At its core, an electric muffle furnace is used to heat materials to very high temperatures in a precisely controlled and clean environment. Its primary applications include analytical processes like ashing, heat-treating metals to alter their properties, and conducting high-temperature materials research. The key feature is the "muffle"—an insulating chamber that isolates the sample from the electric heating elements, preventing contamination.
A muffle furnace is not just a high-temperature oven; it is a specialized tool for transforming materials. Its defining purpose is to provide an exceptionally uniform and pure heating environment, making it indispensable for any process where sample integrity and precise temperature control are paramount.
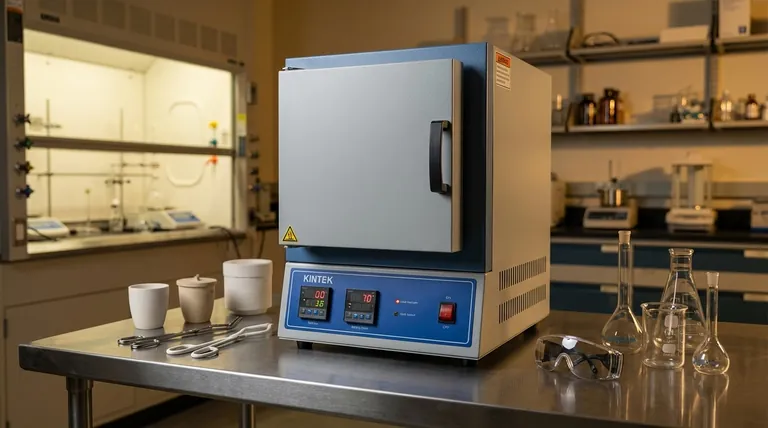

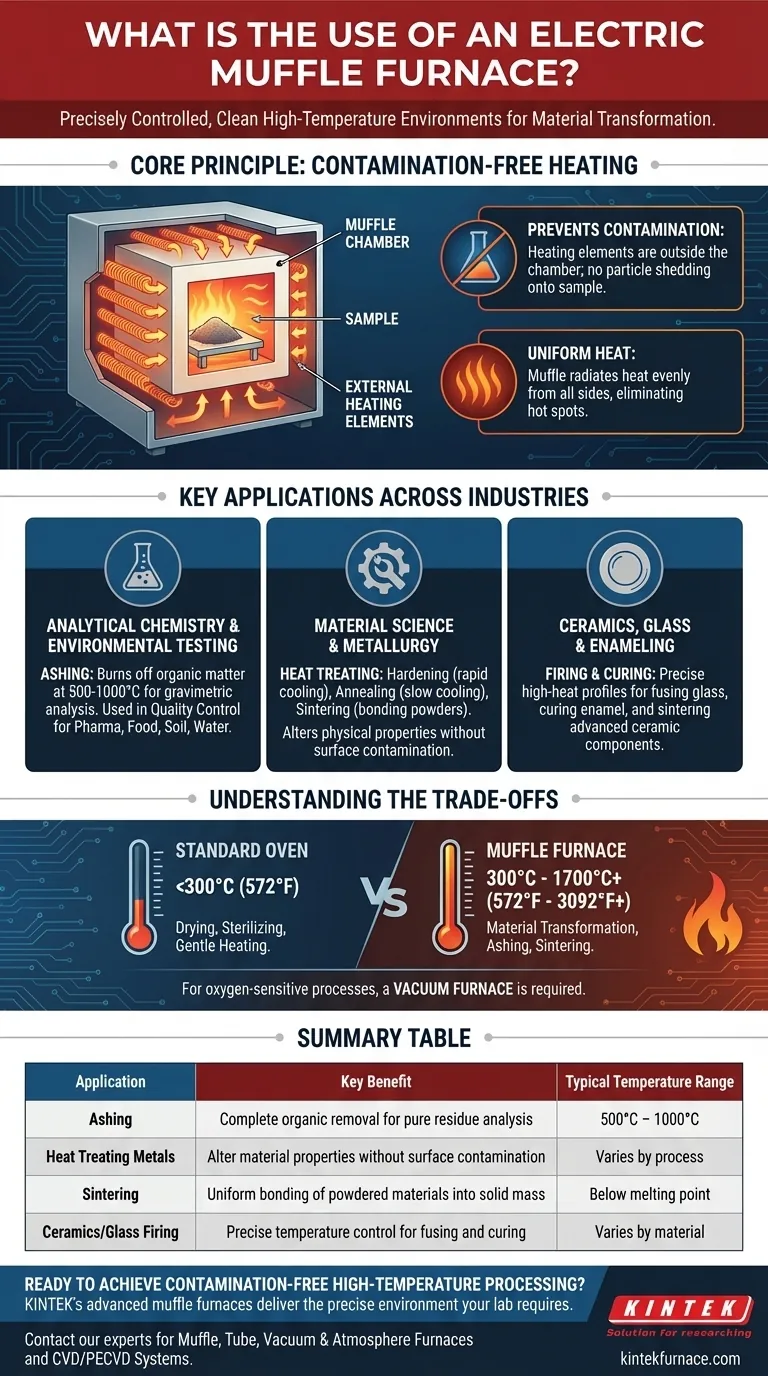
The Core Principle: Contamination-Free Heating
A standard oven heats a chamber, but a muffle furnace takes this a step further by creating a chamber-within-a-chamber. This design is central to all of its applications.
What is a "Muffle"?
The "muffle" is a refractory ceramic box that sits inside the furnace's insulated cabinet. Your samples go inside this muffle.
The electric heating coils wrap around the outside of the muffle. This means the sample is heated by radiation and convection within the muffle, never coming into direct contact with the heating elements themselves.
Why This Separation Matters
This separation achieves two critical goals. First, it prevents contamination. As heating elements age, they can shed microscopic particles that could alter the chemical composition of a sample.
Second, it ensures exceptionally uniform heat. The muffle absorbs and radiates heat evenly from all sides, eliminating the hot spots that can occur with direct element exposure and ensuring the entire sample experiences the same temperature.
Key Applications Across Industries
The unique heating environment of a muffle furnace makes it a fundamental tool in scientific laboratories and specialized industrial settings.
For Analytical Chemistry & Environmental Testing
The most common use here is ashing. This process involves burning a sample at high temperatures (typically 500-1000°C) to completely remove all organic matter.
The clean environment is essential for gravimetric analysis, where the remaining inorganic ash is weighed to determine its concentration. It is widely used for quality control in pharmaceuticals, food science, and environmental analysis of soil or water.
For Material Science & Metallurgy
In metallurgy, heat is used to change a material's physical properties. A muffle furnace is used for:
- Hardening: Heating metals to a specific temperature and then rapidly cooling them to increase hardness.
- Annealing: Heating and slowly cooling a material to reduce hardness and increase ductility.
- Sintering: Heating powdered materials (like ceramics or metals) below their melting point until their particles bond together, forming a solid piece.
In all these cases, preventing surface contamination is critical to achieving the desired material properties.
For Ceramics, Glass, and Enameling
These applications rely on precise temperature profiles. A muffle furnace provides the controlled, high-heat environment needed for fusing glass, curing enamel coatings on metal, and firing or sintering advanced ceramic components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a muffle furnace is not always the right tool. Its utility is defined by its specific capabilities.
Muffle Furnace vs. a Standard Oven
A laboratory oven is generally used for drying, sterilizing, or gentle heating, rarely exceeding 300°C (572°F). A muffle furnace is a high-temperature device designed for material transformations like ashing or sintering, operating at temperatures from 300°C to over 1700°C (3092°F).
When Contamination Control is Key
A muffle furnace prevents contamination from the heating elements but typically operates in an air or controlled gas atmosphere. For processes that are sensitive to oxygen or nitrogen, a vacuum furnace is required to provide a completely inert environment.
Energy and Time Considerations
Muffle furnaces are designed to be energy-efficient for their temperature range, but reaching very high temperatures requires significant energy and time. The thermal mass of the insulating muffle means both heat-up and cool-down cycles are slower than in a simple oven.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Choosing the right heating instrument depends entirely on the transformation you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is analytical testing (ashing): The furnace is essential for burning off organic material to leave a pure, uncontaminated inorganic residue for accurate analysis.
- If your primary focus is metal treatment (annealing/hardening): Its value is in altering a metal's internal structure with precise heat, without introducing surface impurities from the heating elements.
- If your primary focus is materials development (sintering): It provides the uniform, high-temperature environment needed to fuse powdered materials into a solid, high-density mass.
Ultimately, a muffle furnace is the definitive tool when you must fundamentally change a material with high heat while guaranteeing its purity.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit | Typical Temperature Range |
|---|---|---|
| Ashing (Analytical Chemistry) | Complete organic removal for pure residue analysis | 500°C - 1000°C |
| Heat Treating Metals | Alter material properties without surface contamination | Varies by process |
| Sintering (Materials Science) | Uniform bonding of powdered materials into solid mass | Below melting point |
| Ceramics/Glass Firing | Precise temperature control for fusing and curing | Varies by material |
Ready to achieve contamination-free high-temperature processing? KINTEK's advanced muffle furnaces deliver the precise, uniform heating environment your lab requires. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems with deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your ashing, heat treatment, or materials research workflows.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- How does a muffle furnace contribute to kaolin-modified biochar? Optimize Pyrolysis & Mineral Integration
- What is the primary use of a muffle furnace in the assembly of side-heated resistive gas sensors? Expert Annealing Guide
- How does a stainless steel reactor function within a muffle furnace for PET to graphene? Master Carbon Synthesis
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the conversion of S-1@TiO2? Achieve Precision Calcination of Nanospheres
- Why are precision stirring and drying equipment necessary for photocatalytic materials? Master Microstructure Control



















