While dental furnaces operate across a wide range, the most demanding applications, such as sintering zirconia, require them to reach and precisely maintain extremely high temperatures, typically between 1450°C and 1600°C (2642°F to 2912°F). This high heat is essential for transforming the pre-sintered material into a dense, strong, and aesthetically pleasing final restoration.
The specific temperature of a dental furnace is not a single value but rather a highly controlled variable. The core challenge is achieving the exact, material-specific temperature profile required to guarantee the strength, fit, and color of a dental prosthetic.
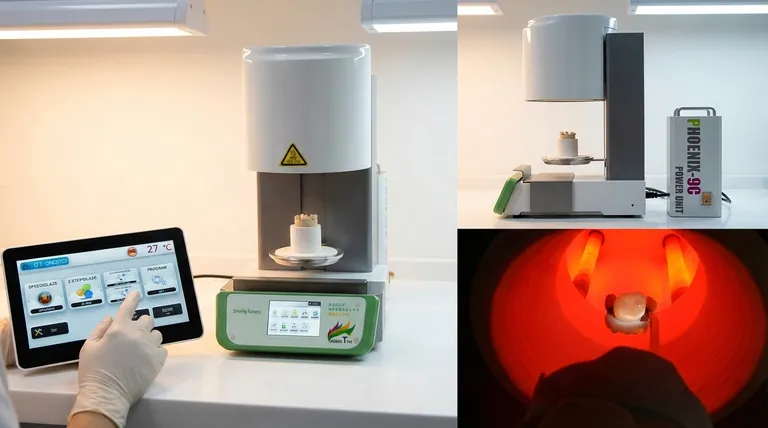
Why Temperature is the Critical Factor
The furnace is the heart of the modern dental lab, and temperature is its most critical function. It's not simply about getting hot; it's about applying the right amount of heat, at the right time, in a controlled environment.
The Process of Sintering
Sintering is the process that gives materials like zirconia their exceptional strength. The furnace applies precise heat to densify and crystallize the material, shrinking it into a solid, durable state without melting it.
This transformation from a porous, chalk-like block to a hard, translucent restoration is entirely dependent on achieving the correct sintering temperature.
Material-Specific Requirements
Different dental materials have unique thermal requirements. A furnace must be versatile enough to handle various temperature profiles.
Zirconia demands the highest temperatures, while various porcelains and ceramics require different, often more complex, multi-stage heating and cooling cycles at lower temperatures to achieve the desired look and function.
The Role of a Controlled Environment
Temperature does not work in isolation. Most high-end dental furnaces operate under a vacuum to remove air from the chamber.
This prevents air bubbles from being trapped in the material, ensuring a smooth, dense, and non-porous surface on the final restoration.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Cost of Imprecision
In dental prosthetics, "close enough" is not good enough. Even minor deviations from the target temperature can have significant consequences for the final product and the lab's bottom line.
The Impact on Strength and Durability
If the furnace temperature is too low, the sintering process will be incomplete. This results in a weak, porous restoration that is prone to fracture, compromising its clinical performance.
The Effect on Aesthetics and Color
Temperature has a direct impact on the final shade and translucency of a restoration. Inaccurate heating can cause the color to be off, failing to match the patient's adjacent teeth and rendering the prosthetic useless.
The Financial Cost of Failure
A single failed restoration due to temperature inaccuracy means wasted materials and, more importantly, wasted technician time. The need to remake the prosthetic directly impacts a lab's profitability and turnaround time. This is why furnaces with proven accuracy of +/- 1°C are the industry standard.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a furnace or setting a program requires understanding its direct link to your final product. Your goal determines the necessary thermal capabilities.
- If your primary focus is high-strength zirconia restorations: You require a furnace capable of reliably reaching and sustaining temperatures up to 1600°C with exceptional accuracy.
- If your primary focus is aesthetic porcelain work: You need a furnace with highly customizable temperature programs and precise control over heating and cooling rates to manage different materials.
- If your primary focus is operational efficiency: You must prioritize a furnace with documented temperature uniformity and accuracy to minimize costly remakes and ensure consistent, predictable results.
Mastering the use of temperature in your dental furnace is the key to consistently producing high-quality, reliable restorations.
Summary Table:
| Dental Material | Typical Furnace Temperature Range | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Zirconia | 1450°C - 1600°C (2642°F - 2912°F) | High Strength & Durability |
| Porcelain/Ceramics | Varies (Complex Multi-Stage Cycles) | Optimal Aesthetics & Color Match |
Achieve Unmatched Precision in Your Dental Lab
Every restoration depends on perfect temperature control. Inconsistent heat leads to weak, discolored prosthetics and costly remakes.
KINTEK understands this critical challenge. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide dental laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including specialized Dental Sintering Furnaces, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique material and workflow requirements.
Ensure every zirconia crown and porcelain veneer meets the highest standards of strength and aesthetics. Contact us today to discuss how a KINTEK furnace can bring reliability and efficiency to your lab.
Visual Guide

Related Products
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What role does temperature range and accuracy play in dental furnace performance? Ensure Precision for Superior Dental Restorations
- What is the working principle of a dental furnace? Mastering Precision Sintering & Firing for Crowns
- Why is accurate temperature control important in dental furnaces? Ensure Perfect Restorations Every Time
- What are the recommended maintenance practices for dental furnaces? Ensure Precision and Longevity for Your Lab
- Why is temperature range important when selecting a dental furnace? Unlock Material Compatibility and Precision



















