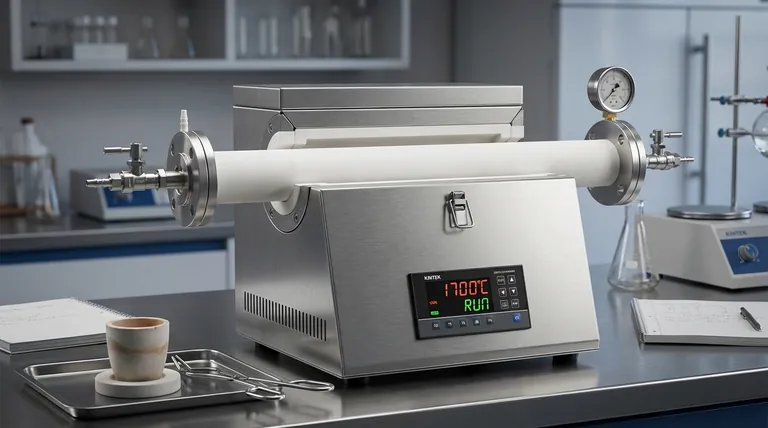

The Core Distinction: Process Tube vs. Furnace Components
Before evaluating materials, it is crucial to understand what the "tube" is. In a tube furnace, the sample is placed inside a process tube. This tube is a separate, often removable component.
The process tube is then heated by external heating elements (like silicon carbide rods) which are surrounded by insulation (like refractory bricks or fiber) that makes up the furnace body. Your question concerns the process tube, not the heating elements or insulation.
A Closer Look at Common Tube Materials
Each material offers a distinct set of properties, making it suitable for different applications. The 70mm diameter is a standard size and does not fundamentally change these material considerations.
Quartz (Fused Silica): The Versatile Standard
Quartz is a form of high-purity glass, often the default choice for general-purpose applications up to approximately 1200°C (2192°F).
Its primary advantage is its outstanding resistance to thermal shock. You can heat and cool a quartz tube relatively quickly without it cracking, which is ideal for processes requiring rapid temperature cycling. It is also optically transparent in many forms.
Alumina (Ceramic): The High-Temperature Workhorse
High-purity alumina is a dense, robust ceramic capable of handling extremely high temperatures, often up to 1700°C (3092°F) or even higher depending on purity.
This makes alumina the go-to material for high-temperature synthesis, annealing, and sintering. It offers excellent chemical inertness and structural integrity at temperatures where quartz would soften and fail.
Stainless Steel: For Robustness and Vacuum
While having a lower maximum operating temperature than ceramics, stainless steel tubes offer unique advantages in mechanical strength and vacuum integrity.
They are not brittle and can withstand mechanical stress far better than quartz or alumina. This makes them ideal for high-pressure or high-vacuum applications where a perfect, non-porous seal is critical.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a material is always a matter of balancing competing factors. An expert decision requires understanding these compromises.
Temperature vs. Thermal Shock
Alumina can go to much higher temperatures than quartz. However, it is significantly more sensitive to thermal shock. Alumina tubes must be heated and cooled slowly and evenly to prevent cracking.
Quartz, on the other hand, excels with rapid temperature changes but has a much lower maximum operating temperature.
Chemical Compatibility
While both quartz and alumina are considered highly inert, they are not immune to all chemical attacks, especially at extreme temperatures.
Strong alkaline substances (like NaOH) can etch quartz, and certain atmospheres or metal vapors can react with alumina. Always verify the compatibility of your specific reactants with the tube material at your target temperature.
Atmosphere and Durability
Metal tubes like stainless steel are perfect for creating robust, high-vacuum systems. Ceramic tubes can sometimes be slightly porous or may outgas, making it harder to achieve ultra-high vacuum levels.
However, metal tubes are reactive in many oxidizing or corrosive atmospheres where ceramics remain stable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your application, not the furnace, dictates the correct tube material.
- If your primary focus is rapid heating cycles below 1200°C: Choose a quartz tube for its superior thermal shock resistance.
- If your primary focus is reaching the highest possible temperatures (1200°C to 1700°C): Choose a high-purity alumina tube, but plan for slow, controlled heating and cooling rates.
- If your primary focus is mechanical durability, high pressure, or a robust vacuum seal: Choose a stainless steel tube, ensuring your process atmosphere and temperature are compatible.
Selecting the right tube material is the critical first step to ensuring the success and repeatability of your high-temperature process.
Summary Table:
| Material | Max Temperature | Key Advantages | Ideal Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quartz | Up to 1200°C | Excellent thermal shock resistance, optically transparent | Rapid heating cycles, general-purpose use |
| Alumina | Up to 1700°C+ | High-temperature stability, chemical inertness | High-temp synthesis, sintering, annealing |
| Stainless Steel | Lower than ceramics | Mechanical strength, vacuum integrity | High-pressure, high-vacuum systems |
Optimize your laboratory's high-temperature processes with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with tailored high-temperature furnace systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific requirements and drive your research forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Molybdenum Disilicide MoSi2 Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide



















