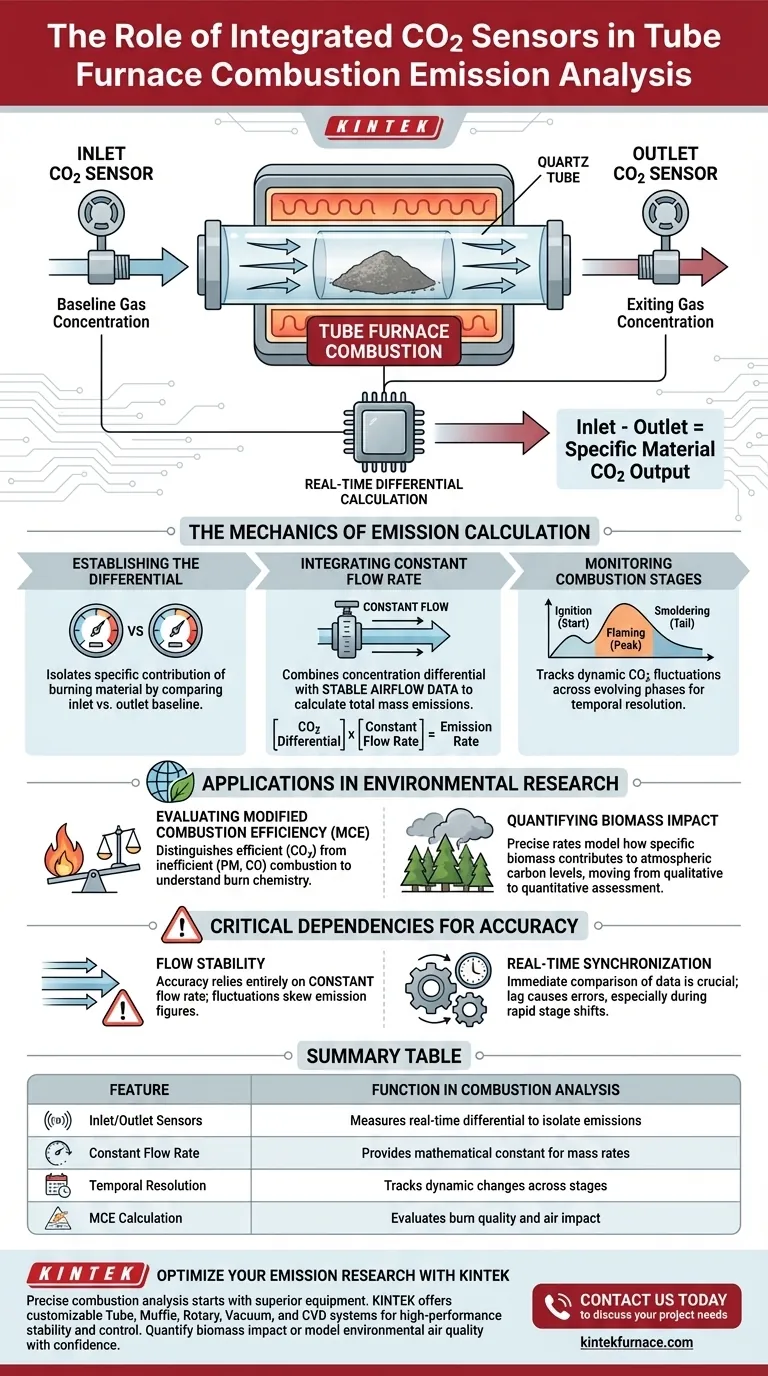
The role of integrated carbon dioxide sensors is to provide the quantitative foundation for calculating combustion emission rates. By simultaneously monitoring gas concentrations at the inlet and outlet of a quartz tube furnace, these sensors measure the real-time difference in CO2 levels. When this differential is combined with constant flow rate data, researchers can mathematically determine the specific CO2 output of materials across different stages of combustion.
By isolating the differential between inlet and outlet concentrations, these sensors allow for the calculation of Modified Combustion Efficiency (MCE). This data is essential for quantifying the environmental impact of biomass burning on air quality.
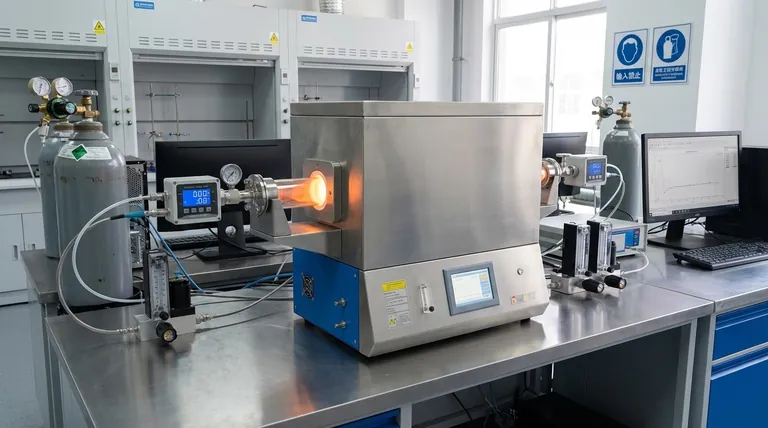

The Mechanics of Emission Calculation
Establishing the Differential
The primary technical function of these sensors is to monitor real-time changes in gas concentration.
Rather than simply measuring the presence of gas, the system compares the baseline CO2 entering the tube against the CO2 exiting the tube. This "inlet-minus-outlet" calculation isolates the specific contribution of the burning material.
The Role of Constant Flow Rate
Concentration data alone is insufficient to determine the total mass of emissions.
To calculate the actual emission rate, the concentration differential must be integrated with data regarding the system's air flow. The reference specifies that a constant flow rate is required to convert these concentration readings into quantifiable emission rates.
Monitoring Combustion Stages
Combustion is not a static process; it evolves through different phases (such as ignition, flaming, and smoldering).
Real-time monitoring allows researchers to track how CO2 production fluctuates dynamically during these various stages. This provides a temporal resolution that an aggregate measurement would miss.
Applications in Environmental Research
Evaluating Modified Combustion Efficiency (MCE)
The data derived from these sensors is explicitly used to evaluate Modified Combustion Efficiency (MCE).
MCE is a critical metric for understanding the chemistry of the burn. It helps researchers distinguish between efficient combustion (mostly CO2) and inefficient combustion (which produces more particulate matter and CO).
Quantifying Biomass Impact
A major application of this setup is assessing the impact of biomass burning on air quality.
By obtaining precise emission rates, scientists can model how specific biomass materials contribute to atmospheric carbon levels. This moves the analysis from qualitative observation to quantitative impact assessment.
Critical Dependencies for Accuracy
The Dependency on Flow Stability
The accuracy of the calculated emission rate is entirely dependent on the stability of the airflow.
Because the calculation formula incorporates constant flow rate data, any fluctuation in the air supply that is not accounted for will skew the final emission figures. The sensors rely on this constant variable to produce valid data.
Real-Time Synchronization
The system relies on the immediate comparison of inlet and outlet data.
Any significant lag between the sensor readings or the flow rate data integration can result in errors, particularly when the combustion stage shifts rapidly.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the value of your combustion analysis, align your data interpretation with your specific research objectives:
- If your primary focus is calculating total emission rates: Ensure your flow rate remains strictly constant to allow for accurate mathematical integration with the sensor differential.
- If your primary focus is environmental impact modeling: Prioritize the analysis of Modified Combustion Efficiency (MCE) data to characterize the quality of the burn and its subsequent effect on air quality.
Precision in emission analysis is the result of perfectly synchronizing differential gas sensing with stable airflow control.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in Combustion Analysis |
|---|---|
| Inlet/Outlet Sensors | Measures real-time concentration differential to isolate material emissions. |
| Constant Flow Rate | Provides the mathematical constant needed to convert concentration to mass emission rates. |
| Temporal Resolution | Tracks dynamic changes across ignition, flaming, and smoldering stages. |
| MCE Calculation | Evaluates Modified Combustion Efficiency to assess burn quality and air impact. |
Optimize Your Emission Research with KINTEK
Precise combustion analysis starts with superior equipment. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all fully customizable to meet your specific research demands. Whether you are quantifying biomass impact or modeling environmental air quality, our high-temperature furnaces provide the stability and control essential for accurate data.
Ready to elevate your laboratory’s analytical precision? Contact us today to discuss your unique project needs and discover how KINTEK’s customizable thermal solutions can empower your next breakthrough.
Visual Guide
References
- Casey Coffland, Elliott T. Gall. An open-source linear actuated-quartz tube furnace with programmable ceramic heater movement for laboratory-scale studies of combustion and emission. DOI: 10.2139/ssrn.5687995
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- How do vertical tube furnaces comply with environmental standards? A Guide to Clean, Efficient Operation
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing



















