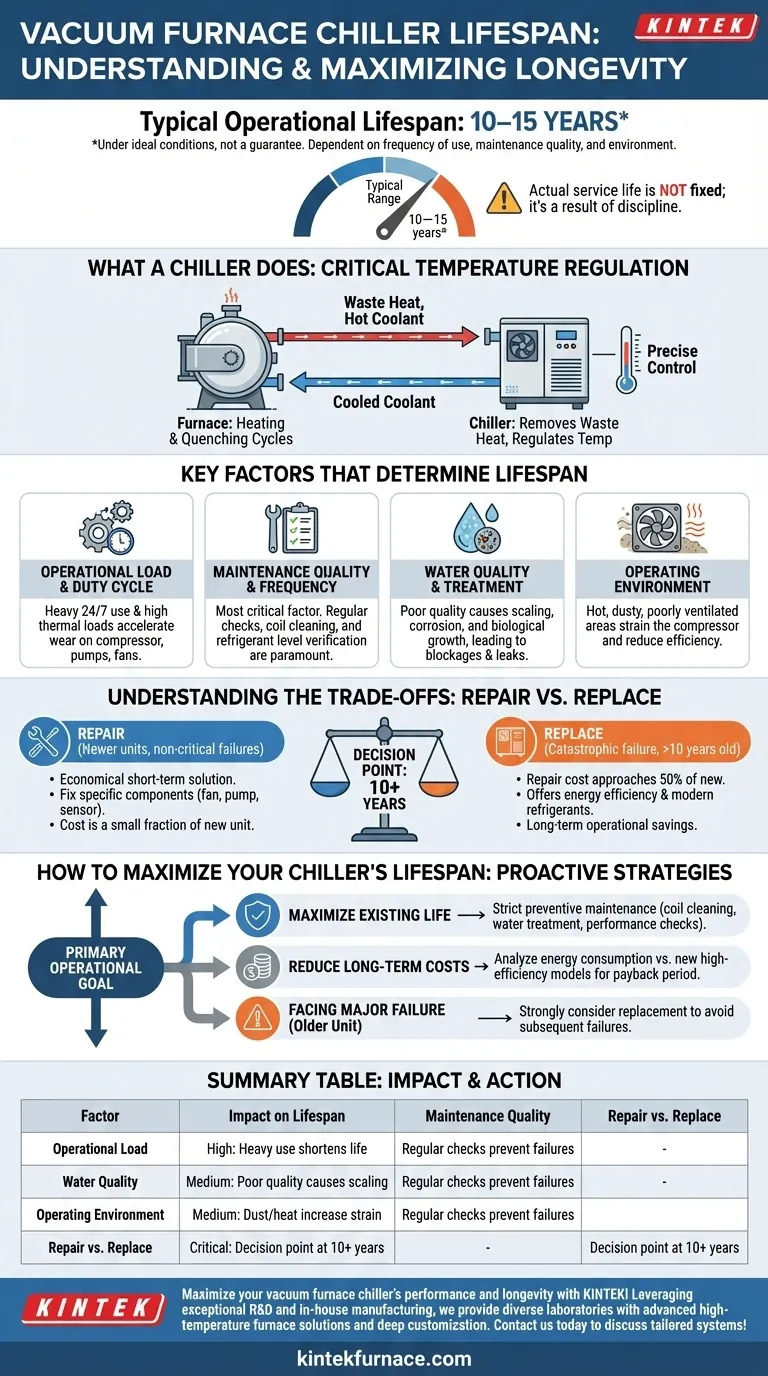
Under ideal conditions, a vacuum furnace chiller has a typical operational lifespan of 10 to 15 years. However, this range is not a guarantee. The actual service life you will achieve is directly dependent on factors such as the frequency of use, the quality of your maintenance program, and the specific operating environment.
The question isn't just how long a chiller lasts, but what actions you can take to maximize its lifespan. Longevity is not a fixed attribute; it is the direct result of operational discipline and proactive maintenance.
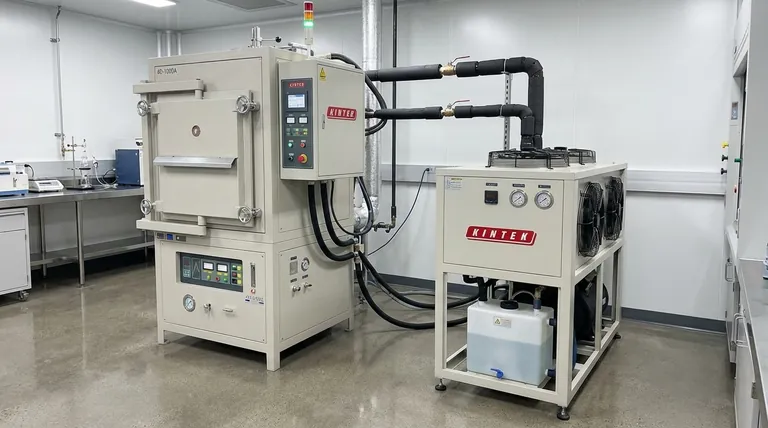

What a Vacuum Furnace Chiller Does
The Role of Temperature Regulation
A vacuum furnace chiller is a critical support system that removes waste heat. Its primary function is to regulate the furnace's temperature during both heating and rapid cooling (quenching) cycles.
How It Works
The chiller circulates a coolant—typically water or a water-glycol mixture—through a closed-loop system connected to the furnace. This fluid absorbs heat from the furnace components and transports it back to the chiller, where it is dissipated into the ambient environment, preventing the furnace from overheating.
The Key Factors That Determine Lifespan
While 10 to 15 years is the benchmark, several variables can significantly shorten or extend a chiller's service life.
Operational Load and Duty Cycle
A chiller supporting a furnace that runs 24/7 under heavy thermal loads will experience more wear on its compressor, pumps, and fans than a unit used for single-shift operations. Higher utilization accelerates the aging of all mechanical components.
Maintenance Quality and Frequency
This is the most critical factor you can control. A disciplined preventive maintenance schedule that includes regular inspection of refrigerant levels, cleaning of condenser coils, and verification of electrical connections is paramount.
Water Quality and Treatment
The coolant itself can be a source of failure. Poor water quality can lead to scaling, corrosion, or biological growth within the heat exchangers and piping. This buildup insulates the system, forcing the chiller to work harder and eventually causing blockages or leaks.
The Operating Environment
A chiller placed in a hot, dusty, or poorly ventilated facility must work harder to reject heat. Clogged air filters and condenser coils from airborne debris reduce efficiency and place a greater strain on the compressor, the heart of the system.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Repair vs. Replace
As a chiller approaches the end of its expected lifespan, you will inevitably face the decision of whether to fund a major repair or invest in a full replacement.
The Case for Repair
Repairing a chiller is often the right choice for newer units or when the failure is limited to a non-critical, easily replaceable component like a fan motor, pump, or sensor. If the repair cost is a small fraction of a new unit's price, it is typically the most economical short-term solution.
The Case for Replacement
Replacement becomes the logical choice when facing a catastrophic failure, such as a seized compressor, on a unit that is over 10 years old. The cost of such a repair can often approach 50% or more of a new unit. Furthermore, newer chillers offer significant improvements in energy efficiency and may use modern, environmentally-friendly refrigerants, providing long-term operational savings.
How to Maximize Your Chiller's Lifespan
Your approach should be guided by your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is maximizing the life of an existing unit: Implement a strict preventive maintenance schedule focusing on coil cleaning, water treatment, and regular performance checks.
- If your primary focus is reducing long-term operating costs: Analyze the energy consumption of your aging chiller versus a new, high-efficiency model to see when the payback period justifies a replacement.
- If you are facing a major component failure on an older unit: Strongly consider replacement, as the risk of subsequent failures on other aging components is high.
Proactive management, not passive operation, is the key to getting the most value and life from your critical furnace equipment.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Lifespan |
|---|---|
| Maintenance Quality | High: Regular checks prevent failures |
| Operational Load | High: Heavy use shortens life |
| Water Quality | Medium: Poor quality causes scaling/corrosion |
| Operating Environment | Medium: Dust/heat increase strain |
| Repair vs. Replace | Critical: Decision point at 10+ years |
Maximize your vacuum furnace chiller's performance and longevity with KINTEK! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored chiller and furnace systems can enhance your lab's efficiency and reliability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Can box type high-temperature resistance furnaces control the atmosphere? Unlock Precision in Material Processing
- What are the primary inert gases used in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Heat Treatment Process
- How does the pressure range change under vacuum conditions in an atmosphere box furnace? Explore Key Shifts for Material Processing
- What are some specific applications of atmosphere furnaces in the ceramics industry? Enhance Purity and Performance
- How do argon and nitrogen protect samples in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Thermal Process with the Right Gas



















