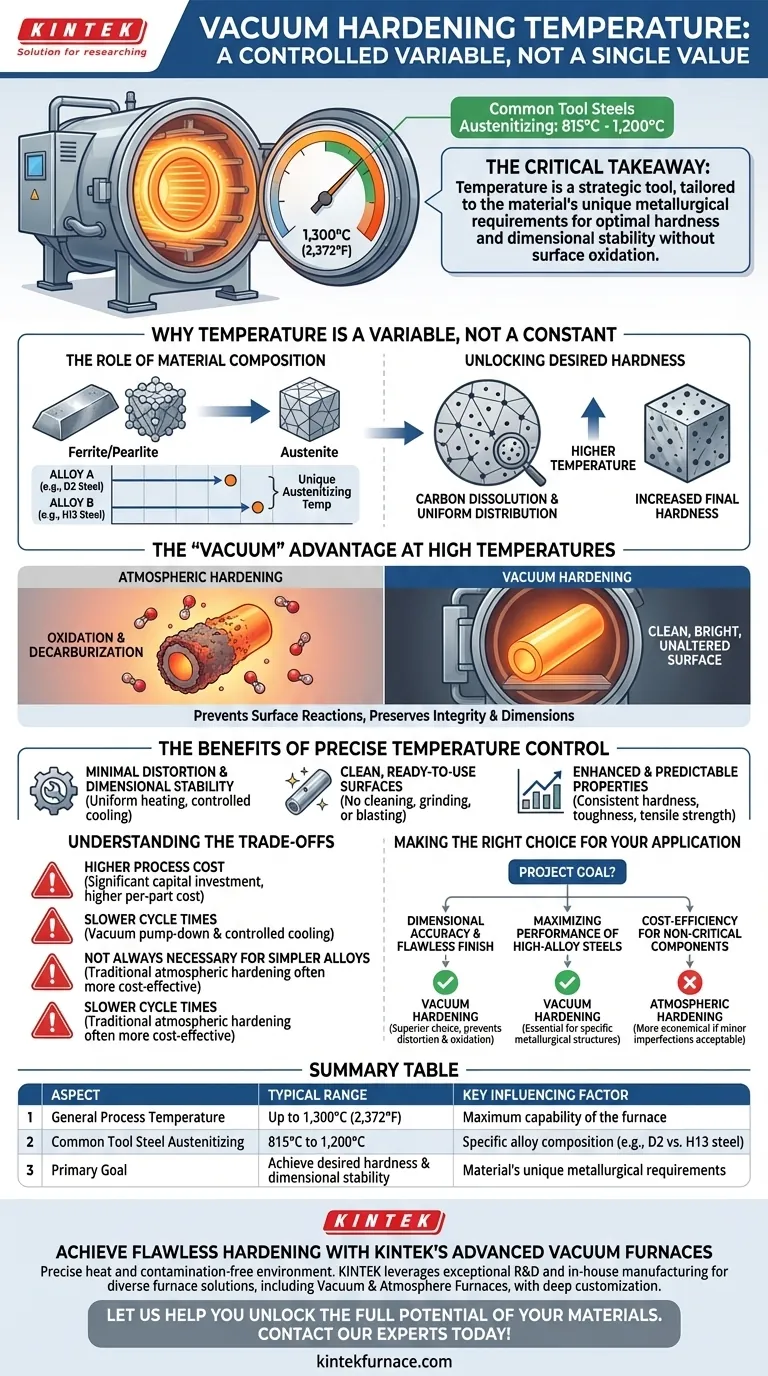
The temperature for vacuum hardening is not a single value but a precisely controlled variable that can reach up to 1,300°C (2,372°F). The exact temperature is determined entirely by the specific metal alloy being treated and the final properties desired. For most common tool steels, this austenitizing temperature typically falls between 815°C and 1,200°C.
The critical takeaway is that in vacuum hardening, temperature is a strategic tool, not a fixed setting. It is tailored to the material's unique metallurgical requirements to achieve optimal hardness and dimensional stability without surface oxidation.
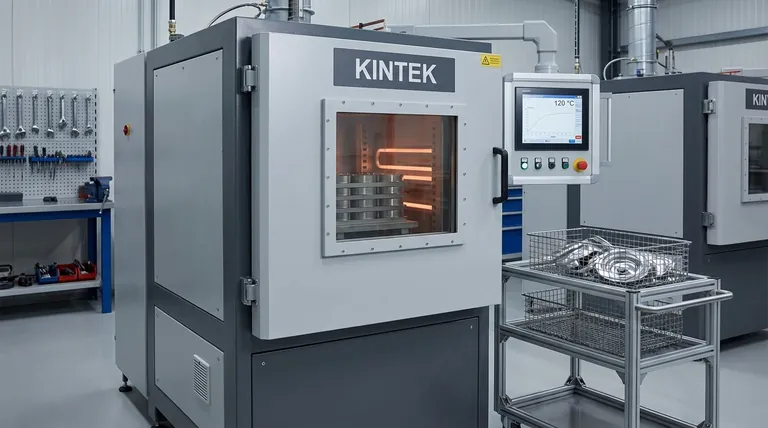

Why Temperature is a Variable, Not a Constant
The effectiveness of vacuum hardening hinges on using the correct temperature for the specific job. Choosing the right temperature is a function of deep material science principles.
The Role of Material Composition
Every metal alloy has a unique "austenitizing" temperature. This is the critical point where the steel's internal crystal structure (ferrite and pearlite) transforms into a new structure called austenite.
Heating the material to its specific austenitizing temperature is the essential first step that makes hardening possible. Different alloys, like D2 tool steel versus H13 tool steel, have different chemical compositions and therefore different critical temperatures.
Unlocking Desired Hardness
The goal of heating is to dissolve carbon and other alloying elements into the austenite structure. Holding the material at this temperature ensures these elements are evenly distributed.
This uniform solid solution is what allows for maximum hardness to be achieved during the subsequent rapid cooling (quenching) phase. The higher the temperature (within the correct range for the alloy), the more carbides can be dissolved, which can lead to higher final hardness.
The "Vacuum" Advantage at High Temperatures
Performing this process in a vacuum (or a controlled partial pressure) is what sets it apart. At these high temperatures, any oxygen in the atmosphere would rapidly react with the metal's surface.
This reaction causes oxidation and decarburization (loss of carbon from the surface), which ruins the part's surface integrity and dimensions. The vacuum prevents these reactions, resulting in a clean, bright, and unaltered surface.
The Benefits of Precise Temperature Control
The ability to precisely manage the thermal cycle in a vacuum environment delivers significant engineering advantages beyond just hardness.
Minimal Distortion and Dimensional Stability
Because the parts are heated uniformly in a still environment with no hot spots from open flames, thermal stress is dramatically reduced. The controlled cooling rate further minimizes the risk of warping or distortion.
This makes vacuum hardening ideal for complex, high-precision components where maintaining dimensional tolerance is critical.
Clean, Ready-to-Use Surfaces
Parts emerge from the vacuum furnace with a bright, metallic finish. They require no subsequent cleaning, grinding, or blasting to remove scale or oxidation.
This eliminates entire steps from the manufacturing process, saving both time and cost, and preserving the precise dimensions of the machined part.
Enhanced and Predictable Properties
The process offers exceptional control over the final outcome. By precisely managing the austenitizing temperature, soak time, and quench rate, metallurgists can reliably produce parts with specific, repeatable properties like hardness, toughness, and tensile strength.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, vacuum hardening is not the default solution for every application. Understanding its limitations is key to making an objective decision.
Higher Process Cost
Vacuum furnaces represent a significant capital investment compared to standard atmospheric furnaces. This translates to a higher per-part cost for the heat treatment process itself.
Slower Cycle Times
The need to pump the chamber down to a vacuum and then execute a highly controlled cooling cycle can sometimes result in longer overall process times compared to simpler hardening methods.
Not Always Necessary for Simpler Alloys
For low-carbon or basic low-alloy steels where surface finish is not a primary concern and some distortion is acceptable, traditional atmospheric hardening can be a more cost-effective solution. The benefits of the vacuum process may not justify the added expense.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right heat treatment method requires aligning the process capabilities with your project's most critical goals.
- If your primary focus is dimensional accuracy and a flawless finish: Vacuum hardening is the superior choice, as the controlled thermal cycle and inert environment prevent distortion and oxidation.
- If your primary focus is maximizing the performance of high-alloy steels: This process is essential for unlocking the full potential of tool steels, stainless steels, and superalloys by achieving specific metallurgical structures.
- If your primary focus is cost-efficiency for non-critical components: A traditional atmospheric hardening process may be more economical if slight surface imperfections and the need for post-processing are acceptable.
Ultimately, choosing the right hardening process is a strategic decision based on the material's value and its end-use requirements.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Typical Range | Key Influencing Factor |
|---|---|---|
| General Process Temperature | Up to 1,300°C (2,372°F) | Maximum capability of the furnace |
| Common Tool Steel Austenitizing | 815°C to 1,200°C | Specific alloy composition (e.g., D2 vs. H13 steel) |
| Primary Goal | Achieve desired hardness & dimensional stability | Material's unique metallurgical requirements |
Achieve Flawless Hardening with KINTEK's Advanced Vacuum Furnaces
Choosing the correct temperature is critical for successful vacuum hardening, but it's only half the battle. You need a furnace capable of delivering the precise, uniform heat and contamination-free environment your high-value components demand.
At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories and production facilities with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line—including Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, and Rotary Furnaces, as well as CVD/PECVD Systems—is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your unique experimental and production requirements.
Let us help you unlock the full potential of your materials.
Contact our experts today to discuss how a KINTEK vacuum furnace can be tailored to your specific hardening process.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion



















