High-purity graphite molds are the multifunctional engines behind the Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) process, serving as far more than simple containers. They act simultaneously as the shaping vessel, the primary heating element, and the mechanical ram responsible for densifying the powder.
High-purity graphite molds do not merely hold the material; they are active participants that convert electrical current into extreme thermal energy while transmitting massive axial pressure, ensuring the rapid densification and structural integrity of high-entropy carbides above 2000°C.
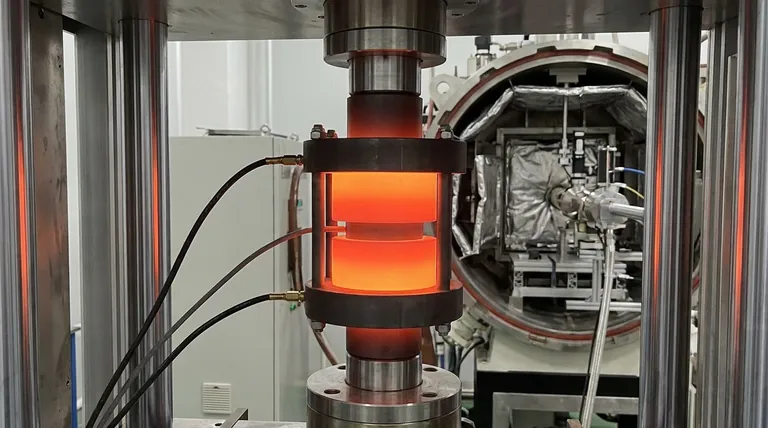
The Three Core Functions in SPS
High-entropy carbides require extreme conditions to form dense, stable structures. The graphite mold facilitates this through three simultaneous physical roles.
1. The Active Heating Element
In standard sintering, the heat comes from an external furnace. In SPS, the graphite mold itself acts as the heater.
The mold possesses specific electrical resistance properties. When the pulsed direct current (DC) passes through it, the mold efficiently converts this electrical energy into thermal energy (Joule heating).
This allows for rapid heating rates and enables the system to reach temperatures exceeding 2000°C, which is critical for sintering refractory high-entropy materials.
2. Axial Pressure Transmission
Densification requires force, not just heat. The graphite mold serves as the pressure transmission medium.
It transfers the load from the machine’s hydraulic rams directly to the powder particles, typically sustaining pressures up to 60 MPa.
This mechanical pressure promotes powder rearrangement and assists in breaking down agglomerates during the initial stages of sintering.
3. Structural Containment at Extremes
The mold defines the final geometry of the sintered sample.
It must maintain excellent thermal shock stability and high-temperature strength to withstand the rapid heating and cooling cycles without fracturing.
High-purity graphite ensures the mold retains its shape and does not deform under the immense unidirectional pressure, ensuring the geometric precision of the final carbide billet.
Impact on Material Quality
The interaction between the mold and the high-entropy carbide powder directly influences the microscopic properties of the final material.
Promoting Atomic Diffusion
The combination of direct heat and pressure facilitates atomic diffusion.
This environment induces the formation of ordered interfaces with semi-coherent characteristics. These microstructural features are essential for optimizing properties like lattice thermal conductivity.
Ensuring Thermal Uniformity
The purity and density of the graphite mold directly dictate the uniformity of the temperature field.
High-quality graphite conducts heat evenly, preventing hot spots or cold zones that could lead to cracking or uneven densification in the ceramic composite.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While graphite is the standard for SPS, it introduces specific challenges that must be managed to ensure high-entropy carbide quality.
Chemical Reactivity and Adhesion
At high temperatures, high-entropy carbides can react with the graphite mold or adhere to it.
This requires the use of interface liners, such as graphite paper often coated with boron nitride (BN).
These liners prevent the sample from chemically bonding with the mold, ensuring easy demolding and preserving the surface quality of the ceramic.
Mechanical Limitations
While graphite has high-temperature strength, it is not infinitely rigid.
Excessive pressure (generally above 60-80 MPa, depending on the grade) can cause the mold to fracture or deform.
Operating within the specific mechanical limits of the graphite grade is vital to prevent catastrophic mold failure during the cycle.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The selection and setup of your graphite mold should align with your specific sintering objectives.
- If your primary focus is Maximum Densification: Prioritize high-strength graphite grades capable of sustaining pressures near the 60 MPa limit to force particle rearrangement.
- If your primary focus is Surface Purity: Ensure the use of boron nitride-coated graphite paper liners to create a diffusion barrier between the carbide and the mold.
- If your primary focus is Thermal Consistency: Select ultra-high purity, high-density graphite to guarantee a uniform temperature field and avoid thermal gradients in the sample.
Ultimately, the graphite mold is not just a consumable; it is the central component that translates electrical and mechanical energy into the physical reality of your material.
Summary Table:
| Core Function | Description | Impact on High-Entropy Carbides |
|---|---|---|
| Joule Heating | Converts pulsed DC into thermal energy | Enables temperatures >2000°C for refractory materials |
| Pressure Transmission | Transfers axial load (up to 60 MPa) to powder | Promotes rapid densification and particle rearrangement |
| Structural Container | Defines geometry and withstands thermal shock | Ensures geometric precision and prevents structural failure |
| Diffusion Driver | Combines heat and pressure at the interface | Facilitates atomic diffusion for optimized microstructure |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK Precision
Unlock the full potential of your Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) processes with our high-purity graphite solutions. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, along with customizable lab high-temp furnace components designed for your unique high-entropy carbide projects.
Ready to achieve superior density and thermal uniformity?
Contact our experts today to discuss your customized furnace and mold requirements!
References
- Wen Jiang, Peng Fu. Achieving efficient almost CO-free hydrogen production from methanol steam reforming on Cu modified α-MoC. DOI: 10.1039/d3ra07448j
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Spark Plasma Sintering SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the typical applications of a circulating water vacuum pump? Essential for Lab Efficiency and Cost Savings
- What is the function of the laboratory-scale condensation collection device? Optimize Multi-Stage Magnesium Separation
- Why are alumina crucibles used for CoNb2O6 synthesis? Ensure High-Purity Ceramic Powder Production
- What are the advantages of using a Boron Nitride crucible? Maximize Purity and Efficiency in Laser Pyrolysis
- How does a lab vacuum pump work? Understanding the Liquid Piston Mechanism
- Which is better graphite or ceramic crucible? Match Your Material & Process for Optimal Melting
- What is the function of an alumina boat during high-temperature activation of porous carbon? Durable Lab Solutions
- What is the role of gold (Au), platinum (Pt), or platinum-iridium (Pt-Ir) foil in silicate melt experiments?

















