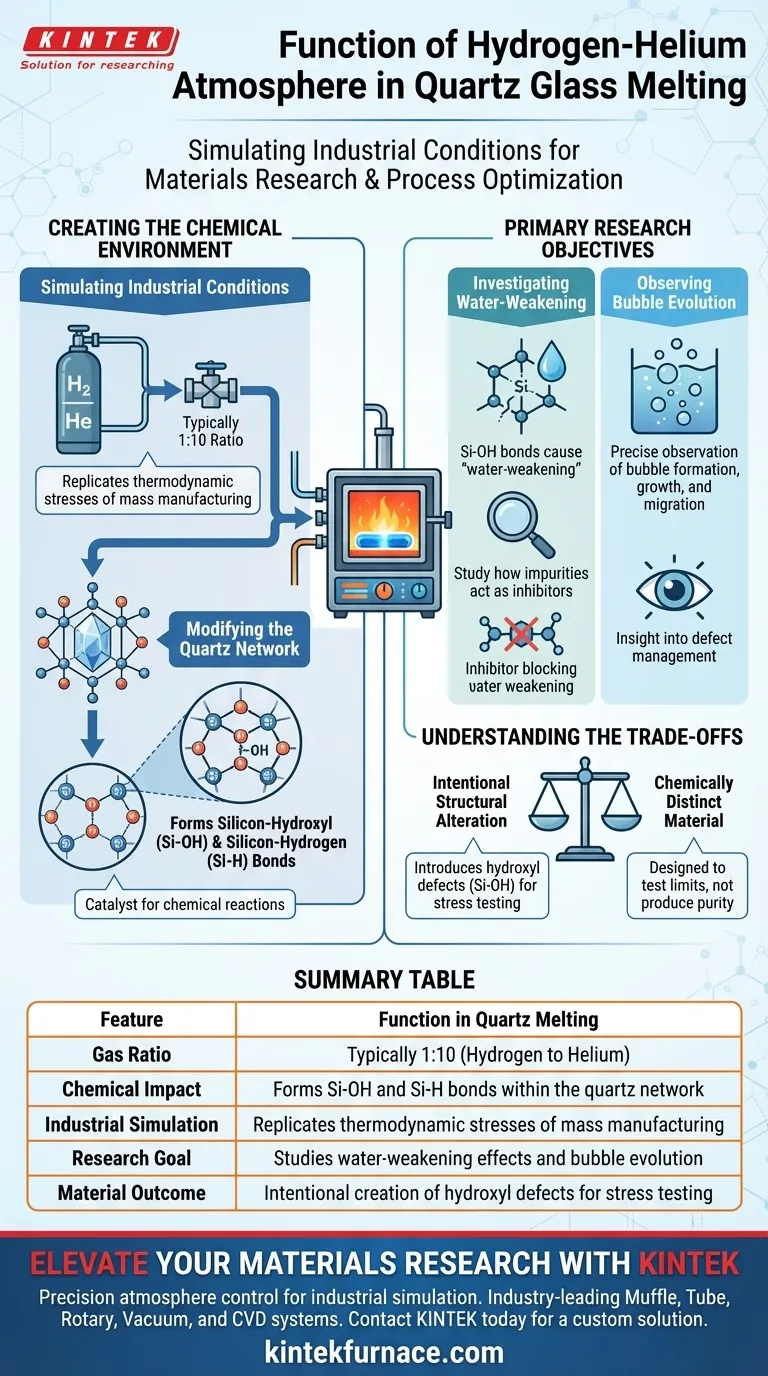
The specific function of a mixed hydrogen and helium atmosphere is to accurately simulate industrial-scale quartz melting conditions within a high-temperature furnace. Typically utilizing a 1:10 ratio, this specific gaseous environment acts as a catalyst for chemical reactions within the quartz network, specifically leading to the formation of silicon-hydroxyl (Si-OH) and silicon-hydrogen (Si-H) bonds.
By introducing reactive hydrogen in a controlled mixture, this process replicates the chemical stresses found in mass manufacturing, allowing researchers to isolate structural vulnerabilities like water-weakening and bubble formation.
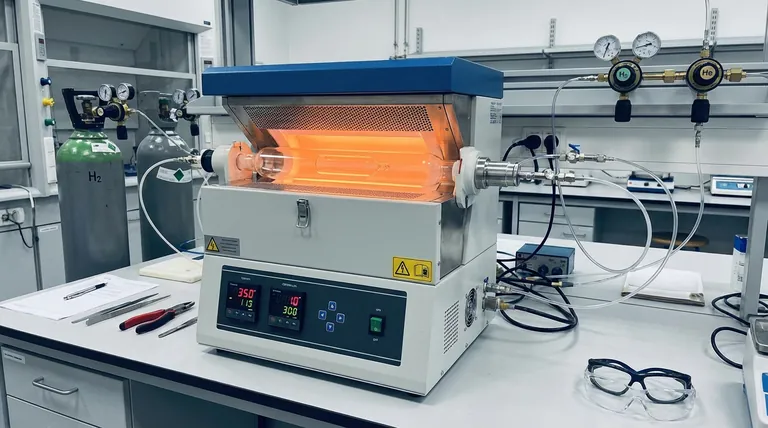

Creating the Chemical Environment
Simulating Industrial Conditions
The primary utility of the hydrogen-helium mixture is simulation accuracy.
By maintaining a specific ratio (often 1:10), researchers can replicate the thermodynamic and chemical environment of industrial-scale melting. This ensures that laboratory observations regarding material behavior are applicable to real-world manufacturing processes.
Modifying the Quartz Network
The hydrogen in the atmosphere is not inert; it is an active participant in the melting process.
It reacts directly with the quartz structure. This reaction fundamentally alters the chemical composition of the glass by forming silicon-hydroxyl (Si-OH) and silicon-hydrogen (Si-H) bonds. These bonds are the focal point for studying material degradation.
Primary Research Objectives
Investigating the Water-Weakening Effect
The formation of Si-OH bonds is associated with the "water-weakening" of quartz.
Using this atmosphere allows scientists to intentionally induce this effect. Consequently, they can study how different impurities act as inhibitors, effectively slowing down or preventing this structural weakening.
Observing Bubble Evolution
The gaseous environment directly influences the physical defects within the glass.
This specific atmosphere enables the precise observation of bubble evolution behavior. Researchers can track how bubbles form, grow, or migrate under these specific chemical conditions, providing insight into defect management.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Intentional Structural Alteration
Using this atmosphere involves an inherent compromise: you are intentionally introducing chemical agents that modify the glass network.
While necessary for simulation, the introduction of hydrogen creates hydroxyl defects (Si-OH). This means the material produced in this environment is chemically distinct from quartz melted in an inert vacuum or pure helium atmosphere, specifically designed to test the material's limits rather than produce a chemically pure sample.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if this atmospheric condition is appropriate for your process, consider your specific objectives:
- If your primary focus is Materials Research: Use this mixture to evaluate how specific impurities can strengthen the quartz network against hydroxyl-induced weakening.
- If your primary focus is Process Optimization: Use this mixture to model bubble behavior and predict defect rates in industrial-scale furnaces.
Ultimately, this mixed atmosphere serves as a specialized diagnostic tool, transforming the melting environment into a laboratory for testing structural integrity and defect dynamics.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in Quartz Melting |
|---|---|
| Gas Ratio | Typically 1:10 (Hydrogen to Helium) |
| Chemical Impact | Forms Si-OH and Si-H bonds within the quartz network |
| Industrial Simulation | Replicates thermodynamic stresses of mass manufacturing |
| Research Goal | Studies water-weakening effects and bubble evolution |
| Material Outcome | Intentional creation of hydroxyl defects for stress testing |
Elevate Your Materials Research with KINTEK
Precision in atmosphere control is critical for simulating industrial quartz melting. KINTEK provides industry-leading Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to handle complex gas mixtures like hydrogen and helium with absolute safety and accuracy.
Whether you are investigating water-weakening effects or optimizing bubble management, our lab high-temperature furnaces are fully customizable to meet your unique R&D requirements. Backed by expert manufacturing, we help you bridge the gap between laboratory insights and industrial-scale success.
Ready to refine your melting process? Contact KINTEK today for a custom solution.
Visual Guide
References
- Bartłomiej Adam Gaweł, Marisa Di Sabatino. Influence of aluminium doping on high purity quartz glass properties. DOI: 10.1039/d4ra01716a
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the role of temperature control in MCM-41 synthesis? Master Precision Pore Engineering
- What are the primary process advantages of using a continuous high-temperature tunnel furnace for copper tube brazing?
- What is the primary function of a vacuum drying oven in CIIR nanocomposite molding? Optimize Your Solvent Removal
- Why are different cooling methods compared for GFRP post-fire performance? Evaluate Thermal Shock & Safety Risks
- Why is high-temperature drying of NaCl particles necessary? Prevent Aluminum Foam Defects and Ensure Integrity
- How does rapid quenching after diffusion treatment affect the material properties of the silicon structure? Lock-in Vital Phases
- What is the function of a high-precision electric oven in ZnO-CuO synthesis? Expert Thermal Control for Nanosheets
- Why is precise heating rate control necessary? Master Activated Carbon Heat Treatment with KINTEK



















