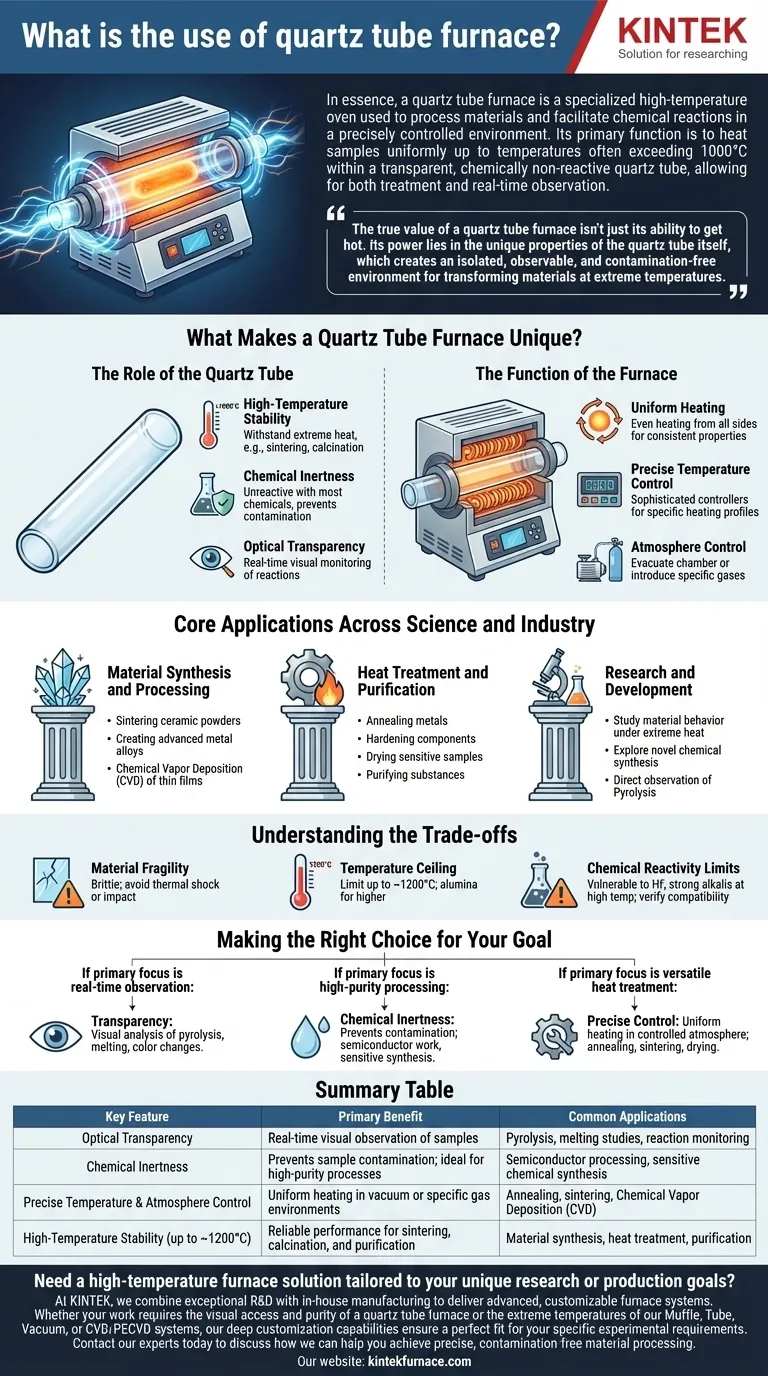
In essence, a quartz tube furnace is a specialized high-temperature oven used to process materials and facilitate chemical reactions in a precisely controlled environment. Its primary function is to heat samples uniformly up to temperatures often exceeding 1000°C within a transparent, chemically non-reactive quartz tube, allowing for both treatment and real-time observation.
The true value of a quartz tube furnace isn't just its ability to get hot. Its power lies in the unique properties of the quartz tube itself, which creates an isolated, observable, and contamination-free environment for transforming materials at extreme temperatures.
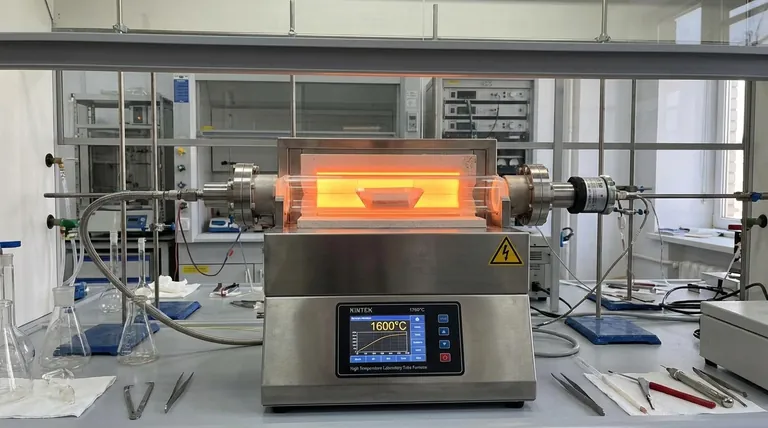

What Makes a Quartz Tube Furnace Unique?
A quartz tube furnace combines two key elements: the heating element (the furnace) and the sample chamber (the quartz tube). Each part contributes specific, critical capabilities.
The Role of the Quartz Tube
The tube is the heart of the system. Fused quartz is used because it offers a rare combination of properties essential for advanced material processing.
- High-Temperature Stability: Quartz can withstand sustained, extreme heat without melting or deforming, making it a reliable chamber for processes like sintering and calcination.
- Chemical Inertness: It is highly unreactive with most acids, solvents, and chemicals. This prevents the tube from contaminating the sample and ensures the purity of the final product.
- Optical Transparency: Unlike ceramic or metal furnaces, the transparent quartz allows researchers and technicians to visually monitor the sample in real-time. This is invaluable for observing color changes, melting, or reactions like pyrolysis as they happen.
The Function of the Furnace
The furnace housing provides the controlled environment necessary for repeatable and precise work.
- Uniform Heating: The cylindrical design of the heating elements wraps around the tube, ensuring the sample is heated evenly from all sides. This uniformity is critical for consistent material properties.
- Precise Temperature Control: Modern furnaces use sophisticated controllers to maintain a specific temperature profile, allowing for controlled heating, soaking, and cooling cycles required for processes like annealing.
- Atmosphere Control: The sealed tube design allows users to evacuate the chamber to create a vacuum or introduce specific gases. This is essential for preventing oxidation or enabling reactions that require a particular atmosphere, such as Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
Core Applications Across Science and Industry
The unique features of quartz tube furnaces make them indispensable tools in a variety of fields, from fundamental research to industrial production.
Material Synthesis and Processing
This is a primary use case. The furnace provides the energy needed to create new materials or refine existing ones.
Applications include the sintering of ceramic powders into dense solids, the creation of advanced metal alloys, and the growth of thin films on substrates via Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
Heat Treatment and Purification
Heat can fundamentally alter the properties of a material. Tube furnaces provide the control needed to achieve specific outcomes.
This includes annealing metals to increase their ductility, hardening components, drying sensitive samples without contamination, and purifying substances by burning off impurities at high temperatures.
Research and Development
For materials scientists and chemists, the quartz tube furnace is a window into high-temperature phenomena.
It enables the study of material behavior under extreme heat, the exploration of novel chemical synthesis pathways, and the direct observation of pyrolysis (thermal decomposition) for analytical purposes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly versatile, a quartz tube furnace is not without its limitations. Understanding these trade-offs is crucial for successful operation.
Material Fragility
Quartz is a type of glass. It has excellent thermal stability but can be brittle. Sudden, extreme temperature changes (thermal shock) or physical impacts can cause the tube to crack or shatter.
Temperature Ceiling
While its temperature limit is high, quartz does have a ceiling. For applications requiring temperatures consistently above 1200°C, furnace tubes made from more refractory materials, such as alumina, are often necessary.
Chemical Reactivity Limits
Quartz is exceptionally inert, but it is not completely immune. It can be attacked by hydrofluoric acid and certain strong alkaline substances, especially at high temperatures. Always verify chemical compatibility before processing reactive materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if a quartz tube furnace is the right tool, consider your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is real-time observation: The transparency of quartz is its defining advantage for visually analyzing pyrolysis, melting, or color-change reactions.
- If your primary focus is high-purity processing: The chemical inertness of quartz prevents sample contamination, making it ideal for semiconductor work or sensitive chemical synthesis.
- If your primary focus is versatile heat treatment: A quartz tube furnace offers precise, uniform heating in a controlled atmosphere, perfect for annealing, sintering, or drying a wide range of materials.
By understanding its unique combination of features, you can leverage the quartz tube furnace as a powerful and indispensable tool for material innovation and discovery.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Primary Benefit | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Optical Transparency | Real-time visual observation of samples | Pyrolysis, melting studies, reaction monitoring |
| Chemical Inertness | Prevents sample contamination; ideal for high-purity processes | Semiconductor processing, sensitive chemical synthesis |
| Precise Temperature & Atmosphere Control | Uniform heating in vacuum or specific gas environments | Annealing, sintering, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) |
| High-Temperature Stability (up to ~1200°C) | Reliable performance for sintering, calcination, and purification | Material synthesis, heat treatment, purification |
Need a high-temperature furnace solution tailored to your unique research or production goals?
At KINTEK, we combine exceptional R&D with in-house manufacturing to deliver advanced, customizable furnace systems. Whether your work requires the visual access and purity of a quartz tube furnace or the extreme temperatures of our Muffle, Tube, Vacuum, or CVD/PECVD systems, our deep customization capabilities ensure a perfect fit for your specific experimental requirements.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can help you achieve precise, contamination-free material processing.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab



















