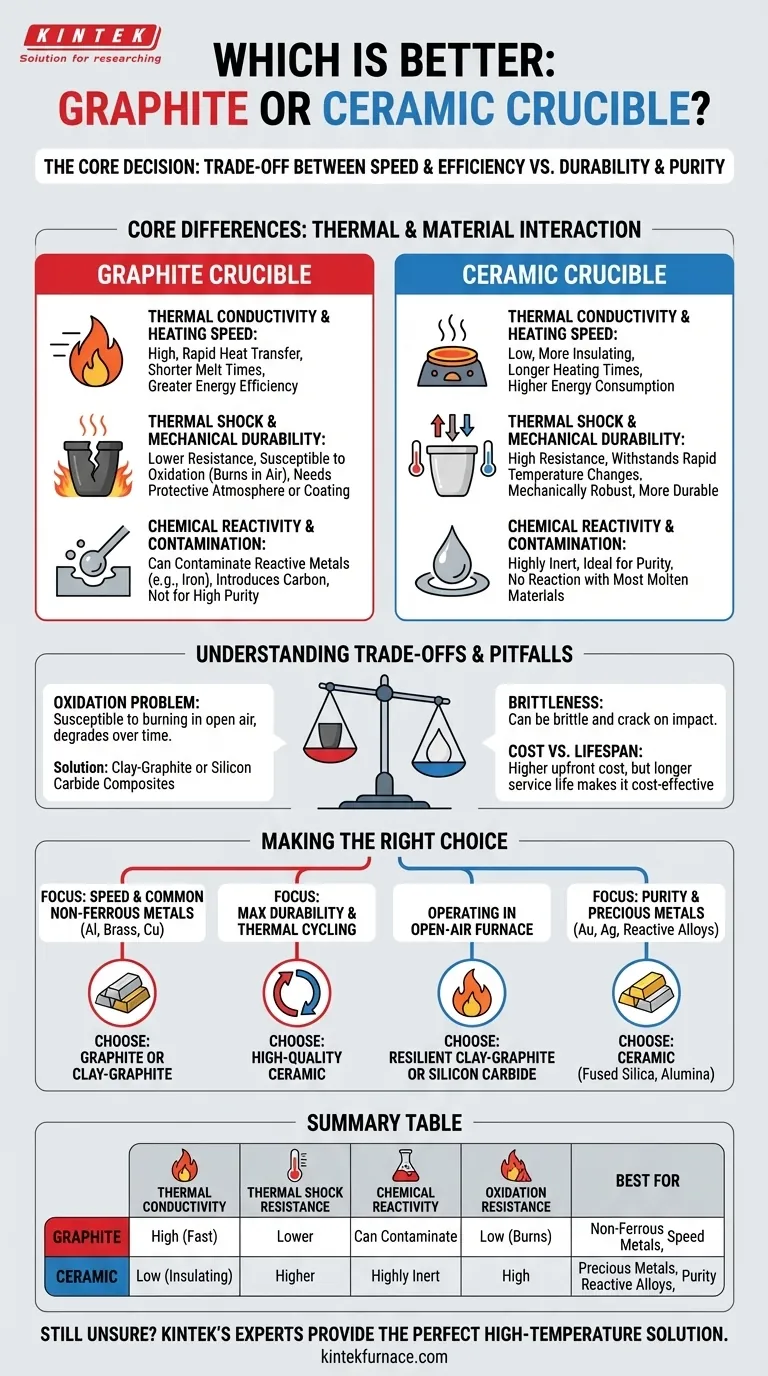
The choice between a graphite and ceramic crucible is not about which one is universally better, but which is the right tool for your specific task. While ceramic crucibles offer superior durability and resistance to thermal shock, graphite crucibles provide significantly faster heating due to their excellent thermal conductivity. The best choice depends entirely on the material you are melting, your need for purity, and your heating method.
The core decision hinges on a fundamental trade-off: graphite offers speed and thermal efficiency, while ceramic provides durability, chemical inertness, and resistance to contamination for sensitive applications.
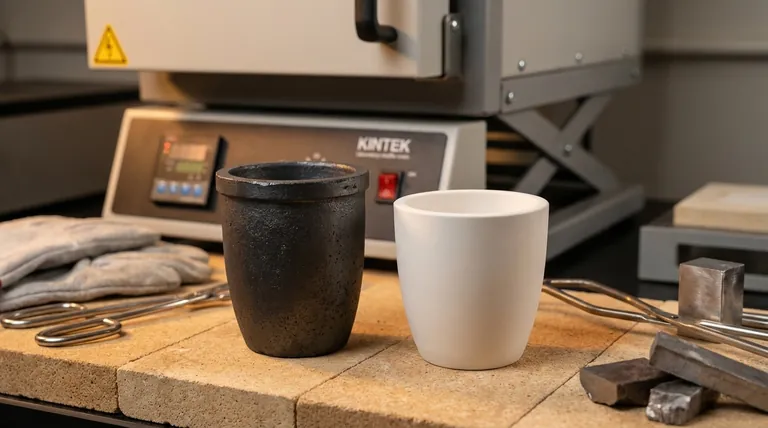

Core Differences: Thermal Properties and Material Interaction
To select the right crucible, you must first understand how each material behaves under intense heat and chemical stress.
Thermal Conductivity and Heating Speed
Graphite has exceptionally high thermal conductivity. This means it transfers heat from your furnace to the metal inside it very quickly and evenly.
This rapid heat transfer translates to shorter melt times and greater energy efficiency, which is a major advantage for production environments.
Ceramics, by contrast, are more insulating. They take longer to heat up, which can mean longer furnace run times and higher energy consumption.
Thermal Shock and Mechanical Durability
Ceramic materials are engineered to be highly resistant to thermal shock. They can better withstand rapid changes from hot to cold without cracking.
As noted, ceramics also tend to be more mechanically robust, making them less prone to damage from handling. This durability can lead to a longer service life under the right conditions.
Chemical Reactivity and Contamination
This is a critical distinction. Ceramics are generally very chemically inert. They do not readily react with most molten materials, making them the ideal choice when melt purity is the highest priority. This is essential for precious metals, laboratory samples, and reactive alloys.
Graphite is carbon-based and can react with or dissolve into certain molten metals, particularly ferrous metals like iron and steel. This introduces carbon into your melt, which can be a form of contamination that alters the properties of the final product. However, for many non-ferrous metals like aluminum and brass, this is not an issue.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
Every material choice comes with compromises. Being aware of the potential downsides of each crucible type is key to avoiding costly failures.
The Oxidation Problem with Graphite
The primary weakness of a pure graphite crucible is its susceptibility to oxidation. When heated in the presence of oxygen (i.e., in a standard air-breathing furnace), the graphite will burn away over time.
This oxidation degrades the crucible, thinning its walls and shortening its lifespan. While protective glazes can slow this process, it remains a significant factor, especially for hobbyists using open-air furnaces. Clay-graphite and silicon carbide crucibles are common composites that balance graphite's conductivity with better oxidation resistance.
The Brittleness of Ceramic
While robust against thermal shock, some ceramic crucibles can be brittle and may crack or shatter if dropped or subjected to a sharp physical impact. Careful handling is always required.
Cost vs. Lifespan
Graphite crucibles often have a lower initial purchase price. However, their shorter lifespan due to oxidation can make them more expensive in the long run if you need to replace them frequently.
Ceramic crucibles may have a higher upfront cost, but their durability and resistance to chemical attack and oxidation can result in a lower total cost of ownership over many uses.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use your specific goal to guide your decision. There is no single "best" crucible, only the best one for the job at hand.
- If your primary focus is speed and melting common non-ferrous metals (like aluminum, brass, or copper): Choose a graphite or clay-graphite crucible for its superior heating efficiency.
- If your primary focus is purity and melting precious metals (gold, silver) or reactive alloys: Choose a ceramic crucible (like fused silica or alumina) to prevent any contamination of your melt.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability and resistance to thermal cycling: Choose a high-quality ceramic crucible, as it is engineered to withstand repeated heating and cooling.
- If you are operating in an open-air furnace without a protective atmosphere: Be aware of graphite's oxidation and consider a more resilient clay-graphite or silicon carbide composite crucible.
By matching the crucible's inherent properties to your material and process, you ensure a safer, more efficient, and successful melt.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Graphite Crucible | Ceramic Crucible |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | High (fast heating) | Low (insulating) |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Lower | Higher |
| Chemical Reactivity | Can contaminate reactive metals (e.g., iron) | Highly inert, ideal for purity |
| Oxidation Resistance | Low (burns in air) | High |
| Best For | Non-ferrous metals (aluminum, brass), speed | Precious metals, reactive alloys, purity |
Still unsure which crucible is right for your lab? KINTEK's experts leverage deep R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide the perfect high-temperature solution. Whether you need the speed of a graphite crucible or the purity of a ceramic one, our custom furnace systems (including Muffle, Tube, Vacuum, and CVD/PECVD) are engineered to meet your exact experimental requirements. Contact us today for a personalized consultation to enhance your melting efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation



















